CONTENTS
Chapter 2 Installation Size 10
Chapter 3 Controller Real Picture and Interface 12
Chapter 4 Interface Signal of Controller 15
- Interface of Main Power Source CN0 15
- Controller-display panel Interface HMI 15
- Udisk Interface 15
- PC-USB Interface 15
- Ethernet Interface 15
- General /Dedicated Output Port CN1 16
- General /Dedicated Input Port CN2 16
- 4-axis limit Input Interface CN3/CN4 17
- X/Y/Z/U-axis Motor Driver Interface AXIS_X~AXIS_U 18
- Laser Power Control Interface CN5/CN6 18
Chapter 5 Examples of Laser Power Interface 20
Chapter 6 Interface Examples of Step-servo Motor Driver 23
Chapter 7 Examples of IO-Port Wiring 25
Chapter8 Human-Computer Interface Operating Instruction 27
Chapter 9 Manufacturer/User Parameters Details 44
Chapter 1 Overview
Briefing
RDC644XG system is a new generation system for control of laser engraving and cutting, which is developed by RD technology, Ltd. High hardware stability, high voltage or static electricity rejection, and friendly 3.5TFT man-machine display. This system is provided with stronger software function including perfect 4-axis motion control function, large-capacity file storage, two-channel adjustable digits laser power control interface, USB driver of stronger compatibility, multi-channel general/special IO control, and, this system can communicate with PC by USB2.0 or Ethernet, and the communication mode is automatically checked by the system.
Description of Controller Model
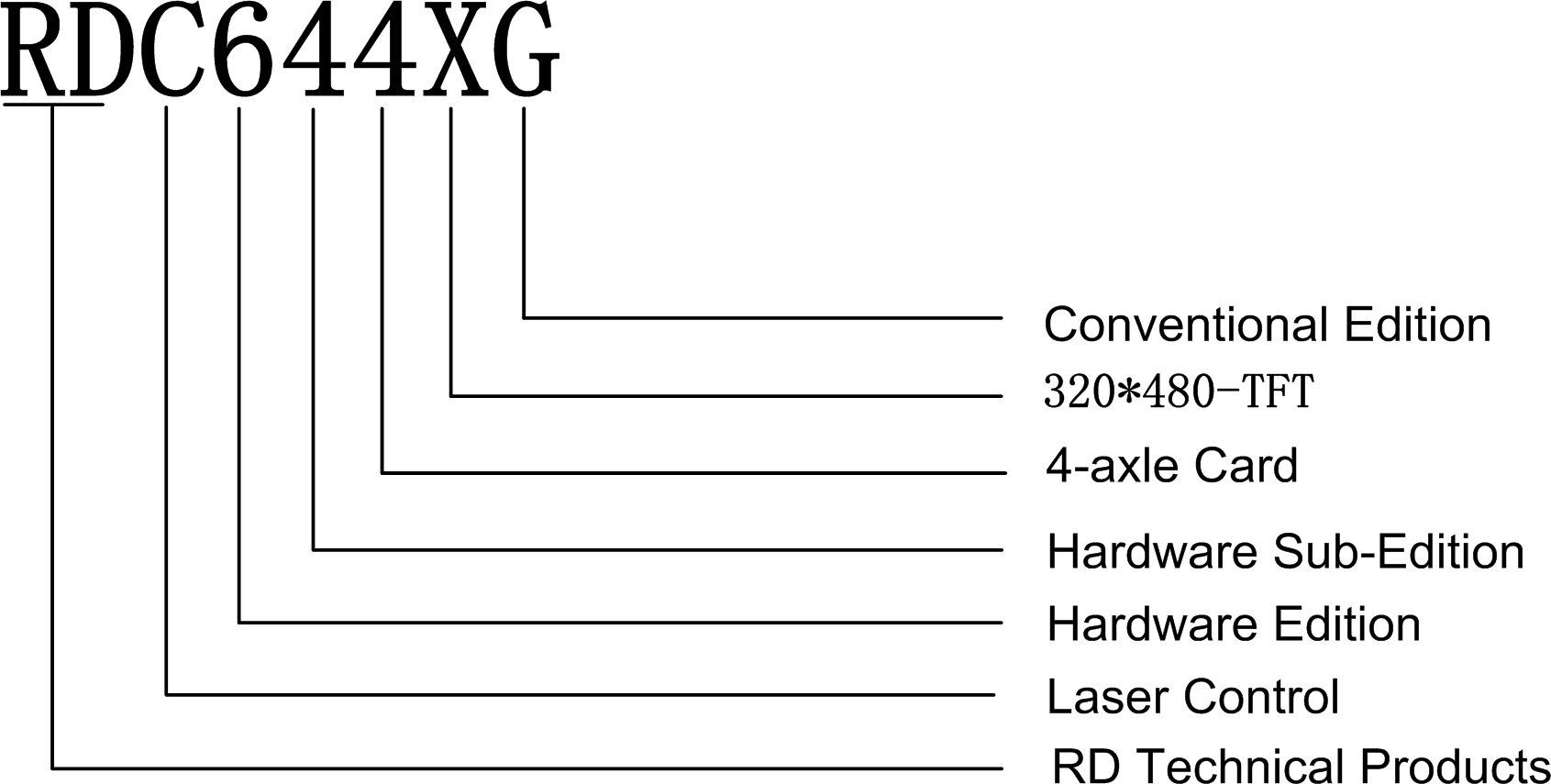
Comparison of Controller Performance
| RDLC420 | RDC6332G | RDC6342G | RDC644XG | |||||||
| Power Feature | One-way 5V, one-way 24V, independent | Only one-way 24V (compatible with 36V for power supply, but not recommended) | Only one-way 24V (compatible with 36V for power supply, but not recommended) | Only one-way 24V (compatible with 36V for power supply, but not recommended) | ||||||
| Laser Feature | Port | One-way digit one-way analog | and | Two-way digits and two-way analog port, settable independently and non-interacted | Two-way digits and two-way analog port, settable independently and non-interacted | Two-way digits port, settable independently and non-interacted | ||||
| USB Feature | Copying Speed | Common | Quick | Quick | Very Quick | |||||
| Compatibili ty | Support USB disks with small capacity | Support all USB disks with different capacities | Support all USB disks with different capacities | Support all USB disks with different capacities | ||||||
| Memory Feature | Capacity | 64M | 256M | 256M | 128M | |||||
| Fault Tolerance | Common | Capable of checking defective track and formatting and good in fault tolerance | Capable of checking defective track and formatting and good in fault tolerance | Capable of checking defective track and formatting and good in fault tolerance | ||||||
| General IO Feature | Input Port | Two ways | 4 ways (two general, two specialties) | for for | 4 ways (two for general, two for specialties) | 4 ways general, specialties) | (two two | for for | ||
| Output Port | 1-way (low current, so additional drive is needed) | 4-ways (500mA high current for each, OC output, no reverse current protection) | 4-ways (500mA high current for each, OC output, no reverse current protection) | 4-ways (500mA high current for each, OC output, reverse current protection included) | ||||||
| Software Feature | Power-off restart for Engraving | YES | YES | YES | YES | |||||
| Multi-origin Logics | NO | YES | YES | YES | ||||||
| Parameter | NO | YES | YES | YES | ||||||
| Backup Logics | ||||||||
| Work time Preview | NO | YES (the work time accurate to 1ms) | YES (the work time accurate to 1ms) | YES (the work time accurate to 1ms) | ||||
| Online Update Controller Program | NO | YES | YES | YES | ||||
| Display Feature | Online Modificatio n Laser Power/Spee d | YES | YES | YES | YES | |||
| Offline Modificatio n Layer parameters | NO | YES | YES | YES | ||||
| Online Update Startup Display | NO | YES | YES | NO | ||||
| File dynamic/sta tic preview | NO | YES | YES | YES | ||||
| Run progress bar display | NO | NO | NO | YES | ||||
| Modificatio n Factory/Use r’s para on display | NO | YES | YES | NO | ||||
| Display type | 128*64, display | dot | 320*240 display | TFT | 320*240 display | TFT | 320*480 TFT display | |
| Motion-axis Feature | Soft Limit | YES | YES | YES | YES | |||
| Hard Limit | NO | YES | YES | YES | ||||
| Z-axis Linkage | NO | YES | YES | YES | ||||
| Feeding Feature | Single direction | Single/double direction for option | Single/double direction | for | Single/double direction for option | |||
| option | ||||||||
| Power-on | Fixed | Configurable | for | Configurable for | Configurable for each | |||
| Resetting | each axes | each axes | axes | |||||
| Key Speed | Fixed | Configurable | Configurable | Configurable | ||||
| Axiss | 4 | 3 (Z | axes is | 3 (Z axes is | 4 | |||
| configurable to flat | configurable to | |||||||
| or feedin axes) | flat or feedin | |||||||
| axes) | ||||||||
| Encryption | Encryption | Realtime clock and | Realtime clock | No | realtime clock, | |||
| Feature | based on the | battery | integrated | and battery | but | encryption | ||
| PC time | for | hardware | integrated for | included | ||||
| encryption | hardware | |||||||
| encryption | ||||||||
| Communicat | USB2.0 | 10/100MHZ | 10/100MHZ | 10/100MHZ Ethernet | ||||
| e | Ethernet or USB2.0 | Ethernet or | or | USB2.0, | ||||
| Mode | USB2.0 | communication mode | ||||||
| is | automatically | |||||||
| checked | ||||||||
Chapter 2 Installation Size
Installation Size of Controller
The unit of all sizes is millimeter (mm) and the size accurate to 0.1mm (the four holes are symmetrical).

Figure 2.1-1
Size of Panel
The unit of all sizes is millimeter (mm) and the size accurate to 0.1mm.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Figure 2.2-1
Chapter 3 Controller Real Picture and Interface
Picture of Controller
For more detailed pin description, see the Chapter 4: Description of Interface Signal for Controller.
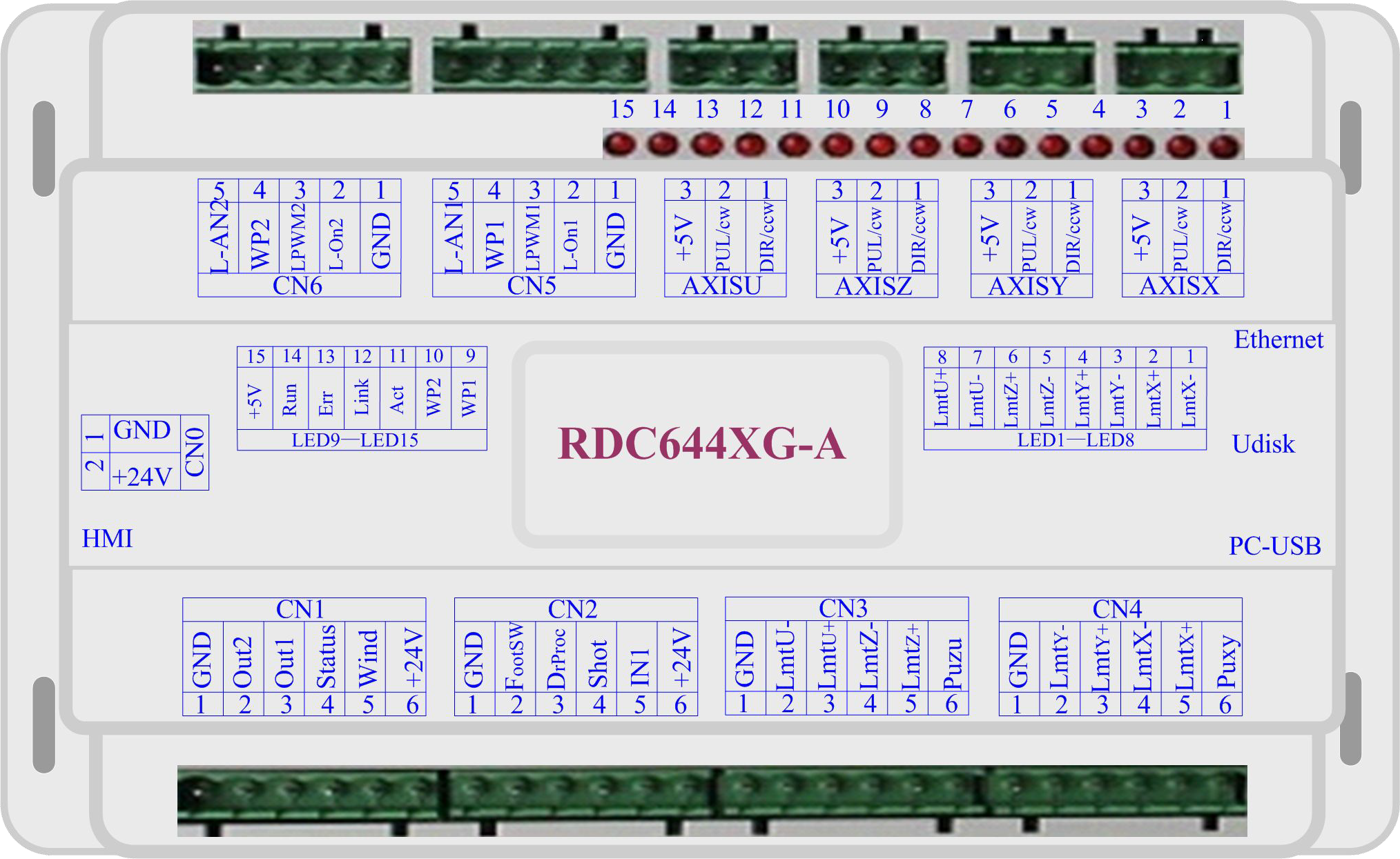
Figure: 3.1-1 Picture of Controller
Pictures of Panel
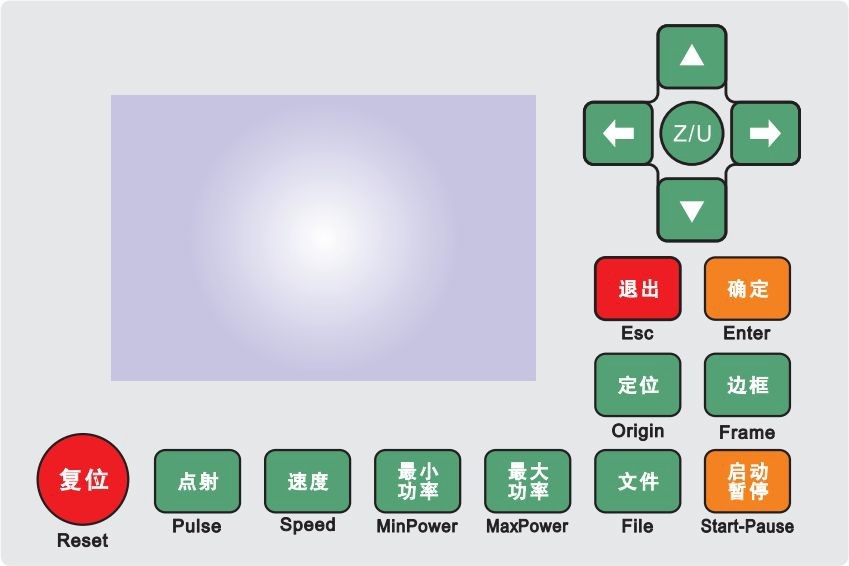
Figure: 3.2-1 Picture of Panel
Electrical Connection of Control System
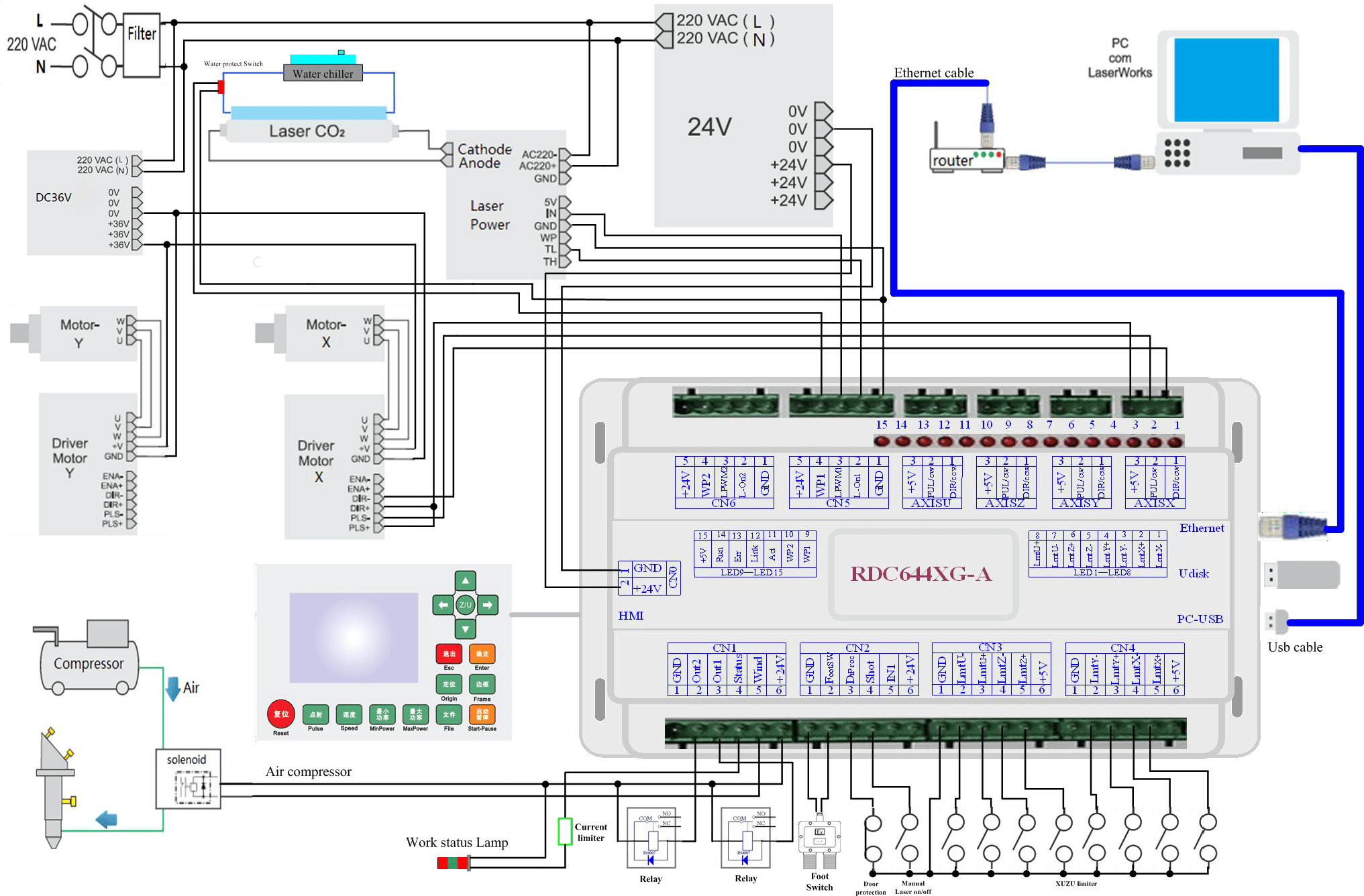
Figure 3.3-1 Electric Connection
Chapter 4 Interface Signal of Controller
Interface of Main Power Source CN0
| Pin | Symbols | Definitions |
| 1 | GND | 24V power ground (input) |
| 2 | +24V | 24V power positive (input) |
This control system employs single 24 power supply. For a certain margin, it is suggested to select 24V/2A above power. Besides, this system is compatible with 36V power, that is to say, the 36V power of Motion driver can directly be connected to this main power port of this system, but generally it is not
suggested to do so.
Controller-display panel Interface HMI
![]()
Caution
The connecting wire is parallel line of pin-to-pin.
Udisk Interface
Udisk is a USB-AM interface; the controller visits the u-disk by this interface.
PC-USB Interface
PC-USB is a USB-BM interface. The controller may communicate with PC by this port.
Ethernet Interface
Using this interface, the controller can communicate with PC by 10/100MHZ Ethernet.
![]()
Caution
Pin to Pin Ethernet parallel line is recommended.
General /Dedicated Output Port CN1
Definition of general/dedicated output port
| Pin | Symbols | Definitions |
| 1 | GND | Power ground (output) |
| 2 | Out2 | General output, with the function reserved. |
| 3 | Out1 | General output, with the function reserved. |
| 4 | Status | General output for the signal port of running status. If this port is |
| externally connected with the relay, the relay coil is broken over | ||
| when it works; no influence is produced when it suspends | ||
| working. When its work ends or is stopped manually, the relay | ||
| coil will be cut off. | ||
| 5 | Wind | General output for blower control. When the blower control is |
| enabled, this port will output the control signal of the blower, | ||
| otherwise it will output other special control signals. When the | ||
| blower is connected and its control enabled, the blower switch | ||
| can be set separately on each layer. If the relay is connected | ||
| externally, the relay coil will be broken over when the blower is | ||
| on; the relay coil will be cut off when the blower is off. | ||
| 6 | +24V | 24V Power positive output (If the interface of main power source |
| is powered with 24V power supply, this pin should be 24V; if it is | ||
| powered with 36 V power supply, this pin should be 36V.) |
![]()
All outputs are isolated through the optocoupler, and 500mA current for each, OC gate output, each can directly drive the 6V/24V relay.
Prompt
General /Dedicated Input Port CN2
| Pin | Symbols | Definitions |
| 1 | GND | Power ground (output) |
| 2 | FootSW | Input port of foot switch. The connection method is: when the |
| pedal is stepped down, the low-level signal will be inputted to | ||
| this port; when the pedal is released, the port will be | ||
| disconnected or the high-level signal can be inputted to this | ||
| port; when the stepped-down pedal is held for not less than | ||
| 100 ms, if the machine lies idle, it can be started for work; if | ||
| the machine is in the working state, the work will be | ||
| suspended; of the machine is in the suspension, the work will |
4-axis limit Input Interface CN3/CN4
X/Y axis limit input CN4.
| Pin | Symbols | Definitions |
| 1 | GND | Power ground (output) |
| 2 | LmtY- | The limit from axis Y- and Y to 0 coordinate |
| 3 | LmtY+ | The limit from axis Y+ and Y to max. coordinate |
| 4 | LmtX- | The limit from axis X- and X to 0 coordinate |
| 5 | LmtX+ | The limit from axis X+ and X to max. coordinate |
| 6 | Puxy | 5V Power positive (output) |
The limit polarity is optional, that is to say, when the motion axis reaches the limit position, it will trigger a low-level signal so as to make the corresponding LED (under the cover) light; when the motion axis leaves the limit position, it will trigger a high-level signal or disconnect the limit signal so as to make the limit indicator go out, but when it leaves the limit, the corresponding indicator will light and the limit polarity become positive. The mistaken setting of limit polarity will result that the limit can’t be detected when the system is reset so as to lead to the collision of axis.
The pin definitions of Z/U axis limit input CN3 are the same as CN4.
X/Y/Z/U-axis limit inputs are compatible to 5V/12V/24V logic level inputs.
X/Y/Z/U-axis Motor Driver Interface AXIS_X~AXIS_U
The interfaces of the four motion axis are the same. The AXIS-X interface is exampled.
| Pin | Symbols | Definitions |
| 1 | DIR | Directional signal (OC output) |
| 2 | PUL | Pulse signal (OC output) |
| 3 | +5V | 5V Power positive (output) |
The polarity of directional signal for driver pulse signal can be set. Where a certain axis is reset, it will move to the opposite direction of machine origin, which means the polarity of directional signal for this axis is not correct. In such a case, the connection between this axis and the motor driver can be broken first (otherwise the controller cannot be detected to the limit so as to lead to the collision of this axis), and then such a polarity can be corrected after this axis is reset completely. Upon the correction, the reset key can be pressed against to reset the controller.
And, the pulse signal can be falling edge valid or rising edge valid. The default setting is falling edge valid.
![]()
The Pulse signal and the directional signal are all OC outputs. The Controller must be common anode with the motor driver
Prompt
Laser Power Control Interface CN5/CN6
This control system has two independent and adjustable digital laser power control interfaces.
Signals of the two interfaces are similar and the first digital interface (CN5) is hereby example:
| Pin | Symbols | Definitions |
| 1 2 3 | GND L-ON1 LPWM1 | Power ground (output) Laser-enabled control interface
Power control interface of laser/laser tube |
| 4 5 | WP1 L-AN1 |
The input port of water protector for the first laser power source. When the water protector 1 is enabled, the controller will detect the input port of water protector 1. If this port is of low level, it will be deemed normal; if this port is of high level, the controller will forcibly close the laser to suspend the work in progress and the system will warn. If the water protector 1 is not enabled, the controller will not detect the input port of water protector 1 and so the water protector 1 can be unconnected. Water protection input must be 24V logic level. The analog signals for Laser Power. If Glass Tube is used, this pin is recommended to control the power of the Laser. |
![]()
Please correctly select the laser type in the factory parameters.
Prompt
Chapter 5 Examples of Laser Power Interface
Brief Introduction
This control system has two independent and adjustable digital laser power control interfaces, which can be used to control glass tube laser power and RF-laser.
Please correctly select the laser type in the factory parameters when connecting to different laser types, otherwise, the laser switching is incorrect.
Examples of Glass tube Laser Power
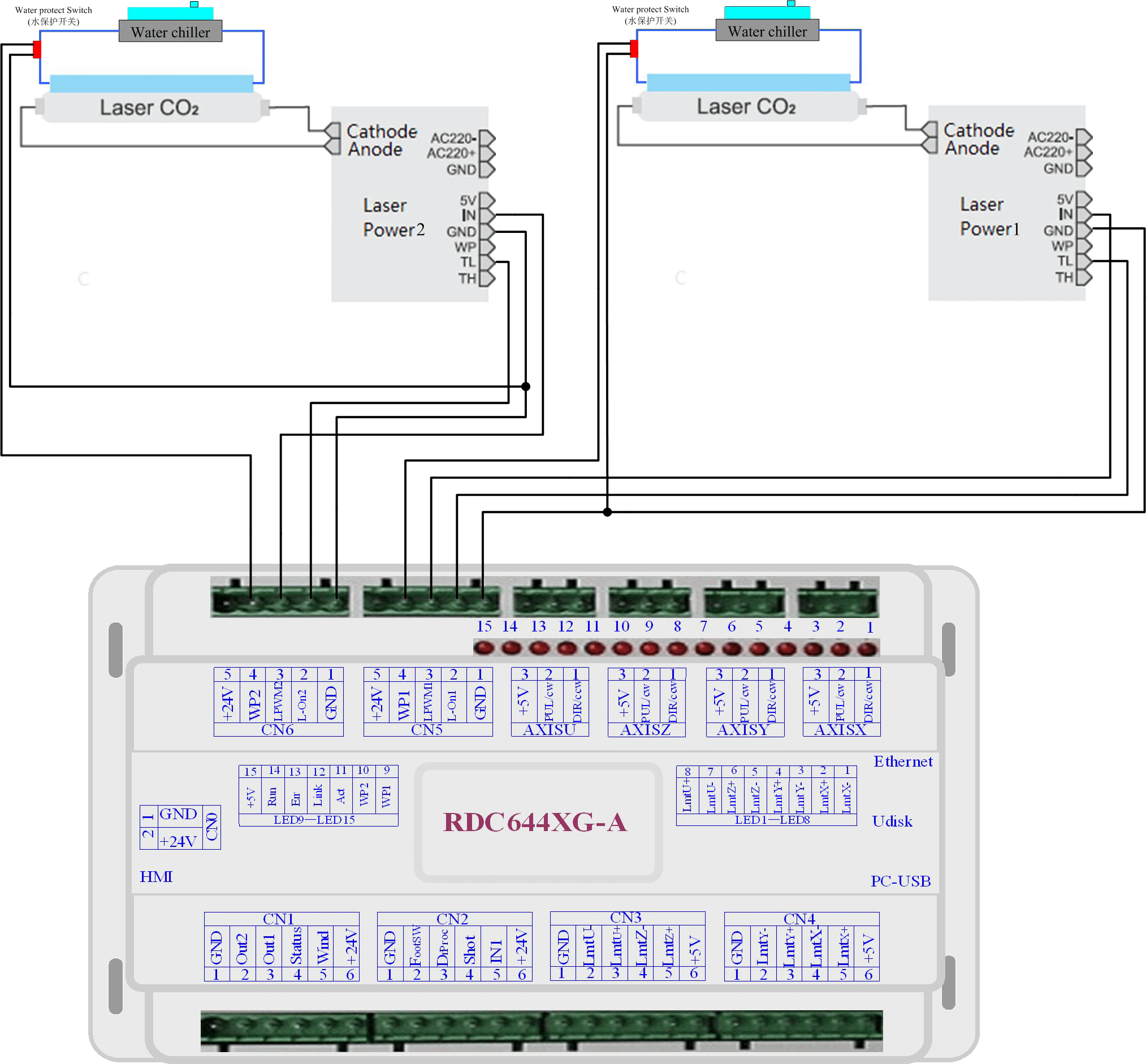
Examples of RF- CO2 Laser
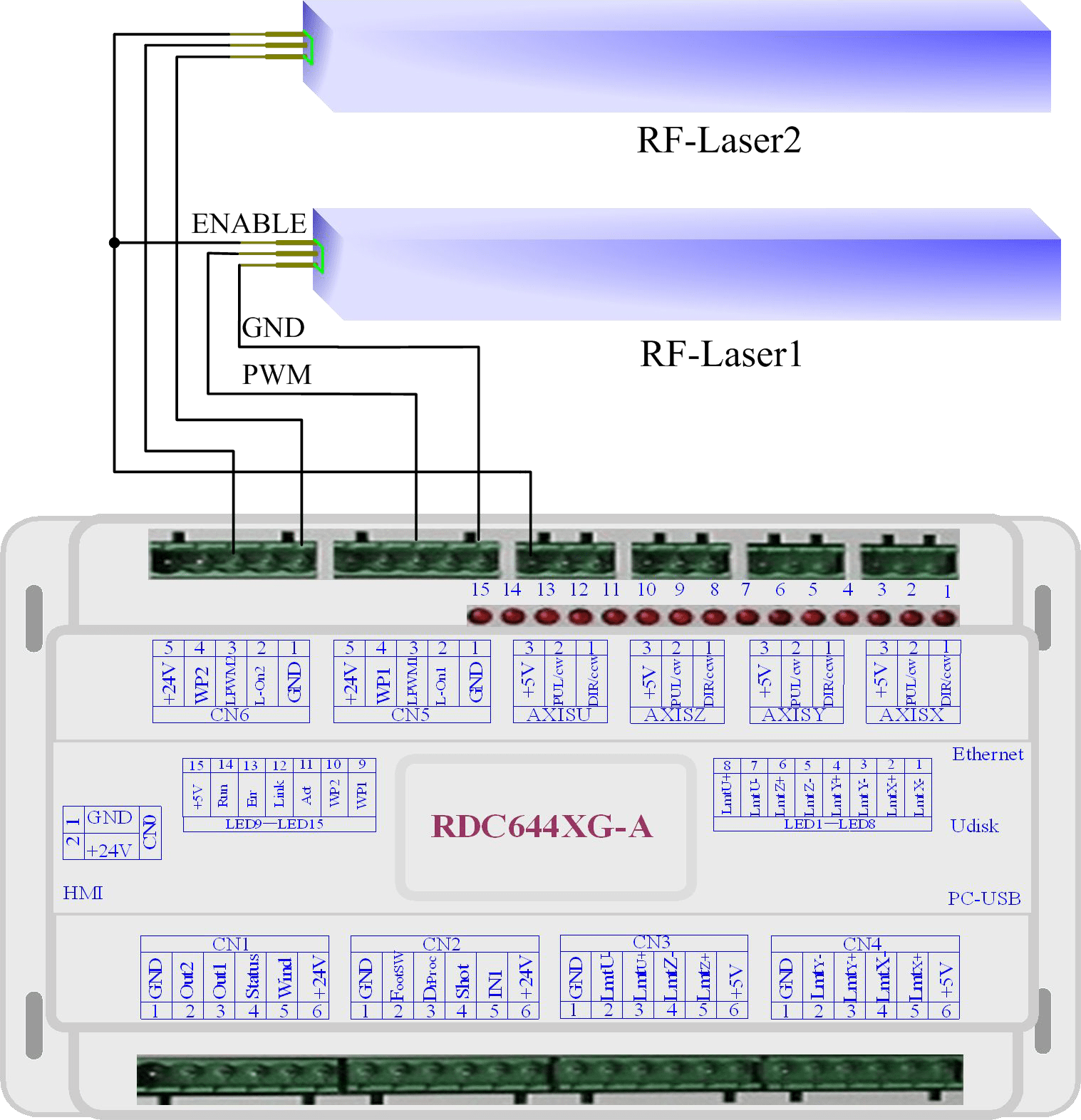
Chapter 6 Interface Examples of Step-servo Motor Driver
Brief Introduction
The input signal end of step-servo motor driver employs the opto-isolator technology. For the step pulse signal, some isolate the side OC diode from cutoff to conduction (e.g. the valid falling edge of pulse signal inputted from the diode minus end) and some do so from conduction to cutoff (e.g. the valid rising edge of pulse signal inputted from the diode minus end).
When it is indicated whether the pulse signal of motor driver is the valid rising edge or the valid falling edge, it will be subject to the pulse signal inputted from the minus end of side OC diode.
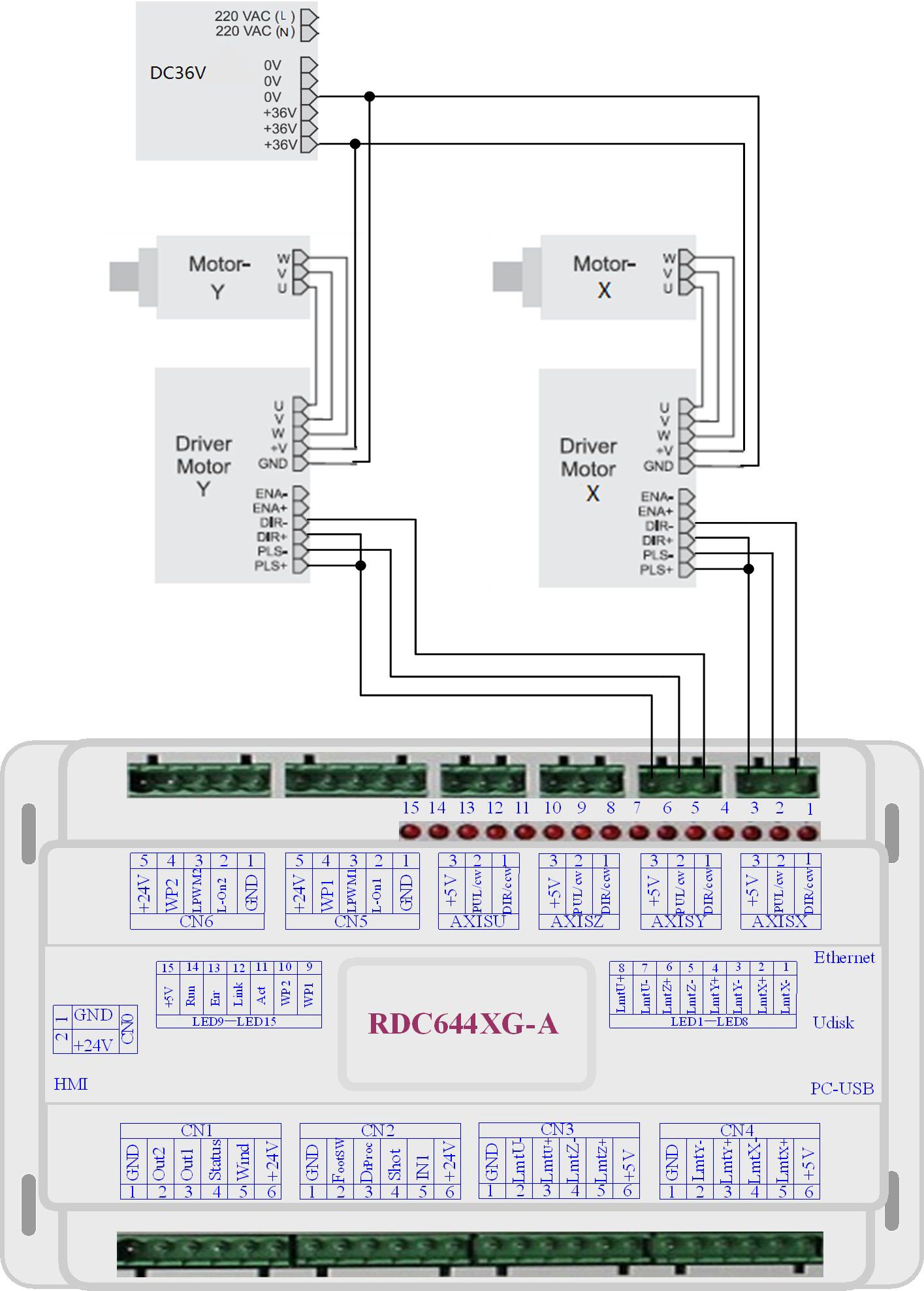
Some input signals of motor driver are independent and some are internally of common anode, so some have 4 external leading-out wires and some 3 wires (only the pulse and directional signals are counted) as shown in Figure 6.1-1 and 6.1-2.
RDC644XG Controller has four groups of 3-wires motion driver interface, each interface has one direction signal, one pulse signal, and one 5V positive output, the direction signal and the pulse signal are all OC output.
RDC644XG controller must be common anode with the motor driver. The polarity of the direction signal can be changed in the factory parameters, and the valid edge of the pulse signal can also be changed.
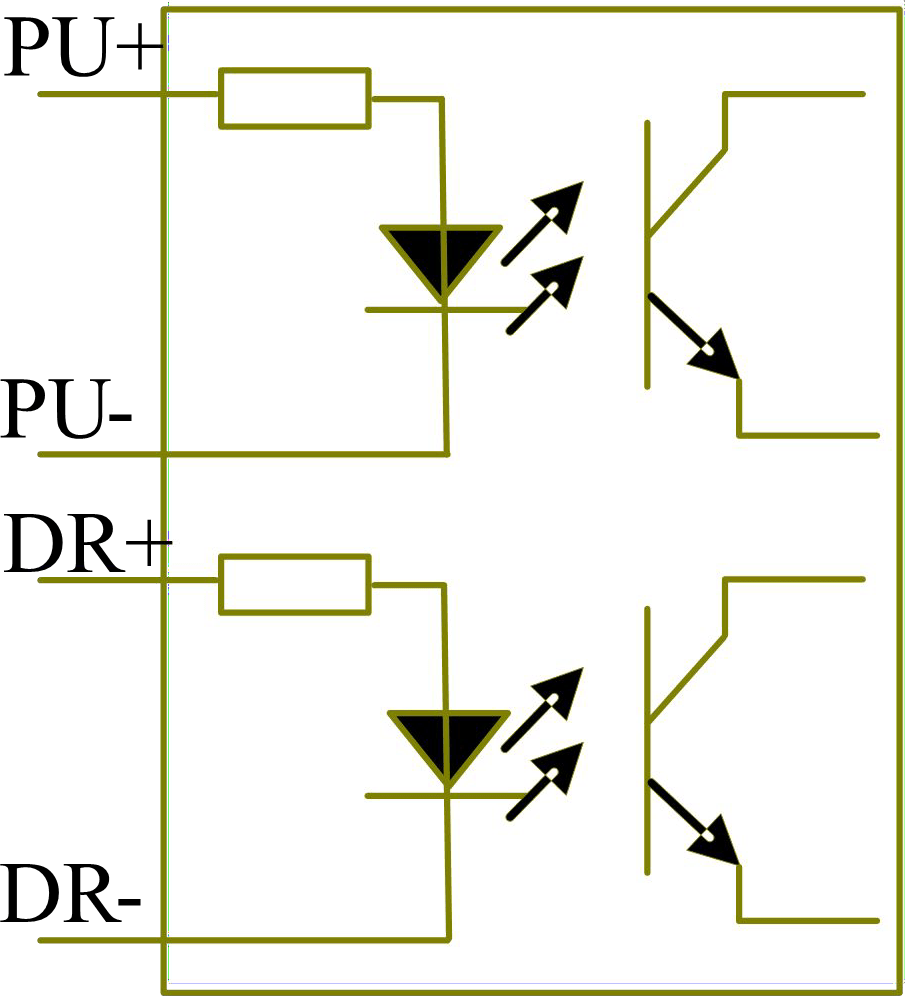
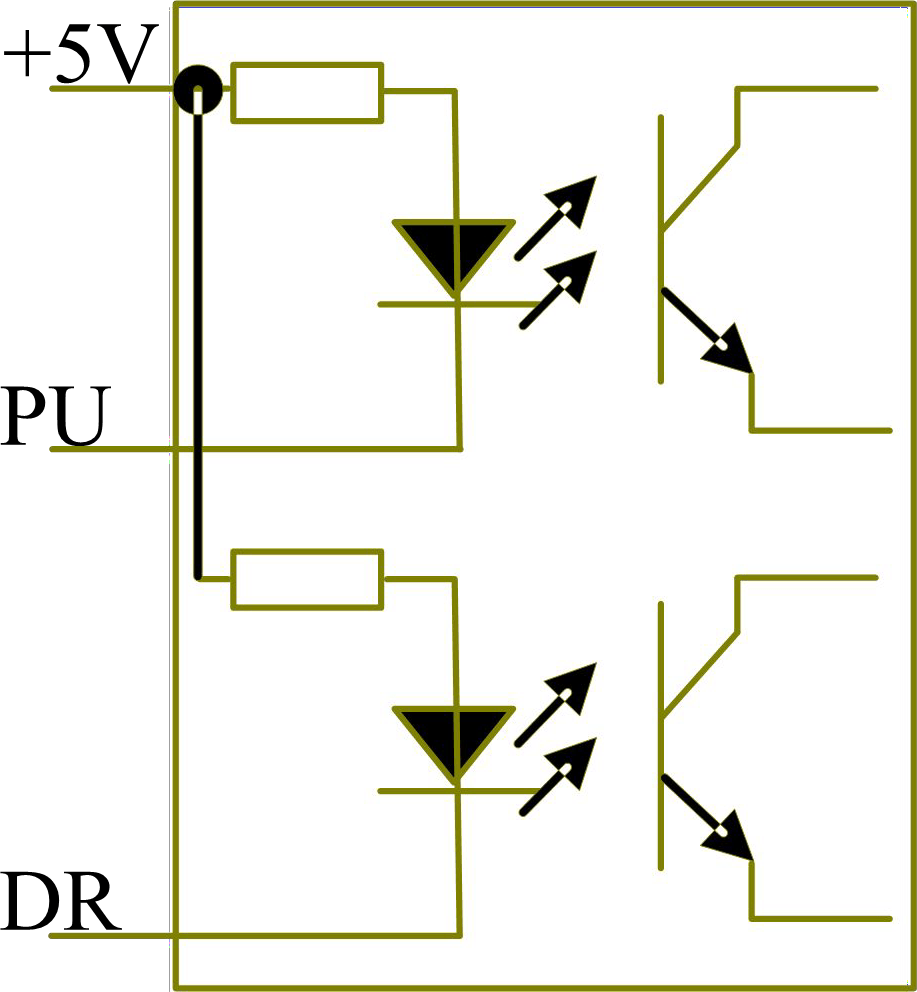
Figure: 6.1-1 Four Inputs, Independent Input Signal of Driver
Figure: 6.1-2 Three Inputs, Common-anode Input Signal of Driver
Examples of Motor Driver Connection
Chapter 7 Examples of IO-Port Wiring
Input port
The two water protection inputs are WP1 and WP2 with 24V logic level; all other inputs are compatible with 5V/12V/24V logic level.
Input connection is shown as below:
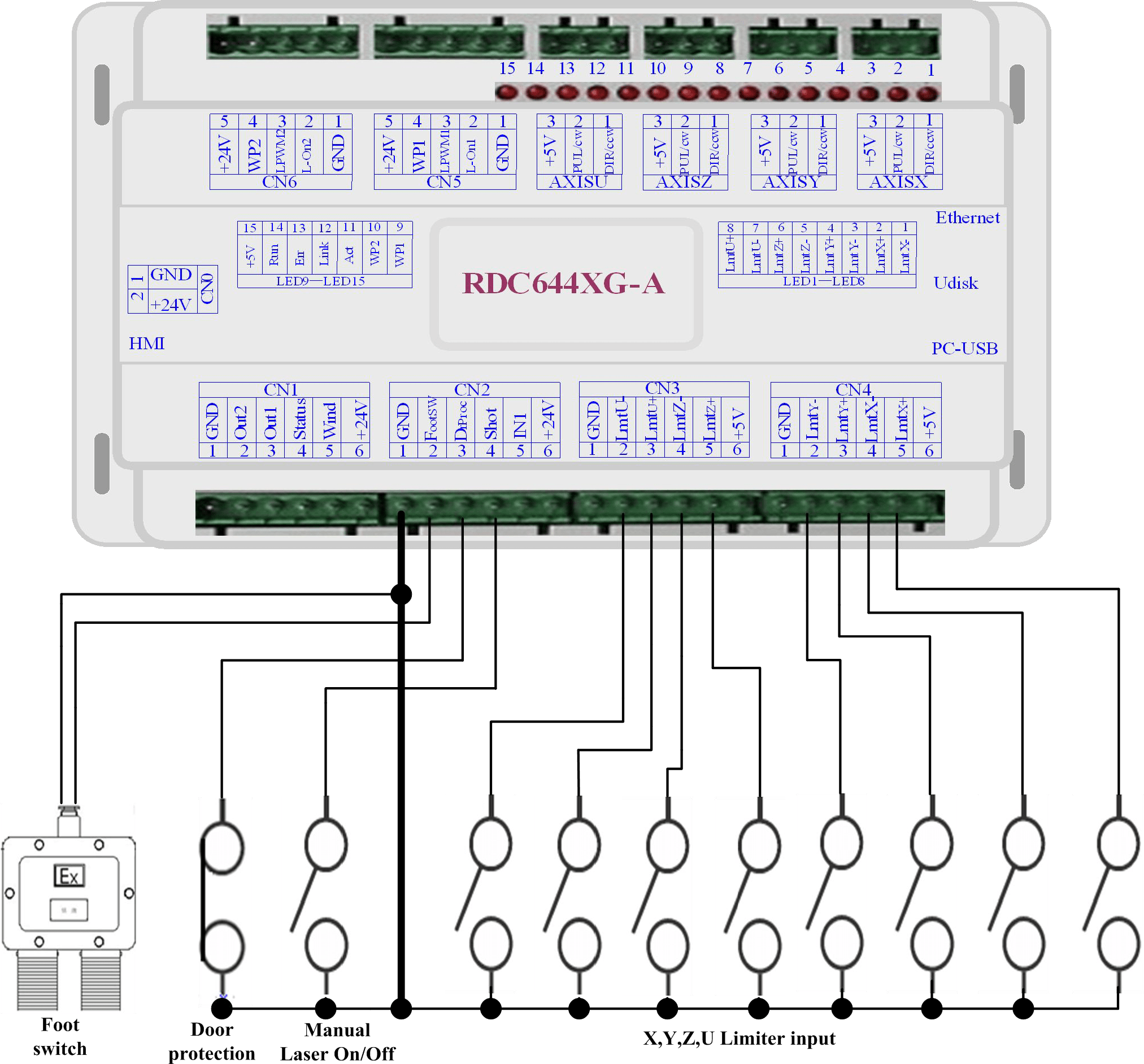
Figure 7.1-1 Input Example
Output port
All outputs are isolated through the optocoupler, and 500mA current for each, OC gate output, each can directly drive the 6V/24V relay, led lamp, buzzer etc.
Output connection shown as below
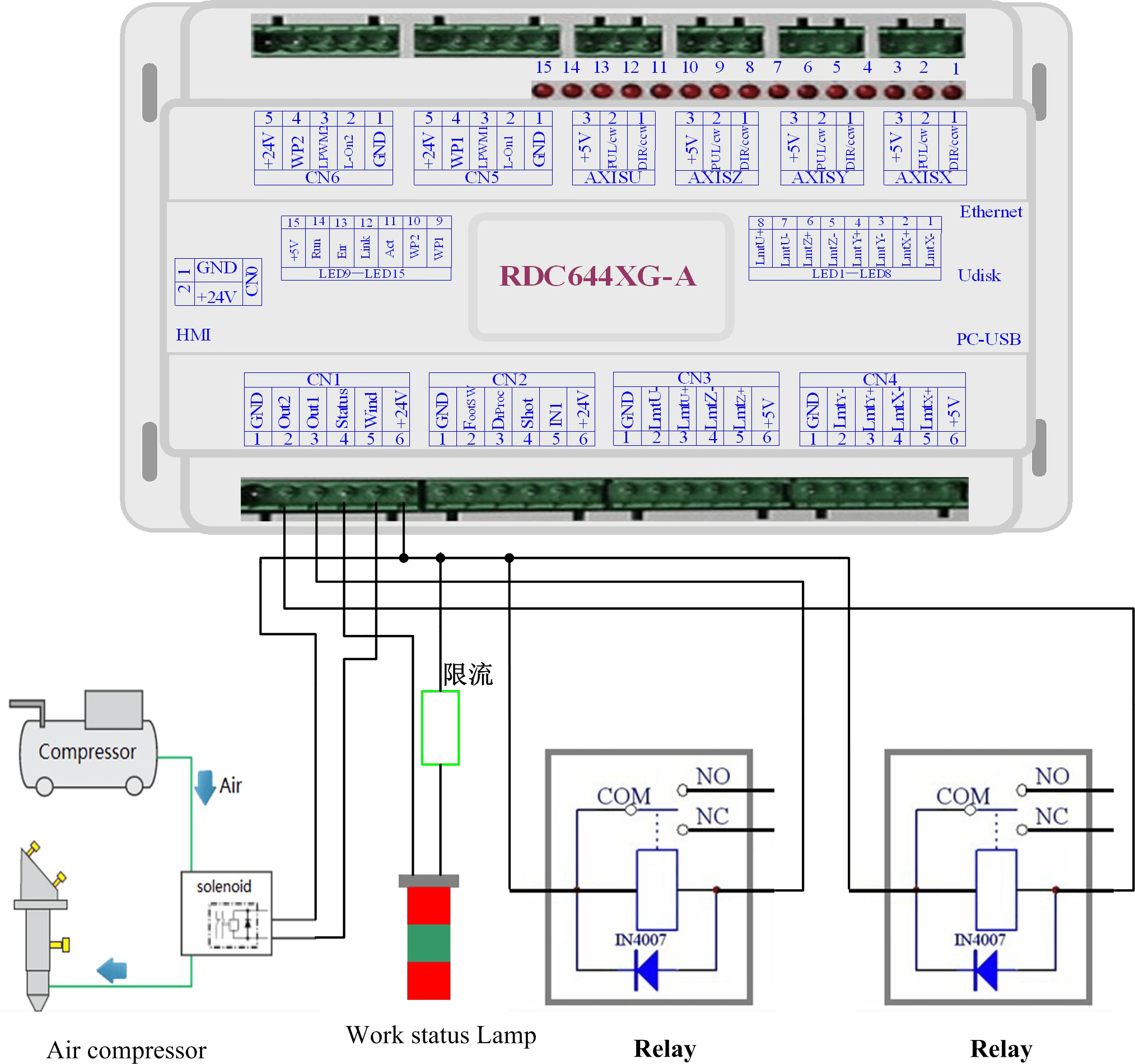
Figure 7.2-1 Output Example
Chapter8 Human-Computer Interface Operating Instruction
Panel and Keys
The Operation Panel
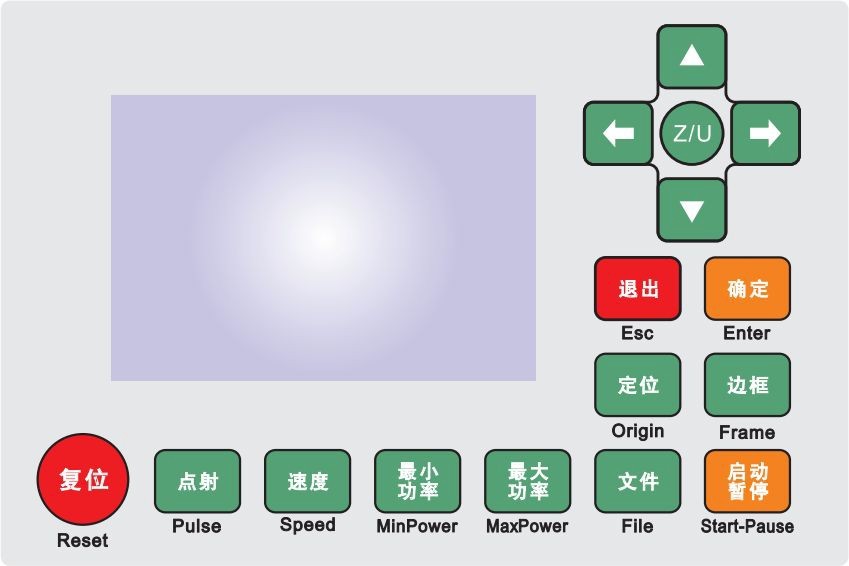
Introduction to the Keys
 Reset : : Reset the controller;
Reset : : Reset the controller;
: Set the relative origin;
Origin
: The laser tube emits laser;
Pulse
:
Frame
: Frame of the current file;
- : The management of the memory and U disc files;
File
- SpSeetetdhe: Speed of the current running layer, or set the direction keys move speed;
- :Set the max laser power of the current running layer, or set the power of “Laser” key;
Max. Power
- :Set the min laser power of the current running layer,
Min.
Power
- :To start or pause the work;
Start/ Pause

 :To move the X axes or the left/right cursor;
:To move the X axes or the left/right cursor;

 :To move the Y axes or the up/down cursor;
:To move the Y axes or the up/down cursor;
 : The Z/U key can be pressed when the system is idle or the work is finished. On pressing this key, it will show some entries in the interface, each entry includes some functions, Z axes move, U axes move, each axes to go home etc.;
: The Z/U key can be pressed when the system is idle or the work is finished. On pressing this key, it will show some entries in the interface, each entry includes some functions, Z axes move, U axes move, each axes to go home etc.;
Esc
- “:To stop work, or to exit to some menu;
Enter
- : Validate the change;
Main Interface Introduction
The main interface
When the system is powered on, the screen will show as below:
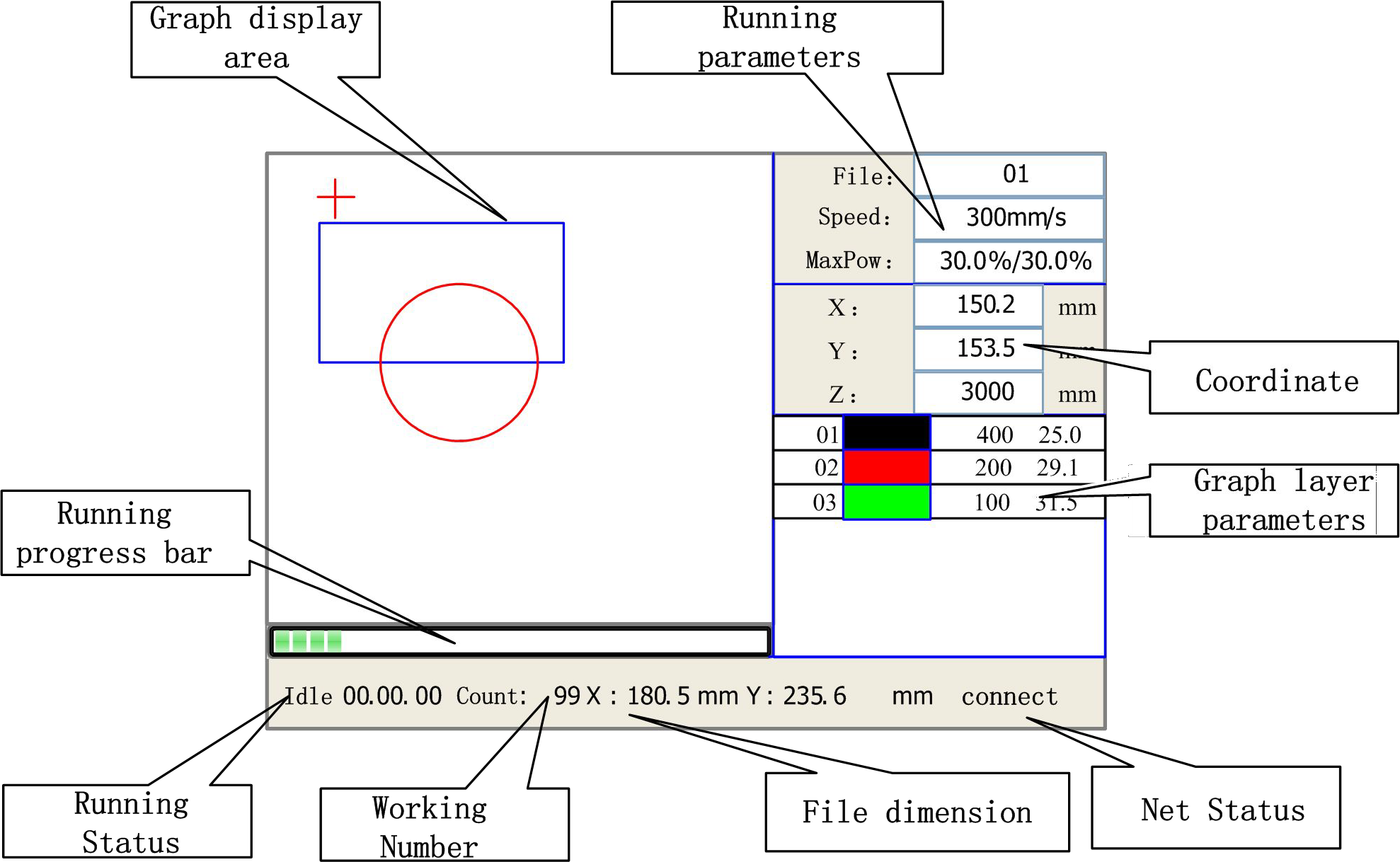
Figure 8.2-1
- Graph Display Area: To display the whole file’s track, and display the running track.
- Running parameters display area: To display the running file’s file number, speed, max power etc.;
- Coordinate display area: To display the current coordinate of X,Y and Z axes
- Layer parameters display area: To display the layers’ information of the current file, such as max or min power, speed etc. When system is idle, double click the layer, then users can change the layer’s parameters and the changing would be saved.
- Running Status: To display the current status of the machine, such as Idle, Run, Pause, Finish, etc.;
- Running Progress Bar: To display the progress bar of the current running file;
- Working Number: To accumulate the work number of the current file.
- File Dimension: To display the dimension of the current file;
- Net status: To display the connecting status of the Ethernet.
When work is idle or finished, all keys can be pushed, users can select a file to run, set some parameters, preview to a select file etc. But, when work is running or paused, some keys will not respond when they are pushed.
Speed Setting
Push the “Speed” key when the screen is on the main interface, it will show as below:

Figure 8.2-2
Push the “X+/-“ Keys to move the cursor in the numeral area, and push the “Y+/-” keys to change the value, then push the “Enter” key to save the change, push the “Esc” key to invalidate the change.
Max/Min power keys
Push the “Max Power” or the “Min Power” keys when the screen is on the main interface, it will show as below:
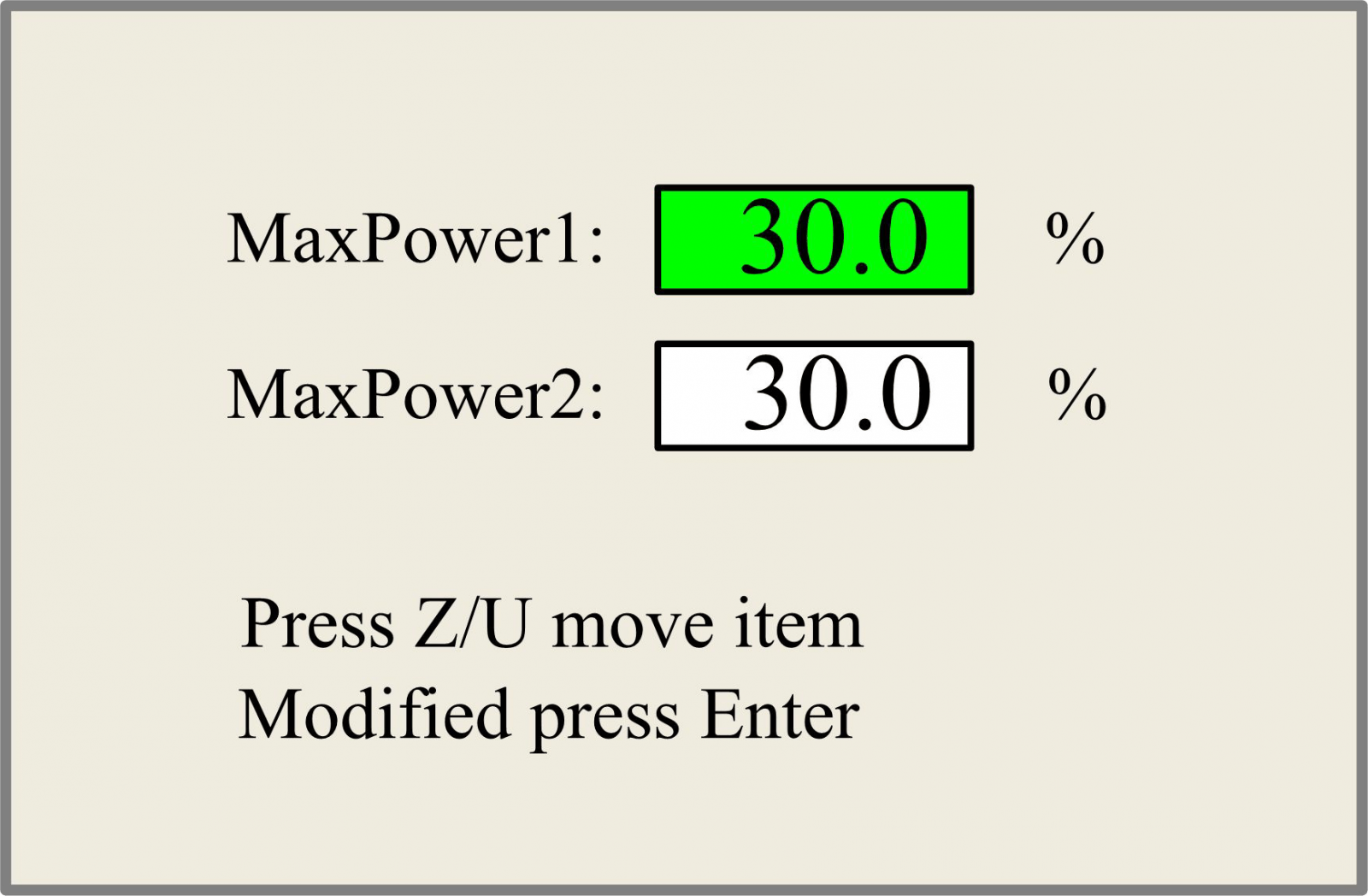
Figure 8.2-3

When “Z/U” key is pushed, the green block can move up and down to denote the changing item, then “Y+/-” keys and “X+/-” keys can be used to change the value.
Layer Parameters Setting
After selecting a file to preview on the main interface, user can push “Enter” key to let the cursor move to the first layer, then “Y+/-” Keys can be pushed to select the intent layer, on that time, user can push “Enter” key to check the selected layer’s parameters, show as below:

Figure 8.2-5
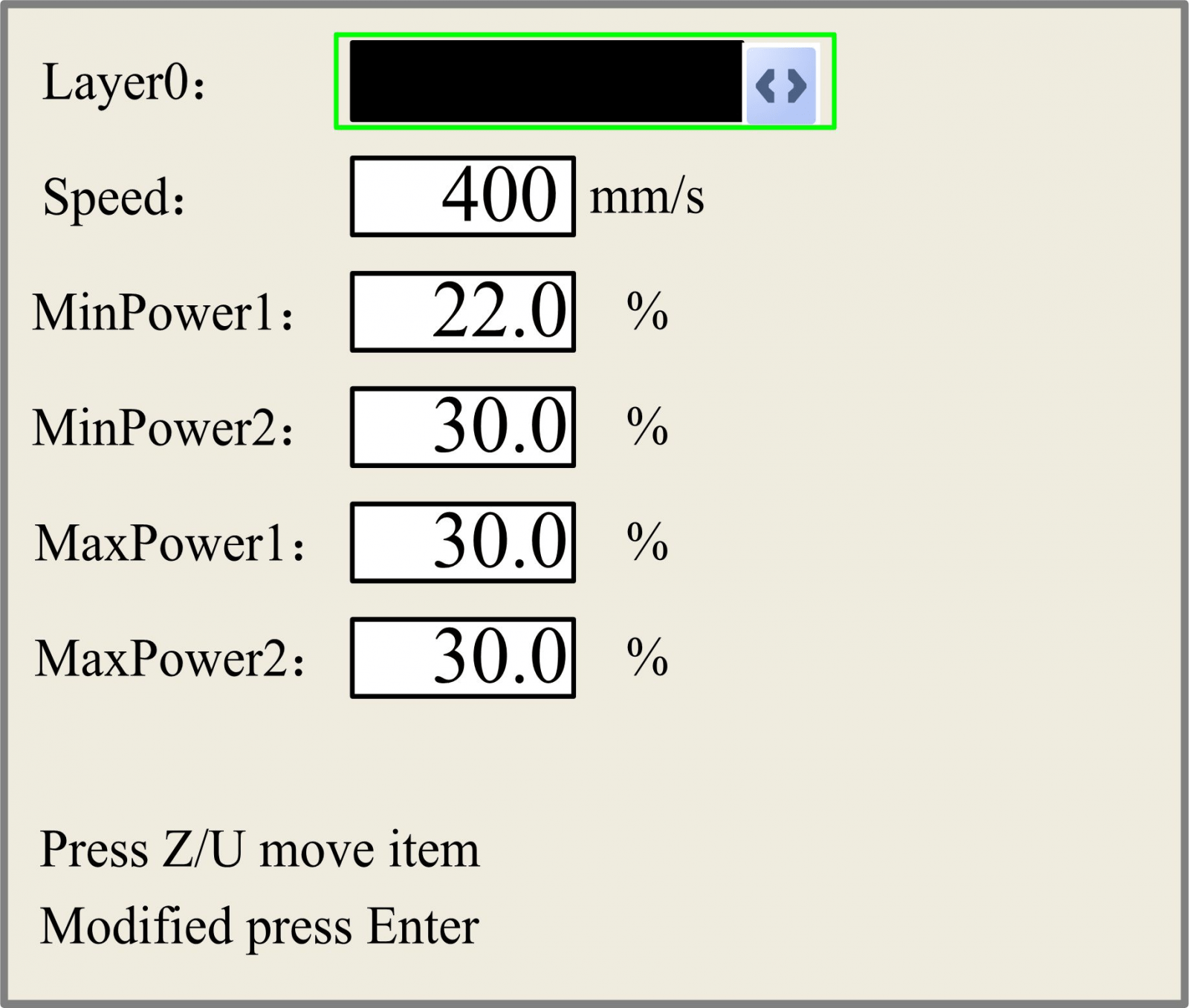
User can push “Z/U” Keys to move the green block on the intent parameter, then to change the parameter if needed. “OK” to validate the change, and “Esc” to invalidate the change.
Z/U Key Menu
The Z/U key can be pressed when the system is idle or the work is finished. On pressing this key, it will show some entries in the following interface:
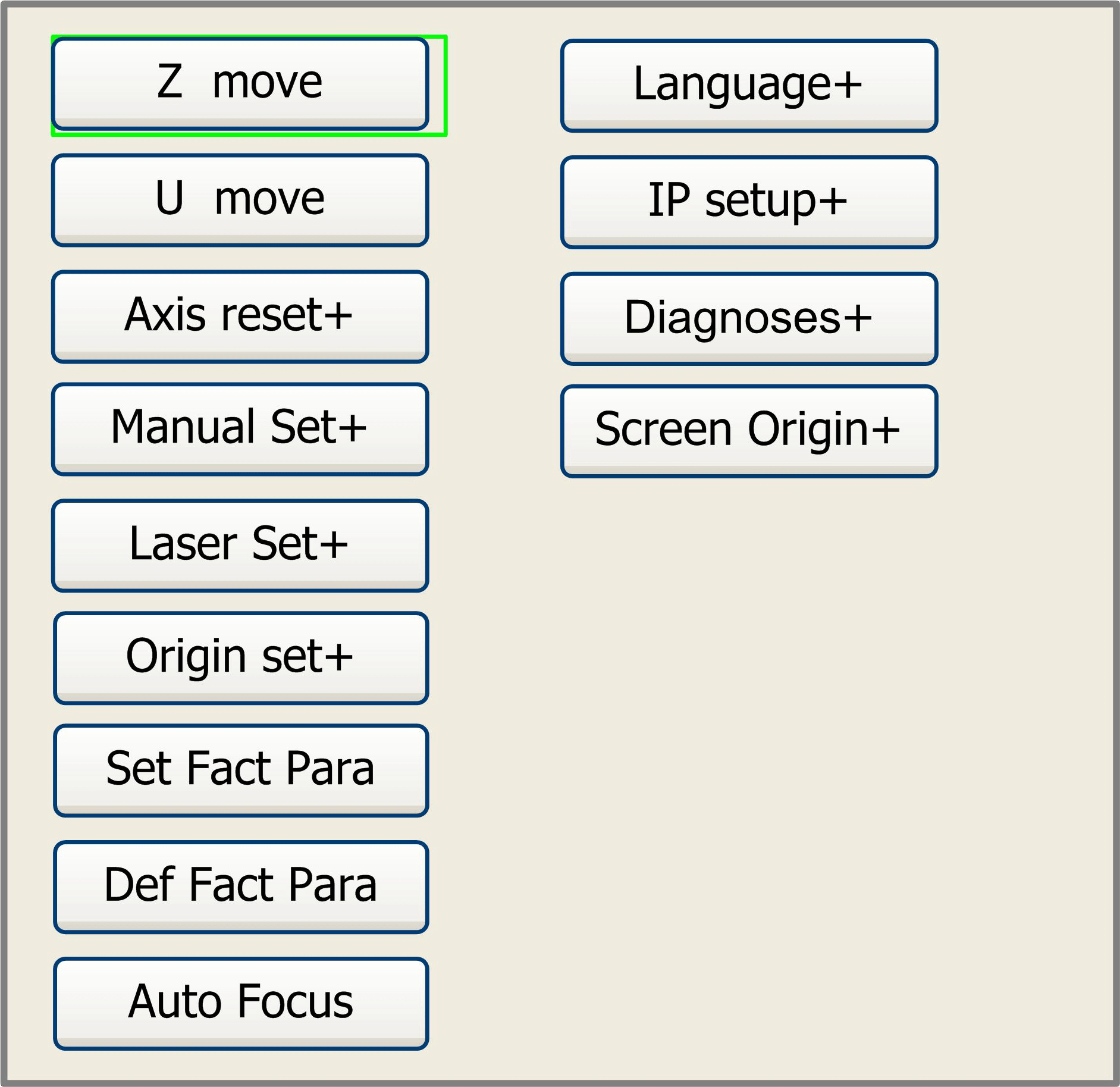
Figure 8.3-1
Push “Y+/-” keys to move the green block to the anticipant item, and then push the “Enter” key to display the sub menu.
Z-axis move
When the green block is on “Z Move” item, “X+/-” keys can be used to move the z axes.
U-axis move
When the green block is on “U Move” item, “X+/-” keys can be used to move the u axes.
Axes reset+
When the green block is on this item, push the “Enter” key to show as below:
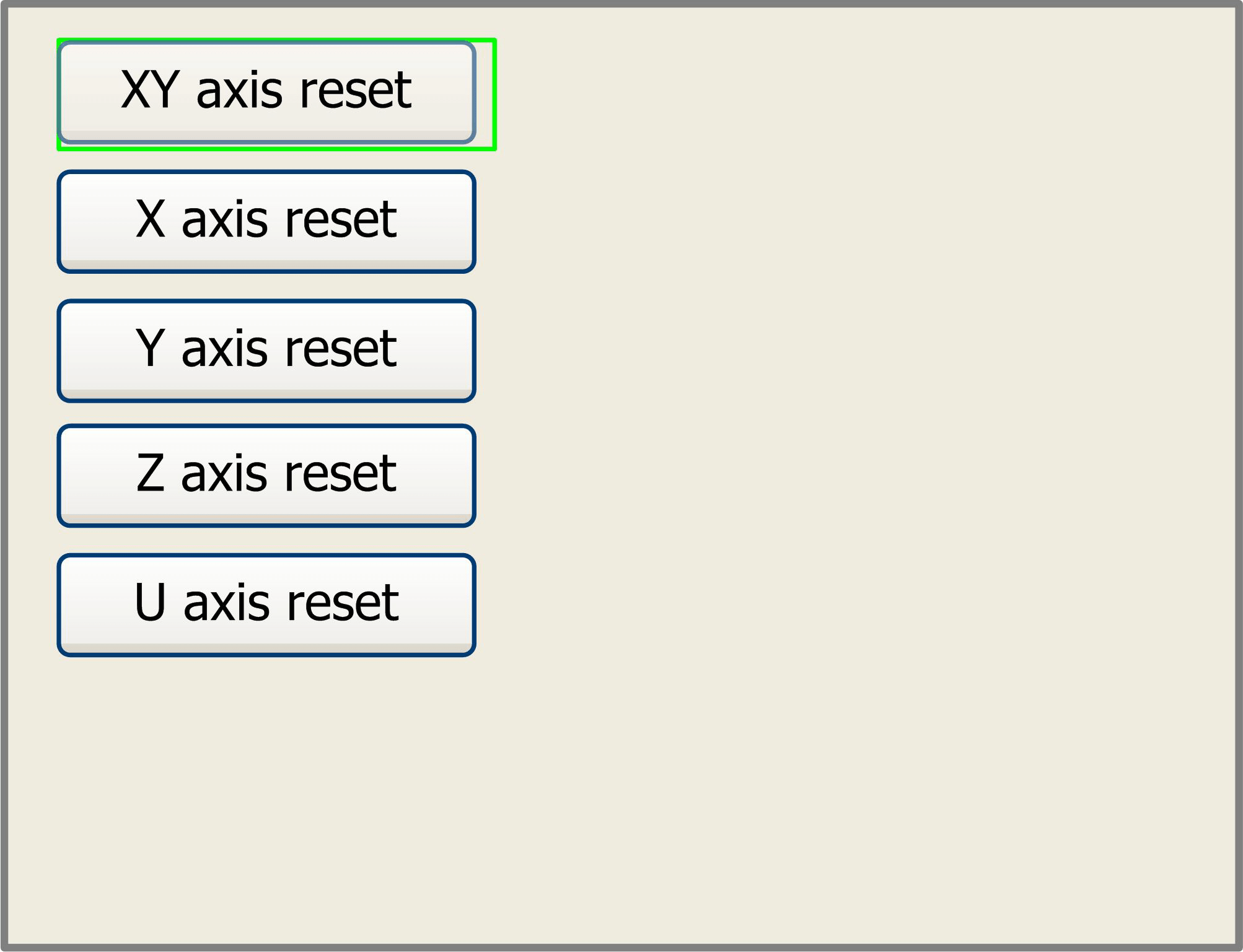
Figure 8.3-2
Push the “Y+/-“ Keys to move the cursor to one of the entry, then push “Enter” key to restart the selected axis, the screen will show some information when resetting.
Manual set+
When the green block is on this item, push the “Enter” key to show as below:

Figure 8.3-3
Push “Z/U” key to move the green block, and when the green block is on the “Mode” item, push “X+-“ keys to select the anticipant value, “Continue” or “Manual”. When “Continue” item is selected, then the “Manual” item is not valid, on that time, push the direction keys to move the corresponding axes, and when the pushed key is loosed, then the corresponding axes will finish moving. When the Mode item is “manual”, then pushing the direction key one time, the corresponding axes will move a fixed length, unless the scope is overstepped.
Laser set+
When the green block is on this item, push the “Enter” key to show as below:

Figure 8.3-4
Push “Z/U” key to move the green block, and when the green block is on the “Mode” item, push “X+-“ keys to select the anticipant value, “Continue” or “Manual”. When “Continue” item is selected, then the “Laser Set” item is not valid, on that time, push the Laser key to splash the enabled lasers, and when Laser key is loosed, then the lasers will finish splashing. When the Mode item is “manual”, then pushing the Laser key one time, the enabled lasers will splash a fixed time.
Origin set+
When the green block is on this item, push the “Enter” key to show as below:
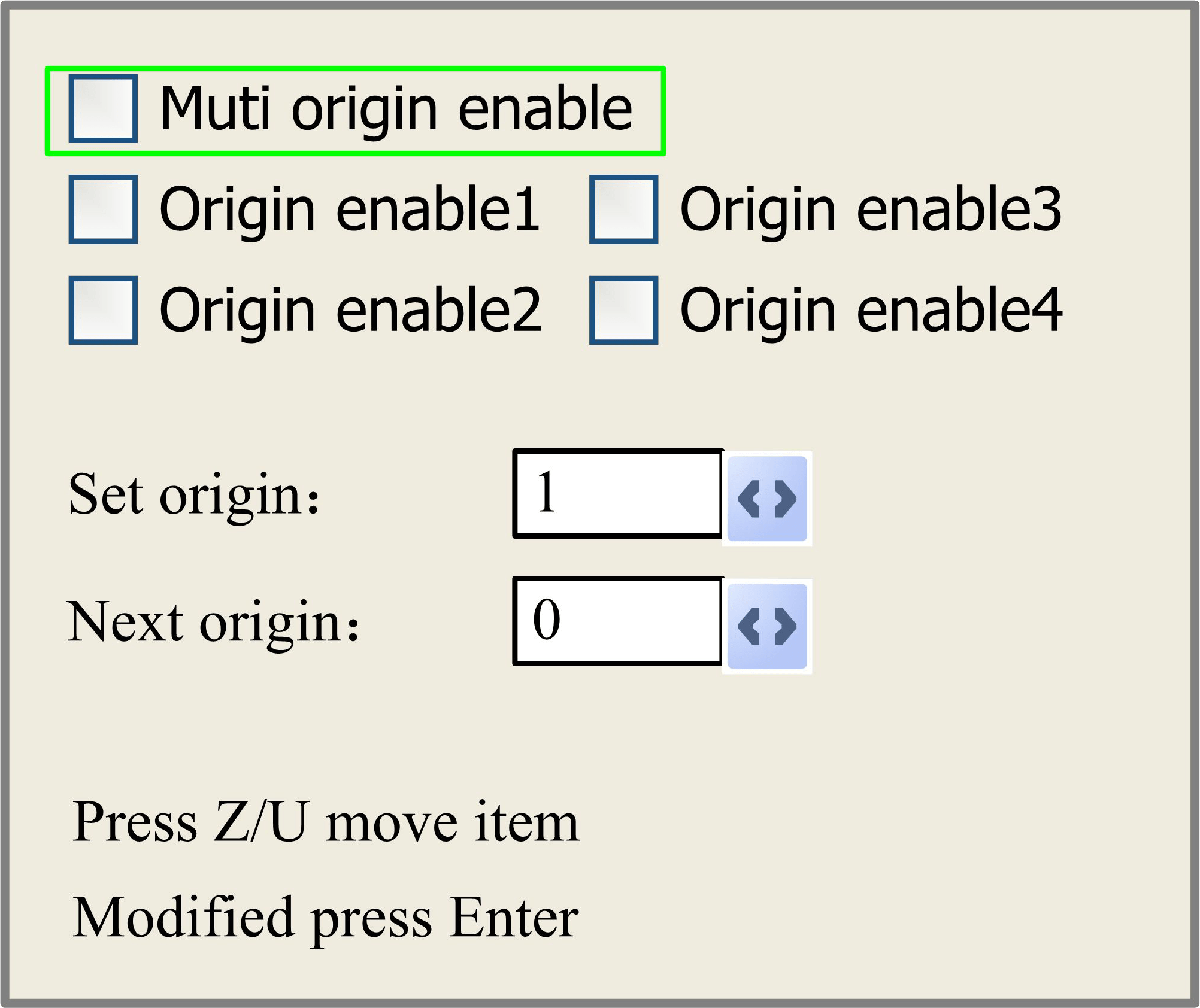
Figure 8.3-5
Push “Z/U” key to move the green block to the anticipant item, and when the green block is on “enable” items, push “Enter” key to enable or disable the item, when enabled, the small diamonds is green, and when disabled, the small diamonds is grey. When the green block is on the “Set origin” item or the “Next origin” item, push the “X+-” keys to select the value.
Pay attention to if when the green block is on the “Set origin” item, push the “X+-“ keys to select a value, then, “Enter” key must be pushed to valid the change, or, the change is invalid.
Each item introduced as below:
- Multiple Origins Enable: “Yes” or “No” can be selected. If you select “No”, the system will use the single-origin logic. You can press the “Origin” key and set the origin, and only this origin can become valid. If you select “Yes”, the system will use the multiple- origin logic and the “Origin” key on the keyboard become invalid. In such a case, the parameter of each origin must be set in the menu as follows.
- Origin Enable1/2/3/4: after the multiple-origin logic is enabled, the four origins can
independently be prohibited and enabled.
- Set Origin 1/2/3/4: after the multiple- origin logic is enabled, you can stop the cursor at “Set as Origin 1/2/3/4”. Press the “Enter” key on the keyboard and the system will take the coordinate figures of current X/Y axis as the corresponding ones to the origin 1/2/3/4.
- Next Origin: there are such five digits as 0~4 for option, which are the origins to be used for the next figure. Origin 0 means the origin set by the “Origin” key on the panel in the single- origin logic. 1~4 means the serial number of the origins in the multiple- origin logic. Next origin can be modified to any one of origin 1~4, so as to control the start location of next work (the premise is that the origin is enabled), but it can’t be modified to origin 0.
![]()
Prompt
Once the multiple- origin logic is selected and if the serial number of the next origin is 1 and four origins are enabled, when the memory file function is started or the processing file is uploaded into the PC and this file selects “Take the Original Origin as current Origin”, the work started for each time will use
different origins. The rotation order of origin is 1->2->3->4->1->2…….
Set Factory Para
After the “Set Fact Para” is selected and the Enter key pressed, the interface will show the specific password to be entered when set as default parameter.

Figure 8.3-6
Push “X+/-” keys and “Y+/-” keys to select the characters, and push the “Enter” key to valid the characters, when finishing enter the password ,that is to say, the six characters, if the password is error, it prompts there is some error, or, all parameters are stored.
After the manufacturer regulates all parameters of the machine well (including all manufacturer parameters and user parameters), this function can be used to store the well-regulated parameters to help users to recover the original parameters (including all manufacturer parameters and user parameters) through selecting “Recover Para” when they regulate
parameters improperly.
Def Factory Para
![]()
Prompt
After the “Def Fact Para” is selected and the Enter key pressed, the “Successful Recovery” dialog box will pop up to prompt that all manufacturer parameters and user parameters are recovered successfully. You can return to the previous menu by press the Enter key.
Auto Focus
When the cursor stops at “Auto Focus”, press the Enter key to search for the focus automatically.
Language Setting
The item “Language” helps you to select an appropriate langue which is displayed on the panel:
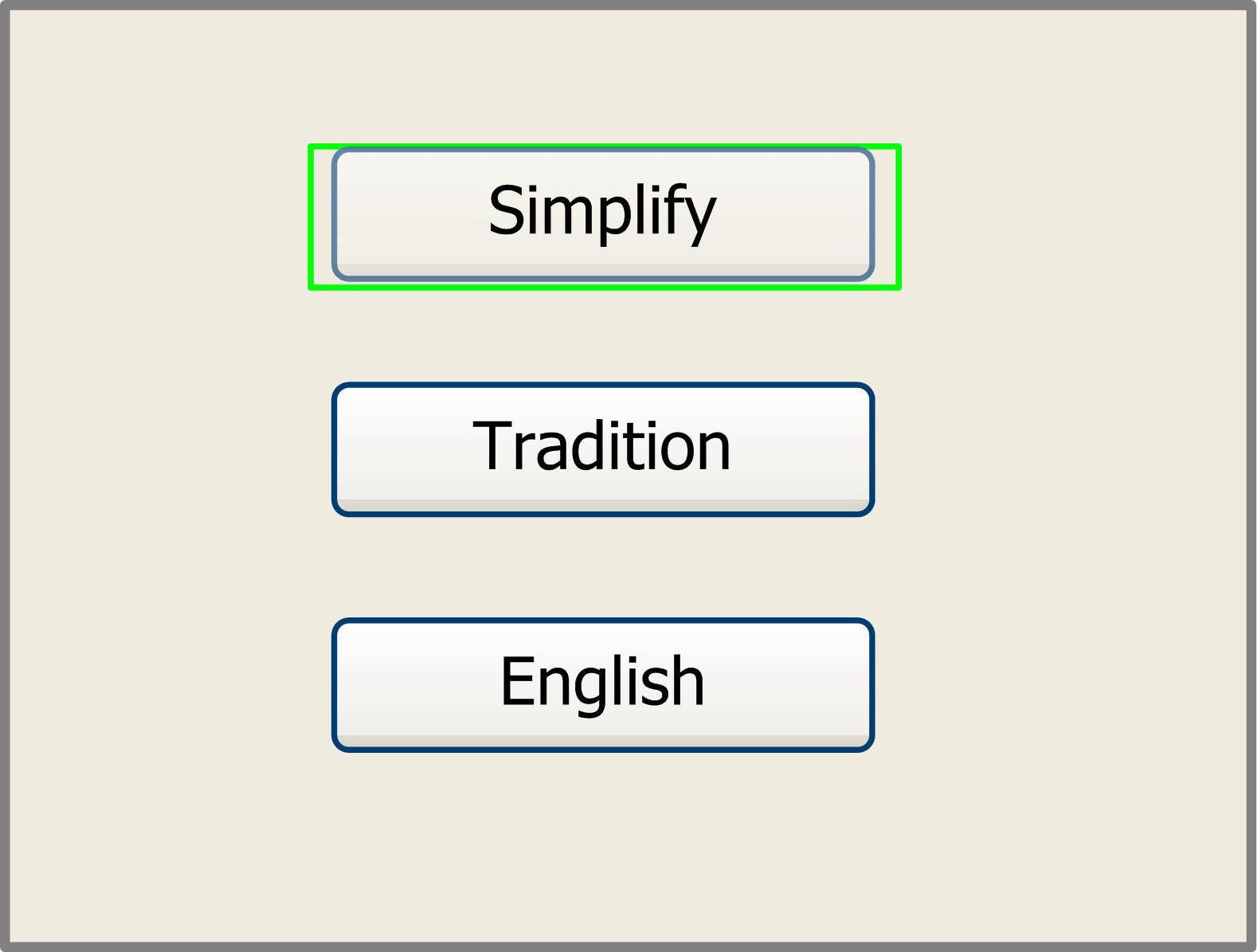
Figure 8.3-7
IP Setup
When the green block is on this item, push the “Enter” key to show as below:
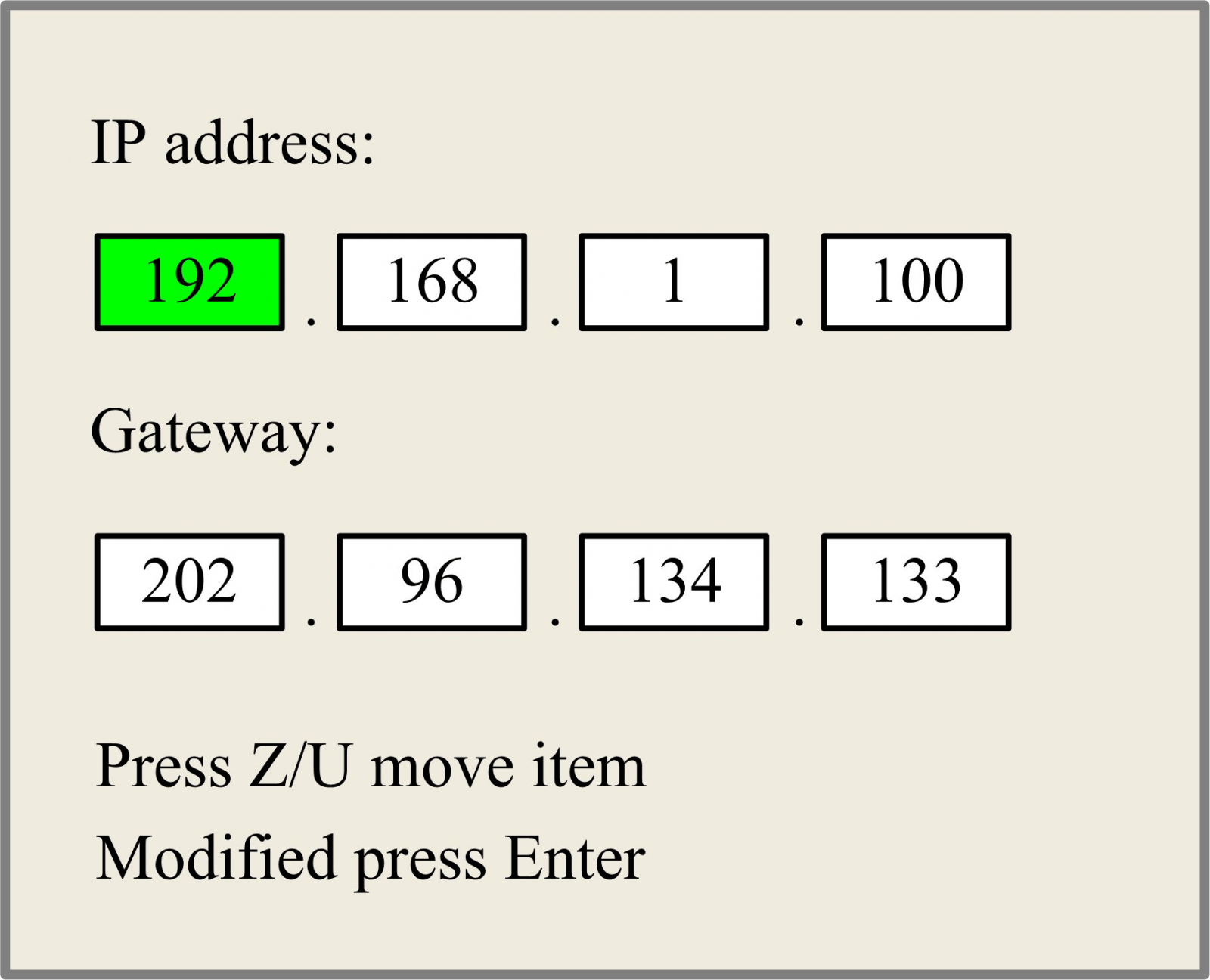
Push “Z/U” key to move the changing item, then push “X+/-” keys and “Y+/-” keys to change the value, when all the IP value and the Gateway value are changed, push “Enter” key to validate the change, or “Esc” key to invalidate the change.
Diagnoses
If the “Diagnoses” item is pressed, the system will show as below:
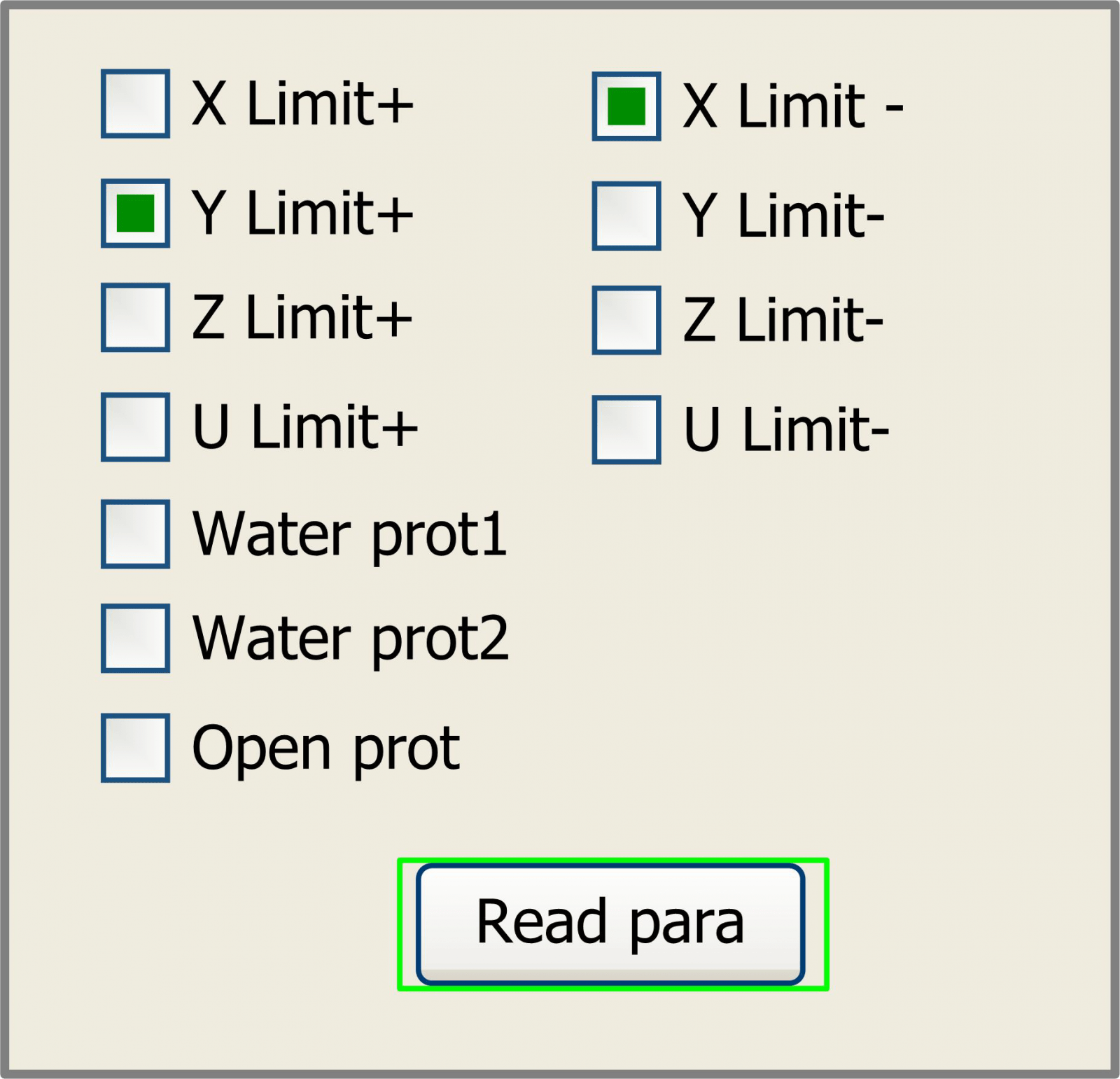
Figure 8.3-9
This interface shows some system input information, such as limiter status, the status of the water protecting, and the status of the foot switch etc.. When the input is validated, the color frame will be green, otherwise it’s gray.
Screen Origin
If the “Screen Origin” item is pressed, the system will be showed as below:

Figure 8.3-10
This function is to set the screen origin position, to choose different origin position, which can mirror the graphics on X/Y direction. The operation way as above mentioned.
File Key
Memory File
On the main interface, if “File” key is pressed, it will be showed as below:
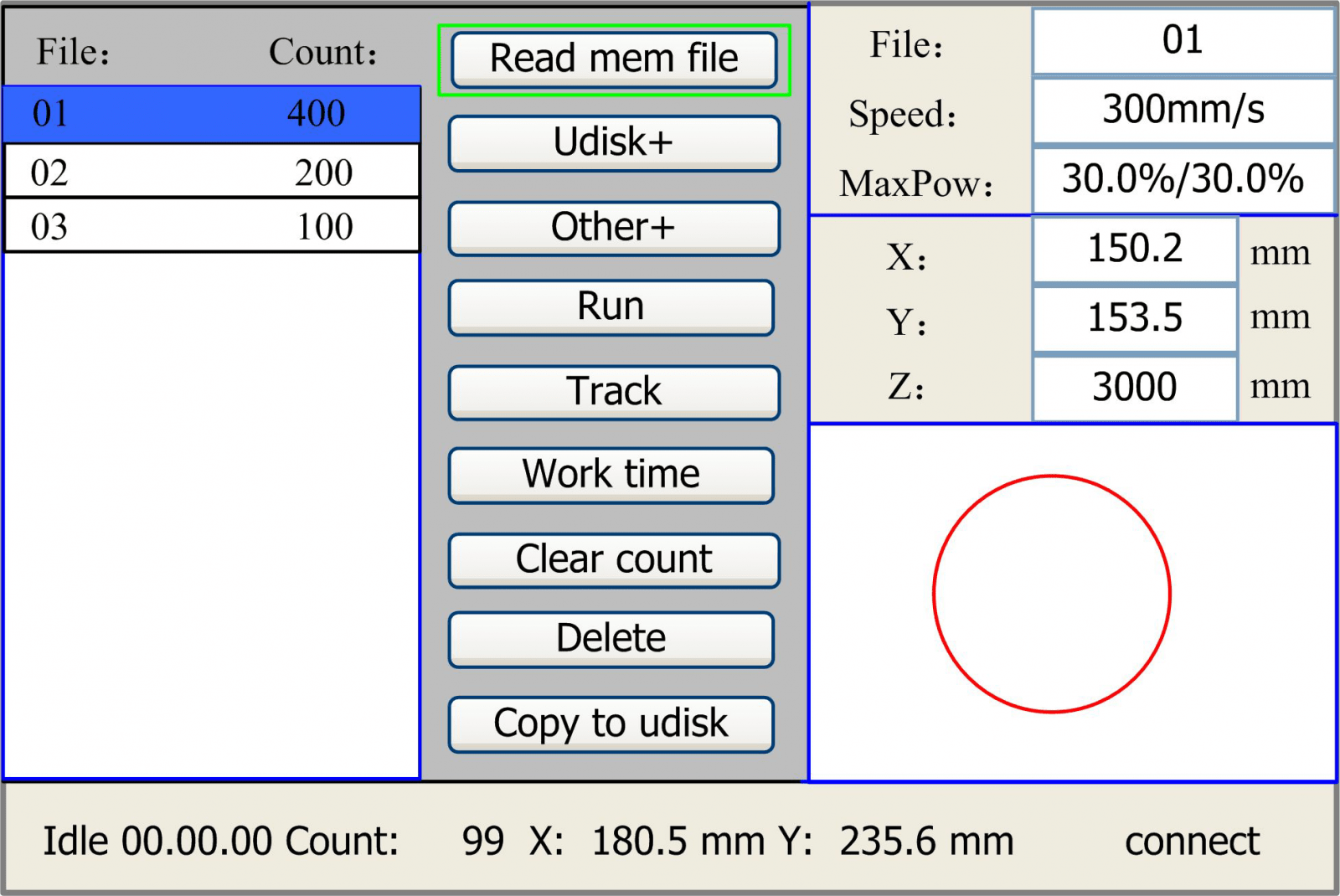
Figure 8.4-1
When showing this menu, the system would read the memory file firstly, the file name and the work times would be listed in the area, and the selected file is previewed in the bottom right area. “Y+/-” keys could be used to move the cursor on the file name list. When the cursor is on a target file name, presses the “Enter” key, the selected file will be previewed on the main interface, and then if “Esc” key is pushed, the preview will disappear.
“X+/-” keys could be used to move the cursor left and right. All the item show as below:
- Read mem file: read the memory file list;
- Udisk: read the U disk file list;
- Other: the other operation of the memory files;
- Run: To run the selected file;
- Track: To track the selected file, and the track mode is optional;
- Work time preview: To forecast the running time of the selected file, and the time is accurate to 1ms;
- Clear count: To clear the running times of the selected file;
- Delete: To delete the selected file in the memory;
- Copy to Udisk: To copy the selected file to Udisk;
If the “Other” entry is pressed, the system will be showed as below:
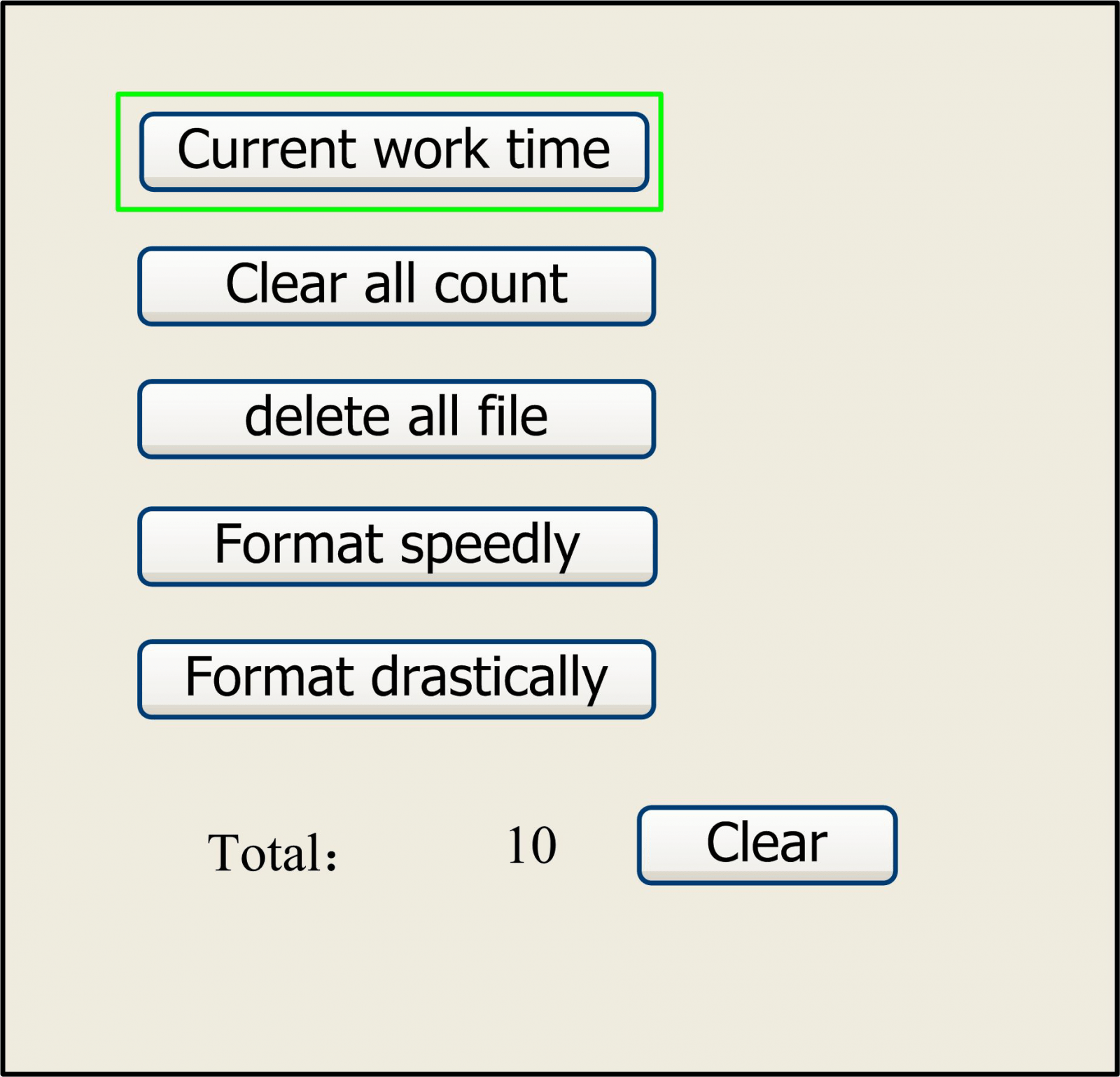
Figure 8.4-2
- Current work time: To forecast the running time of the current file (the current file No. is showed on the main interface), and the time is accurate to 1ms.
- Clear all count: To clear the running times of every file in the memory
- Delete all file: To delete all memory files
- Format speedily: To format memory speedily, and then all the files in memory will be deleted.
- Format drastically: To format memory drastically, and then all the files in memory will be deleted.
- Total: the total running times of all the files.
If press “Udisk” entry in Figure 8.4-1, the system will show as Figure 8.4-3, and the operation method is the same as Figure 8.4-1.
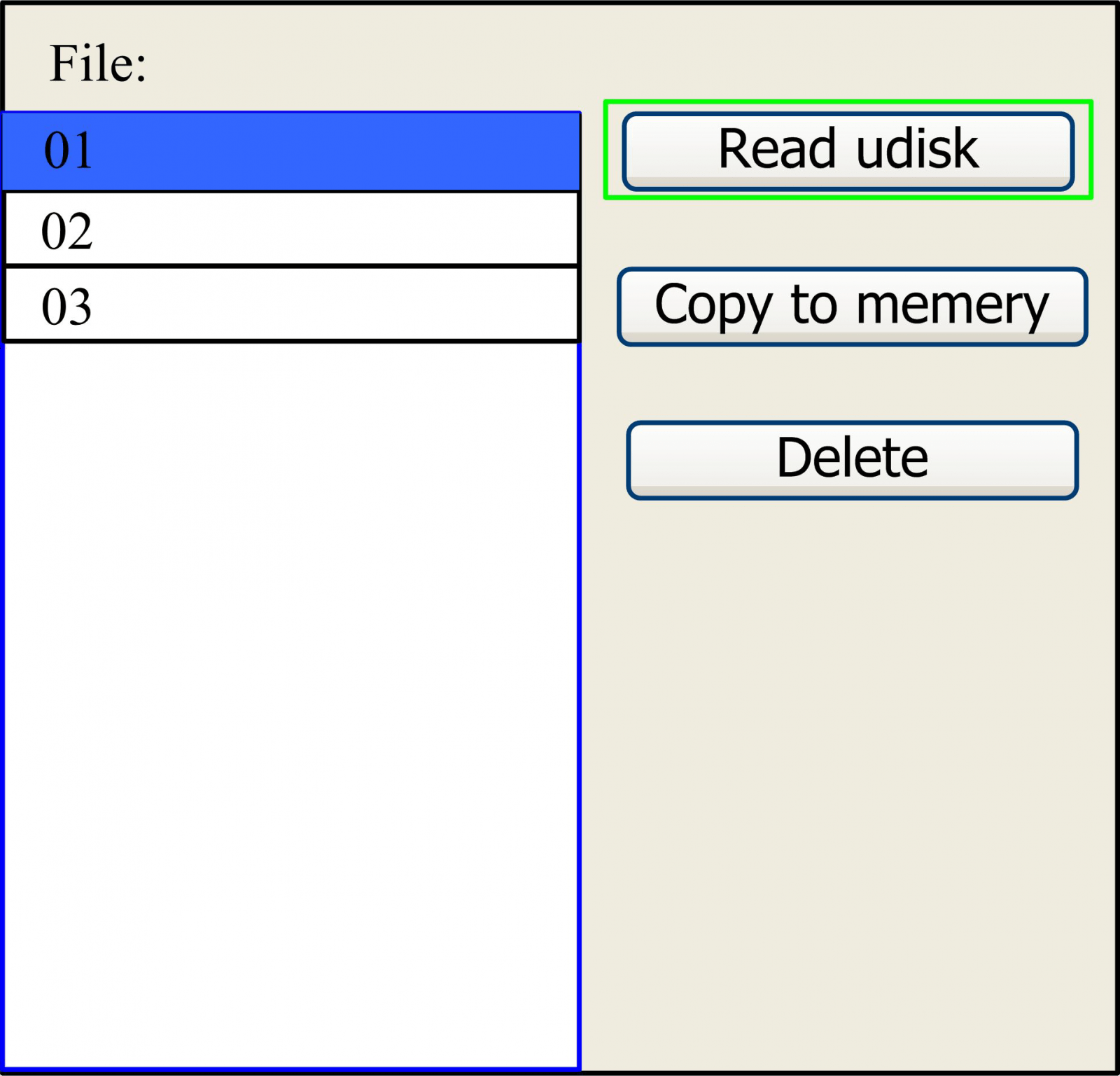
Figure 8.4-3
- Read Udisk: read the file list in the Udisk;
- Copy to memory: copy the target Udisk file to the memory;
- Delete: delete the selected Udisk file;
![]()
Prompt
This system supports such file formats of Udisk as FAT32 and FAT16, but it can identify them when the files are put under the root directory of Udisk. The file name of more than 8 characters will automatically be cut out by the system. The file name that has only English letters and digits will not show when they are copied to the controller. The files copied from the controller to Udisk will
be placed under the root directory of Udisk.
Alarm Info.
When users are operating the system, or when the machine is running, some alarm information such as water protecting error maybe popped-up as below:
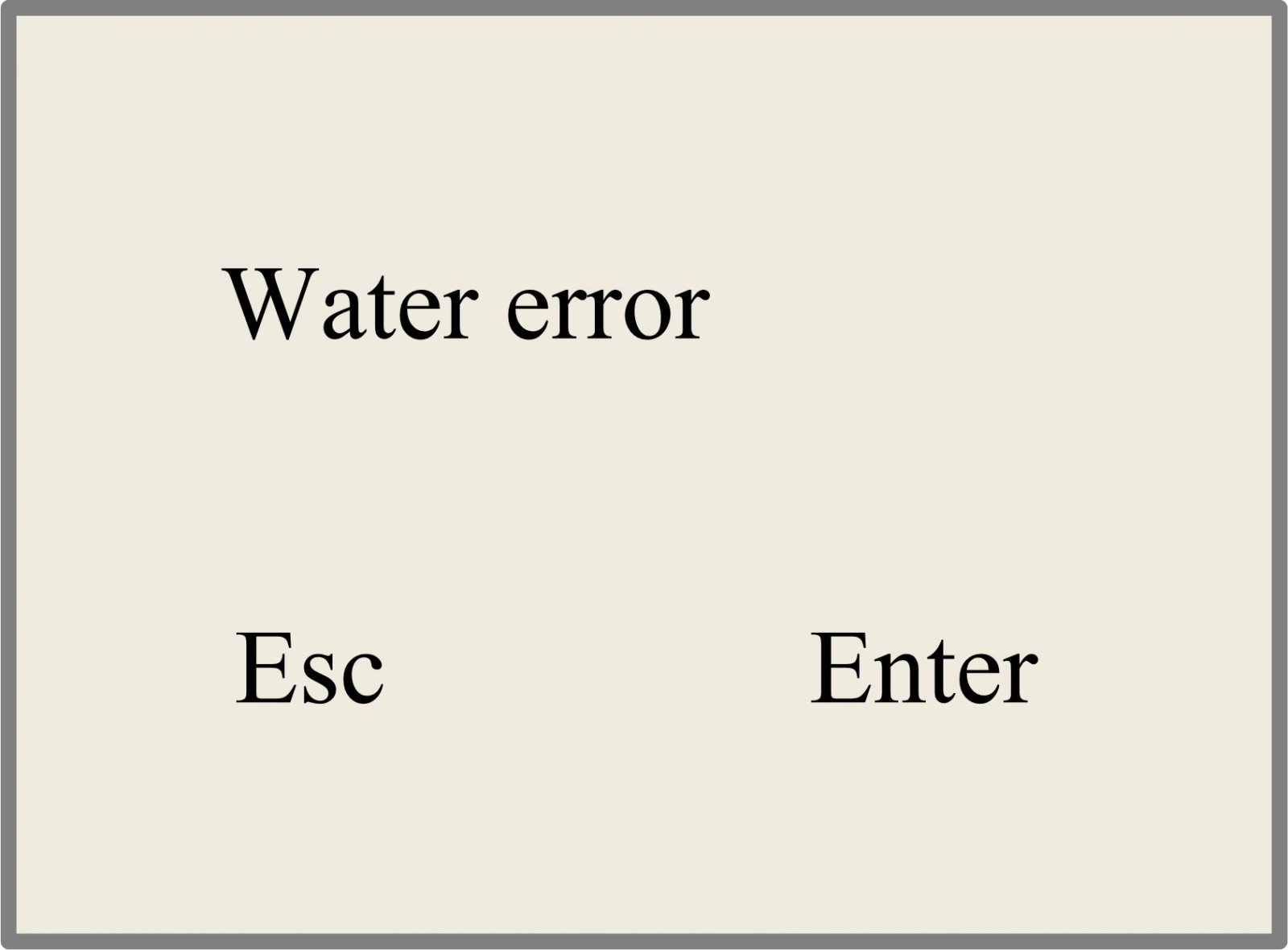
Figure 8.5-1 Push “Enter” key or “Esc” key, the system will execute.
Chapter 9 Manufacturer/User Parameters Details
Manufacturer Parameters
(1)Motor parameters X/Y/Z/U-axis parameters
Direction Polarity: Modification of direction polarity can move the motor to the opposite direction. The modification purpose can move this axle to the origin on resetting. If this axle moves far from the origin on resetting, it means the direction polarity of this axle is wrong in setting and should be modified.
Spacing/limit Polarity: it is used to set the high and low level mode of spacing signal. When the motion axle arrives at the spacing position and input a low-level signal to the controller, the spacing polarity at this time should be set to be minus.
Key Polarity: it is used to control the movement direction of the axle that is moved through manual operation of the keys. After the direction polarity is correctly set, if you press the directional keys on the operating panel, this axle will move to the opposite direction. In such a case the polarity of keys should be modified.
Control Mode: Double-pulse or direction + single pulse are optional; in general, direction + single pulse is selected.
Hard-spacing Protection: it is used for whether the hard-spacing protection of this axle is enabled.
Reset Enable: if the machine is provided with this axle, its “Reset Enable” should be opened; if no, its “Reset Enable” should be prohibited.
Motor Stepping: it means the impulse equivalent, the absolute distance by the corresponding motion axle when a pulse is delivered to the motor. Prior to the correct setting of this value, a larger rectangle can be cut with the machine (the larger the figure is, the smaller the difference is). The motor stepping can automatically be calculated according to the figure length and measuring length.
Takeoff Speed: it means the speed of the motion axle in direct start from the idle condition. If this value is excessively large, it will make the motor lose steps, jar and even squeak; if small, it will reduce the running speed of the whole figure. If the inertia of the motion axle is larger (the axle is heavier), you can set a smaller takeoff speed; if smaller (the axle is lighter), and you can increase the takeoff speed. For
example, the typical value is 5~30mm/s.
Maximum Speed: it means the maximum limit of motion speed that this axis can bear. This parameter has something to do with the driving force of motor, the inertia of motion axle and its drive ratio. For example, the typical value is 200~500mm/s.
Maximum Acceleration: it means the maximum acceleration of the motion axis in accelerated or decelerated motion. If the acceleration is set too large, it will make the motor lose steps, jar and even squeak; if too small, it will cause the reduction of acceleration so as to reduce the running speed of the whole figure. For the axis with larger inertia, such as Y axis corresponding to the beam, its typical setting range is 800~3000mm/s2; for the axis with smaller inertia, such as X axis corresponding to the car, its typical setting range is 8000~20000mm/s2.
Scope: it means the farthest distance that the motion axle can move, which is determined in accordance with the actual condition of the machine.
Key Takeoff Speed: it means the starting speed to move the axis by way of the keys on the keyboard, which can’t be higher than the takeoff speed.
Key Acceleration: it means the acceleration to move this axis by way of the keys on the keyboard, which can’t be higher than the maximum acceleration of this axis.
Key Reverse: to control the motion direction when move the axis by pressing key manually. When set the direction polarity parameters correctly, if press the direction key on the panel, the axis will move to the reverse direction, so enable this item.
- Laser parameters
Laser Tube Configuration: single laser and double lasers are available for option and set in accordance with the laser-tube quantity provided by the manufacturer.
Laser Type: glass tube, RF laser (not need pre-ignition pulse) and RF laser (need pre-ignition pulse) are available for option.
Laser Attenuation Quotiety
Laser Tube Enable: when there are double laser tubes, user can enable laser 1 and laser 2 respectively.
Maximum Power Minimum Power
Laser PWM Frequency Pre-burning Frequency
Pre-burning Pulse width: when the laser is RF laser and need pre-burning pulse, you can configure the features of pre-burning pulse by pre-burning frequency and pre-burning pulse width.
Water protection enables: When the water protection enabled, the controller must connect the wiring, otherwise the machine will not emit laser. If disable, no need to connect the water protect wiring, controller will not test.
Laser PWM Frequency is used to set the pulse frequency of control signal used by the laser, in general, glass tube is about 20KHZ, RF laser is about 5KHZ; the maximum/minimum power (%) is used to set the limit power of the laser, that is to say, during the operation, the maximum power set by the user which can’t be higher than the maximum power and the minimum power set by the user which no less than the minimum power. When the laser power is attenuated after using for a time, then can set the laser power by the attenuation quotiety.
![]()
Prompt
If it is only provided with the single laser, it will show the one-path parameter.
- Other Manufacturer Parameters Machine Configuration
Machine Type: In most cases, the general engraving machine should be selected and other types used for specific purposes.
Feeding Mode: single-way mode and two-way mode for optional. If it is single-way feeding, it is unnecessary to check the coordinates, feeding can be conducted in the single-way mode; if it is two-way feeding, the system will check the maximum and minimum coordinates. The odd sequence means feeding should be done to one direction and the even sequence means feeding done to the other direction. The initial direction for the first time can be changed through setting the directional polarity or modifying the plus and minus values of the feeding length. This parameter is valid only when the “Z axes function” is configured to “Drive for Feeding axes”.
Power-Off-Restart Delay: it can be set to be 0~3000ms. After the electricity grid power-off, the power supply of the system will be not dropped to 0V at once. There is a delay during the time. The delay value set here should basically consistent with the actual off-delay value. If the deviation of set value is larger, on the de-energizing for continuous engraving, either the figure processed for the second time is not closed with that before the cutoff, or it is coincided with that too much.
Transmission Mode: generally choose “Belt Stepping Type”, the control algorithm will be changed a little when other types are selected.
![]()
Prompt
After modified the configuration parameters in the manufacturer parameters, such as directional polarity, control mode, laser type and laser PWM frequency, the system should be reset. Such a modification can function upon
the resetting of the system.
- Enable Parameters
Cover Opening Protection: If enabled this item, the controller must connect the protection wiring, otherwise, the machine will not work.
Enable the blower: if use Wind signal of output port to control the blower switch as layers, you must enable this item, otherwise, the Wind signal outputs other signal.
![]()
Prompt
The Enable Parameters are to enable or disable the above functions. If the machine is provided with the parameters for the single-laser in the manufacturer parameters, the display entry of enabling parameters will be
changed accordingly.
User Parameters
Cutting Parameters (Only affect cutting methods)
Idle Move Speed: this parameter decides the highest speed of all non-lighting lines for the machine in the movement process.
Idle Move Acceleration: it means the highest acceleration of all non-lighting lines. Idle stroke speed and idle stroke acceleration can be set higher to reduce the working time of the whole figure, but if they are
set too high, it may cause the jarring of track, so comprehensive consideration should be given to the setting.
Turning Speed: the turning speed at closed-angle corner, the lowest speed in the whole cutting process. Turning Acceleration: the acceleration speed at the closed-angle corner when cutting. If the two speeds are set too large, vibration will be happened when turning; if set too low, it will influence the cutting speed.
Cutting Acceleration: it means the highest acceleration value in the whole cutting process.
Acceleration Mode: it is divided into T acceleration and S acceleration. T accelerate will quicken the whole cutting process, but it will result in that its cutting effect is inferior to that of S acceleration.
One Key Setting: This is one recommended cutting parameters settings button; it is not a parameter, there are several groups of parameters under this button, which is convenient for selection.
- Scanning Parameters (Only affect scanning mode) X- axis Starting Speed
Y- axis Starting Speed X- axis Acceleration Y- axis Acceleration
The above four parameters are used to set the starting speed and acceleration of two axles when scanning. The higher the two speeds are, the quicker the scanning is.
Scanning Line-feed Speed: this parameter is specially used to control the highest speed at which that the previous line vertically moves to the next line in the scanning mode. If the space between lines is larger during the scanning or if the distance of each block is larger during the scanning and deblocking of figure, it is necessary to position each line or block accurately. In such a case the speed of scanning line-feed can be set as a lower value.
Scanning Mode: it is divided into general mode and special mode for option. If special mode is used, the laser power should be increased. The smaller the speckle percentage is, the more the laser power reduces. The laser power to set should be larger in order to reach the same scanning depth. The purpose to select the special mode is to make the laser light at high power and short time. On the depth scanning the effect that the bottom is flatter is obtained, but it should be noticeable that if the speckle adjustment is not appropriate, it can achieve this goal. If the high power remains short, the lighting mode will influence the life of the laser. The system will default the selection of general mode.
Spot Size: When the general mode is selected as the scanning mode, this parameter will become
ineffective; when the special mode is selected, this parameter will become effective. The controller will control this parameter among 50%~99%.
![]()
Prompt
The cutting and scanning parameters can’t exceed the limited ones in the axle
parameters. If so, the setting will become ineffective and the system will automatically cover the parameters with the axis parameters.
- Feeding parameters
Before-feeding delay: can be set 0~300s, the upper axis will be moved after the last processing finished and delay this item. It is convenient for the user feeding and select during the delay.
After-feeding delay: settable at 0~9.9s. It can facilitate the feeding device’s delaying vibrated after moving to the correct position and waiting for the 2nd work after the feeding axle stands still completely.
If feeding line-by-line: if enabled feeding line-by-line function, the virtual array graphics on Y direction will be processed in the same position.
Line-by-line feeding backlash: You can compensate the feeding length due to the inaccuracy for feeding axis moving.
- Reset Parameters
Reset Speed: it means the speed of X/Y-axle linkage reset to the origin.
X- axis Startup Reset Y- axis Startup Reset
Z- axis Startup Reset U- axis Startup Reset
You can select “Yes” or “No” in the field of the above four parameters, which is used to confirm whether each axis can be reset on the startup.
- Frame Setting
Frame Mode: “Blanked Bordering” means idling to start border preview; “Outputted Border Cutting” can manually cut off the well-processed figure; “4-corner Dotting” means to emit the light at four corner points of the frame to make a point and turn off light. The size and position of this figure can be checked intuitively through the four points. The bordering speed is the speed value set on the keyboard when the system is idle. For light output, its minimum/maximum power is the corresponding value set on the keyboard when the system is idle (The laser power on the 4-corner dotting means the well-set maximum
power).
Margin Distance: It means whether to extend a certain length outside the actual frame of the figure on the preview/cutting of frame.
![]()
Prompt
If the frame crosses the border, the interface will prompt it. If the Enter key is pressed at this time, the system will cut the border at the maximum/minimum
coordinates first, and then border the figure. This bordering can be given up.
- Other User Parameters
Array Mode: Two-way array or one-way array can be selected. Two-way array means the to-and-fro cutting of array in sequence; one-way array means the cutting of array from one direction to another. On selecting one-way array, the elements of each array are the same in action mode and completely uniform in action fluency, which takes a little more time than two-way array. Two-way array is the default option.
Back Position: The origin (the relative origin) and the machine’s absolute origin can be selected. This parameter decides the parking position of laser head after each work.
Focus Setting: it means the distance from the focal point of laser head lens to Z-axle origin. When there is no automatic focusing function, this parameter becomes invalid.
Backlash X: The X axes’ backlash, accurate to 1um.
Backlash Y: The Y axes’ backlash, accurate to 1um.
Thank you very much for using the product from Shenzhen RuiDa Technology!
All parts of this manual description, all rights reserved by Shenzhen RuiDa Technology Co., Ltd. Without our permission, any company or individual shall not reprint, copy or distribute the content related to this product manual. We keep the rights to revise or update the contents without notice.
If any comments and suggestions please feel free to contact us. Phone: 0755-26066687 Fax: 0755-26982287
Website: www.rd-acs.com
Address: 1B-1, Building 5, Tian’an Nanyou Industry Area, Dengliang Road, Nanshan District, Shenzhen, P.R.C.

 Reset : : Reset the controller;
Reset : : Reset the controller;