All you need to know about laser cutting/engraving of different types of fabric (textile)
Contents
- All you need to know about laser cutting/engraving of different types of fabric (textile)
- Types of textile
- Types of synthetic fabrics
- Industrial processing of textiles
- Laser processing of textiles
- Laser cutting of natural & synthetic textiles video footage
- Kevlar laser cutting with a 80 watt Co2 laser
- Laser cutting of white sailcloth with an Endurance laser
- More tests of laser fabric cutting with a 10 watt (10000 mw) diode blue laser 445 nm
- Kevlar laser cutting with a 10 watt diode 445 nm blue laser
- Laser cutting of fishing thread (line) with 15 watt DIY DUOS laser
- Laser engraving of natural and synthetic textiles
- A T-Shirt color laser engraving for Black Friday Norton Method (NWT) – a detailed guide
Fabric (textile) laser cutting with 15 watt water – cooled laser installed on CNC 3018
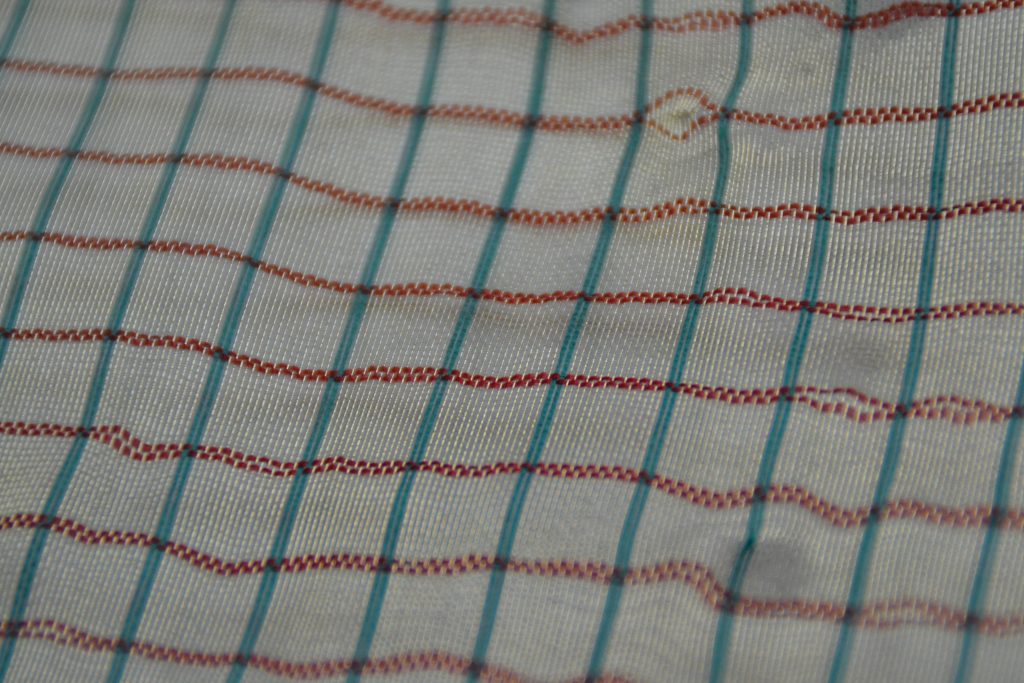
In this post, I would like to highlight all opportunities for laser cutting and laser engraving of various types of fabric.
Fabric, in general terms, is what something is made from. Thus, clothes are made of some type of fabrics (textile) or their combination. The basic structure of a building or a vehicle can also be called fabric, and non-physical things can be represented as fabric too. But here we’ll speak about various types of textile and methods of its processing.
In practice, there are five basic types of textile or cloth: silk, cotton, linen, wool, and worsted.
Fabrics are classified according to their component fibers: natural such as silk, wool, linen, cotton, or synthetic: rayon, nylon, and polyesters, etc., and inorganic fibers, such as metal, glass and asbestos.
Types of textile
There are four main sources of the textile production: animal-based (wool, silk), plant-based (cotton, flax, jute, bamboo), mineral (asbestos, glass, metal), and synthetic (nylon, polyester, acrylic, rayon). The first three are natural.
Here is a list of most popular kinds of fabrics:
- Cotton
- Synthetics (Polyester, Nylon, Spandex, etc.)
- Rayon.
- Linen.
- Cashmere / velvet.
- Silk.
- Wool.
Cotton fabrics
Cotton is used as raw material. After processing, the fibers have different lengths, which is the basis for the manufacture of numerous types of cotton fabrics. Thus, cambric and satin are obtained from long fibers. Loose fleecy fabrics such as flannel are woven from short fibers.
Cotton fabrics differ in: a weaving method, thickness, density, etc.
Uncolored (organic) cotton is distinguished by delicate colors: milky pinkish and yellow-greenish. Perfect for sewing children’s clothing, recommended for people with sensitive skin.
The most popular types of cotton fabrics (other than those mentioned above) are poplin and taffeta, corduroy and velvet, denim, and jeans.
Photo of the three types of fabrics listed above
Almost all types of cotton fabrics are suitable for garments. They are strong and durable; keep toasty well and absorb moisture; easy to care for.
Linen fabrics
Linen fabrics are no less popular; types with a thin and plain weave are mainly used for sewing clothes. Products made from this fabric are stronger than cotton.
Flax “breathes” better, it is comfortable in both summer and winter. Like cotton, the fabric is easy to work with.
Silk fabrics
Natural silk is a fabric, the raw material for which is silkworm thread.
The most popular types of silk fabrics are:
- atlas;
- silk satin;
- crepe;
- chiffon.
The natural material is smooth and soft, quickly takes on body temperature. It goes well with quality wool. Wearing clothes made of natural silk is comfortable at any time of the year!
The fabric is suitable for bedlinen and dresses, it is only important to choose the right types. The only problem is that silk is very difficult to cut and sew.
Woolen fabrics
It is impossible to imagine our basic wardrobe without warm and cozy woolen clothes sewn or knitted. Wool is a type of fabric derived from the hairs of various animal:
lama and alpaca, sheep, camel, angora goat and rabbit and others.
Woolen fabrics are known for its durability and thermally insulating properties. Besides, wool is highly flame resistant. No wonder it is so popular in consumer and industrial applications. Wool is preferably used for outwear and garments that do not contact body directly. Woolen clothes are stylish, comfortable and last for many years without loosing their finest qualities.
Types of synthetic fabrics
This group of tissues, in turn, is divided into two. The first includes materials made from plant-based raw materials. These are viscose, acetate, triacetate, cupro. They are considered the most “natural” fabrics from the synthetic group.
Outwardly, they imitate some types of silk and other natural fabrics, but of course, they do not have the unique properties of the natural materials. At the same time, they keep their shape better, do not wrinkle, and are undemanding to care for.
The second group includes such types of synthetic fabrics as:
- elastane and polyacrylic;
- polyamide and microfiber;
- polyester, nylon, etc.
Advantages and disadvantages of synthetics versus natural fabrics?
The advantages of synthetic fabrics are as follows: they do not wrinkle, do not change shape, do not lose color, some of them hold moisture. Their main disadvantage is that synthetic fabrics are not breathable, which can harm health. Natural fabrics unlike synthetic ones are hygienic and environmentally friendly.
What are fabric products used for?
The application areas of textile, both natural and synthetic, are very diverse and include the clothing industry, medicine, firefighting, space industry, manufacture of decorative items for home and office, etc.
Fabric products are used not only for sewing clothes, bedlinen but also for interior decoration: window blinds, drapery, upholstery, various screens, etc.
Natural fabrics are mainly used for sewing clothes and bedlinen. Most luxurious clothes are often made of silk (chiffon, satin) and wool (cashmere, down, hand-combed from the hair of a mountain goat). Cotton is the fabric behind most everyday clothes, including denim jeans and T-shirts. Linen (cambric, flax) is a go-to choice for a high-quality look on a hot summer day — without the worry of overheating.
Synthetics: viscose, staple, polyester, spandex, acetate are also suitable to sew various types of clothing, while other types of synthetic fabrics are preferably used for technical needs and manufacture of such products as: awning material, rsopes, and furniture fabrics.
Microfiber is a professional material for cleaning; lycra (elastane, spandex, nylon) is added in the form of threads to natural and synthetic fabrics to keep their shape; lavsan is added to industrial materials for strength and durability.
Industrial processing of textiles
In industrial production, for processing fabrics, such agents as belfor are used. Chemicals of this kind absorb the radiation of the violet and ultraviolet spectrum, give the fabric a whiter color, reduce the risk of fading, increase the overall strength of the material, give the fabric an interesting silky sheen and increase shrinkage resistance. To preserve color, the fabric is treated with a solution of concentrated sodium hydroxide. A widely used textile processing is calendering – rolling the material between hot rolls of a special machine. This treatment makes the fabric softer and more pleasant to touch. Anti-shrink treatment includes steaming with hot water and steam.
When sewing jeans, suits, shirts, medical masks, flags, sails, tents, bags, etc. you need to preliminary cut patterns from the fabric. Cutting for further sewing is one of the main parts of the technological process. There are mechanical cutting machines, sharp industrial knives, scissors, and presses. Another way of cutting fabric in production is electric cutting with a heated wire and an electric spark, a thermophysical laser beam and plasma.
What is great about laser cutting is that when the laser cuts a fabric the edges of the fabric melts slightly, which keeps thread layers from slipping.
Laser processing of textiles
Laser cutting of textiles has many positive aspects, such as tightening of the cut edges, no distortion of the fabric, what is especially important for very thin types of the material. An important circumstance is that during laser cutting, almost no dust is generated. This matters for cleanliness maintaining in the production process. There is one more important aspect in laser cutting: you can laser cut textile in any direction: along the lengthwise thread or against it, it will be equally effective.
Most common materials for laser cutting are: polyester, aramid, kevlar, fleece, cotton, polypropylene, polyurethane, fiberglass, interlining fabrics, felt, silk, filter fleece, technical textiles, synthetic fabrics.
Below are some videos demonstrating cutting of different materials.
Laser cutting of natural & synthetic textiles video footage
Kevlar laser cutting with a 80 watt Co2 laser
Laser cutting of white sailcloth with an Endurance laser
More tests of laser fabric cutting with a 10 watt (10000 mw) diode blue laser 445 nm
Kevlar laser cutting with a 10 watt diode 445 nm blue laser
Laser cutting of fishing thread (line) with 15 watt DIY DUOS laser
Laser cutting parameters for different threads and different colors
| Endurance 10 watt SE diode 445 nm laser | ||
| Green color | ||
| speed mm/min | power | |
| 200 lb | 450 | 100% |
| 150 lb | 580 | 100% |
| Endurance 10 watt+ (10000 mw) PLUS PRO laser | ||
| Green color | ||
| speed mm/min | power | |
| 200 lb | 750 | 100% |
| 150 lb | 800 | 100% |
| 4 lb | over 1500 | 100% |
| White color | ||
| 80 lb | ———————- | 100% |
| Moonshine color | ||
| 50 lb | 80 | 100% |
| Onyx color | ||
| 50 lb | over 1500 | 100% |
| Endurance 15 watt DIY DUOS | ||
| Green color | ||
| laser cutting speed, mm/min | power | |
| 200 lb | 850 | 100% |
| 150 lb | 950 | 100% |
| 4 lb | ||
| White color | ||
| 80 lb | ———————- | 100% |
| Moonshine color | ||
| 50 lb | 130 | 100% |
| Onyx color | ||
| 50 lb | 1500+ | 45% |
Laser cutting test of fishing lines with a DIY Endurance Galvo machine (PDF parameters)
Laser engraving of natural and synthetic textiles
Laser engraving on fabric is a process by which you can create a pattern or image on almost any fabric surface. In principle, the technology is quite simple. Patterning (engraving) is done by way of removal (burning up) of the top colored layer of the fabric.
Diode lasers vs. Co2 laser tubes. Advantages and disadvantages
It is important to bear in mind that for laser engraving on fabric, it is necessary to accurately set the following parameters: speed, power, focus and number of passes, as well as to select a correct type of the laser.
Comparison of a different types of lasers and different wavelength
It is important that in the process of laser engraving the laser beam should remove a predetermined layer of the fabric. Laser engraving can be used to create intricate patterns and designs on fabric surfaces. There are only few other methods except laser processing to engrave textiles.
Laser engraving is the most effective method of processing nonwovens (such as felt) or pile fabrics (such as fleece). One of the main applications of engraved fabrics is decoration. For this a diode or CO2 laser is a perfect tool. Woven fabrics cannot be engraved, as the engraving process may break the weave of the fabric and start unraveling. Therefore, you need to be very careful.
Some tissues change color or shade when exposed to the 10600 nm CO2 laser. Changing the appearance of a surface without removing material is called “laser marking”. Laser marking can be used to create patterns and designs on fabric surfaces.
Laser engraving on blue jeans – live demo
You can engrave and cut a variety of fabrics including natural and synthetic.
A T-Shirt color laser engraving for Black Friday Norton Method (NWT) – a detailed guide
To implement our idea we’ll need:
A T-shirt
A diode laser (Endurance 10W PRO PLUS diode laser attachment)
Paint sprays (fluorescent paints are preferable as they look more effective on fabrics)
Masking tape
Acrylic glue
First of all, we cover the area to be engraved on the T-shirt with a thin coat of glue. This glue coat will serve as a paint base for subsequent even paint coating.
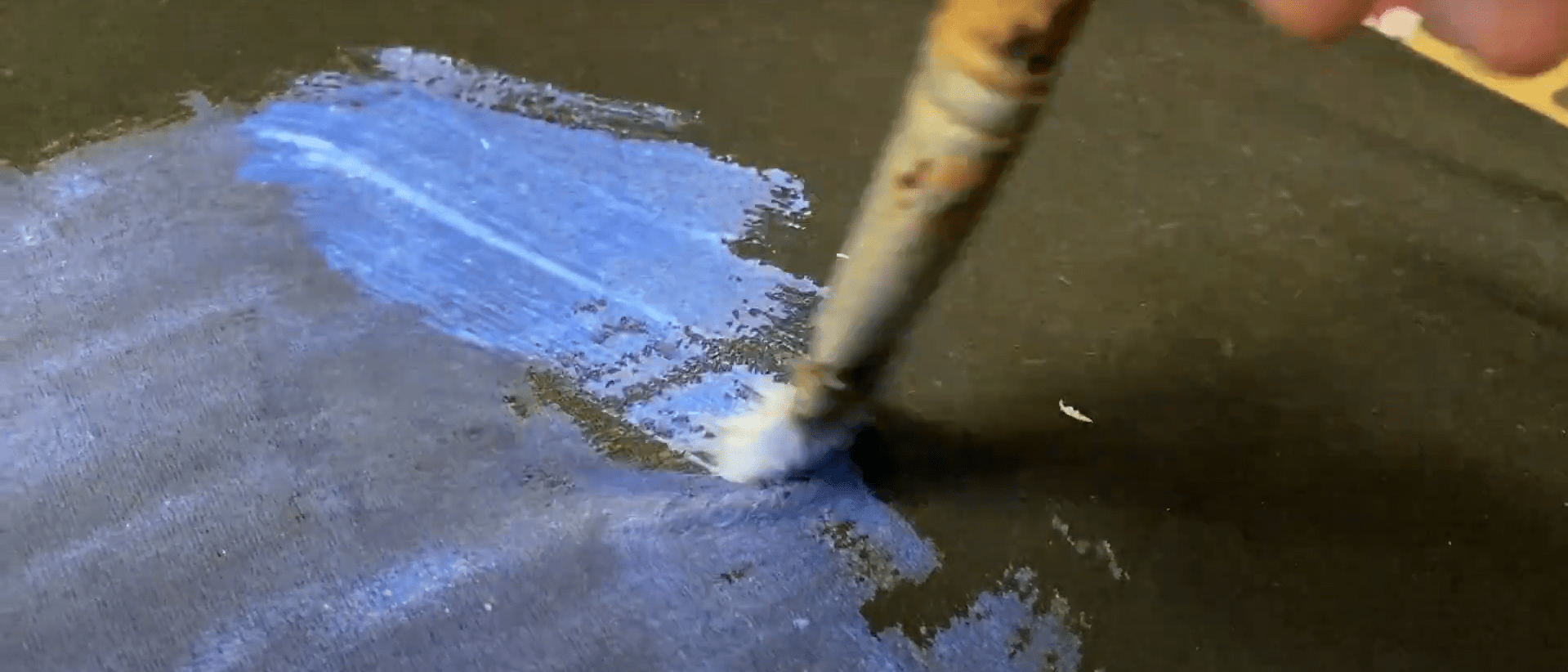

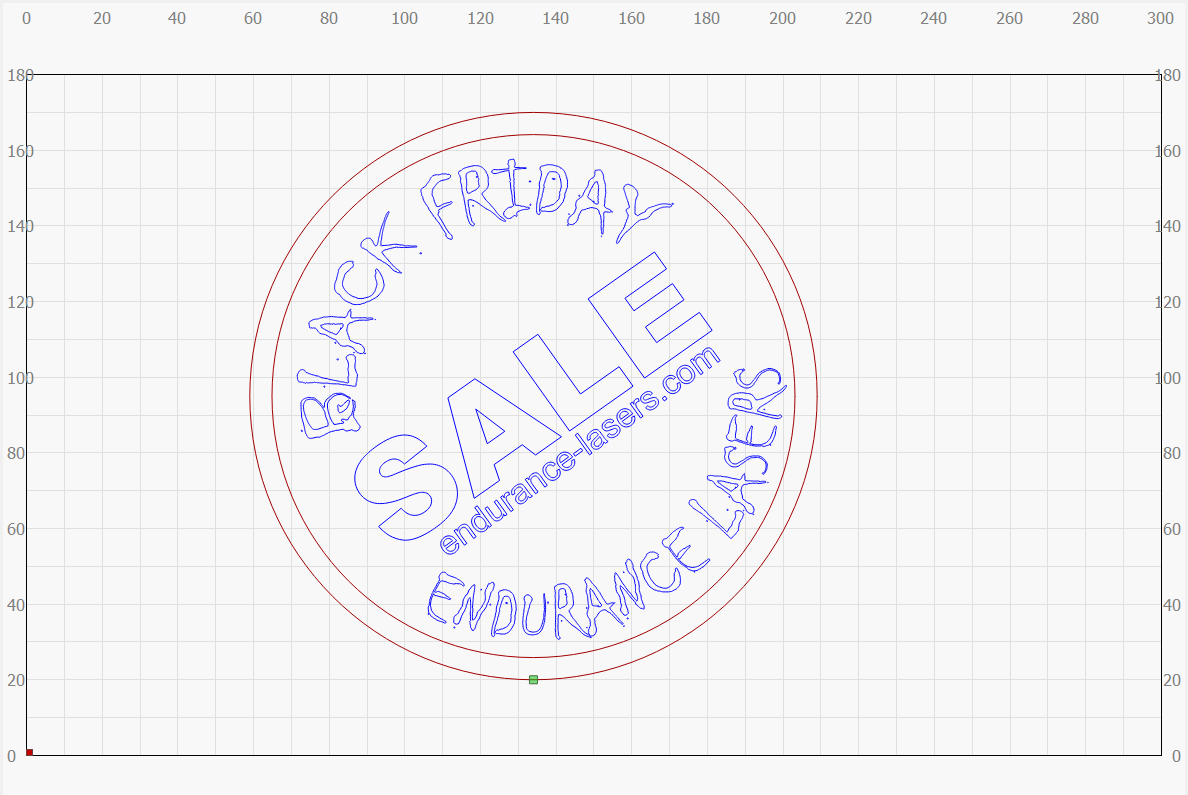
As the glue base is drying, we set to the creation of the engravig design in the LightBurn software:
Meanwhile, the glue has dried, and we are ready to spray the T-shirt with paint. But at first, we need to frame the work field for engraving with masking tapes so that not paint the adjacent areas.
Now we can spray stout-heartedly our framed square with paint.
We cover the work area with blue, green and orange paint in succession and let it dry.
Meantime, we set the engraving parameters in Lightburn.
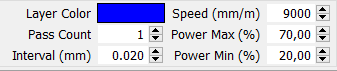
Once the paint is dry we place the T-shirt on the work table and start engraving. To remove the products of combustion we use an air-assist.
It takes us about 60 minutes to make an engraving, 15×15 cm in size.
When engraving don’t forget about your safety googlrs and smoke extraction!

Our engraving is ready and we enjoy the result!

Try do interesting things out with Endurace Lasers!
Learn more about a DIY pillow – how to make your own pillow with the laser.
How to make a DIY toy using a CNC 3018 and a laser.
If you have any more questions about laser fabric engraving or cutting – ask us in a Livechat.