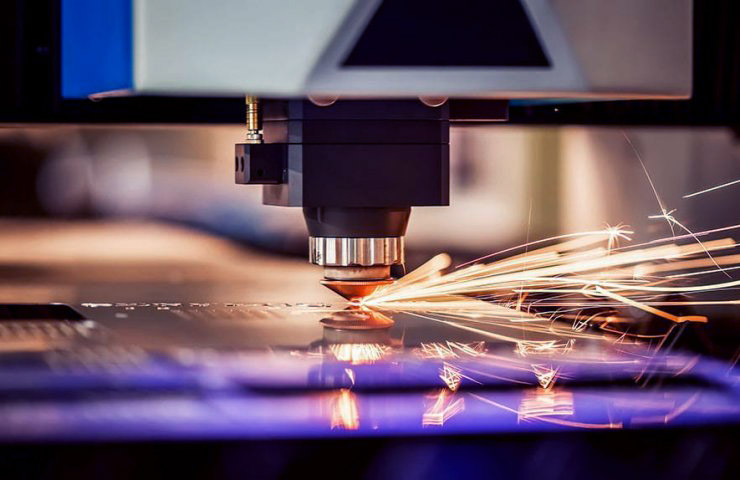
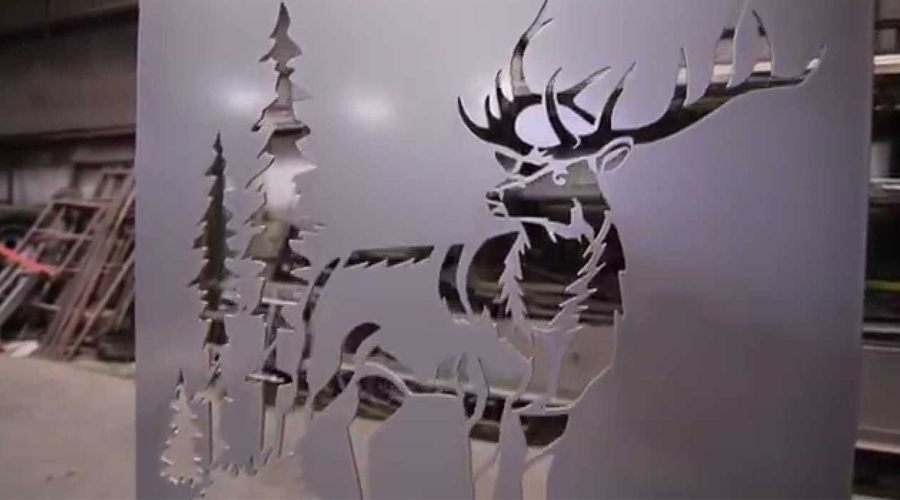
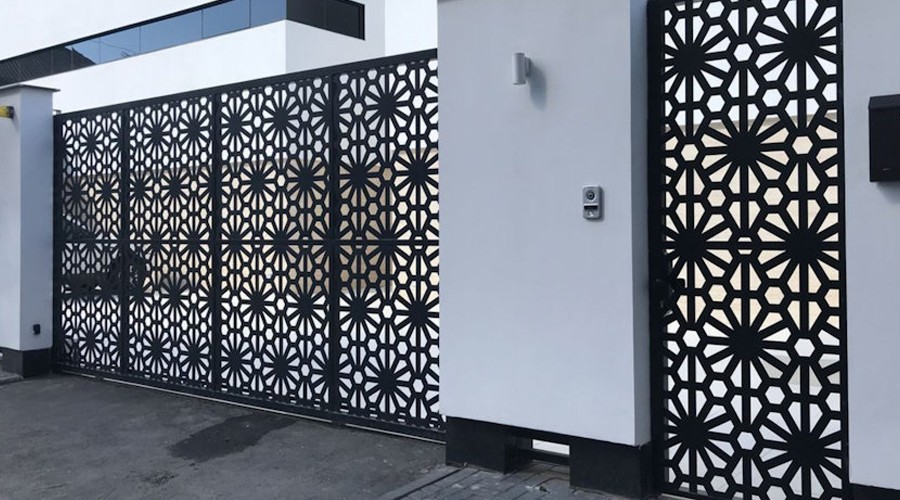
Why is laser metal cutting so important nowadays?!
Effective metal cutting is a very interesting topic which we would like to highlight.
First of all metal processing is one of the most important areas of the global machinery production. Metal processing is required for almost all sectors of the economics: auto, construction, aircraft, space, military, jewelry, etc.
Thus, metal processing technology cannot be underestimated.
Other ways to cut metal
There are a lot of different ways to process metal: waterjet and plasma cutting, CNC milling, wire EDM cutting, etc.
All these methods are widely used all over the world, but along with advantages they have also disadvantages.
Today, laser cutting competes with other methods more and more.
Lasers become cheaper and can be used not only for metal cutting but also for soldering and wiring.
That happens because lasers are more and more affordable and the sphere of their application is quickly growing. Nowadays, there is a growing demand in high-precision metal cutting.
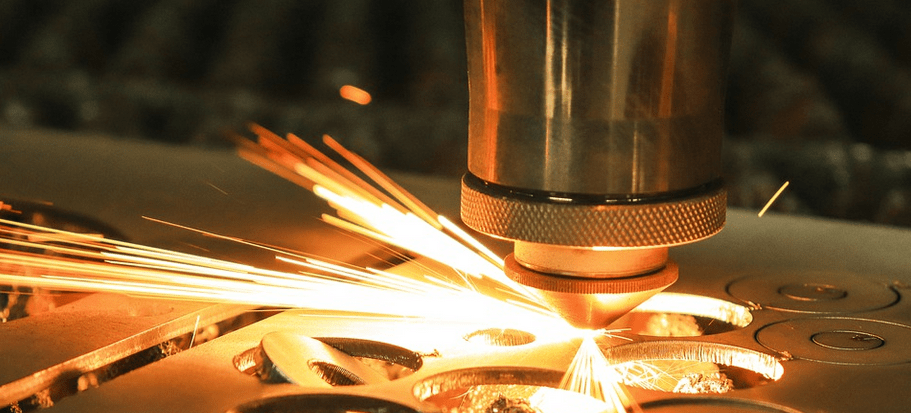
How does laser cutting work?
Laser cutting of metal is a process of heating and destroying metal with a laser beam. This technology is called Laser Beam Cutting (LBC).
Modern lasers are able to cut metal 0.2 mm – 40 mm thick.
The metal cutting technological process includes several steps:
- Focusing of the laser beam at a given point of the processed metal.
- Heating of the metal to the required temperature resulting in its melting with the formation of a depression at the melting boundary.
- Metal boiling and evaporation under the influence of the laser radiation energy.
In practice, metal laser cutting is performed by 2 methods:
- by metal melting along the cutting line;
- by metal evaporation along the cutting line.
The evaporation technology is used mainly for processing thin items.
The melting technology for laser metal cutting is used more widely. To make this process more effective various gases (nitrogen, argon, oxygen, air, and others) are blown into the cutting zone.
Metal laser cutting machines allow to concentrate the energy of up to 108 watts per square centimeter on the surface of the workpiece.
Getting started with laser metal cutting!
The most popular metals and their alloys for laser cutting are:
- copper 0,2 – 15mm,
- brass 0,2 – 15mm,
- aluminum 0,2 – 20mm,
- steel 0,2 – 20mm,
- stainless steel 0,2 – 50mm,
- titanium
- tin.
Also, there are different alloys as well that needed to be cut.
What lasers are good for metal cutting?
Nowadays high-power Co2 lasers and high-power CW fiber lasers are commonly used for effective industrial laser cutting.
Lasers with the power output over 500 watts are used for metal cutting . The more the power of the laser the higher is the speed, so the thicker metal they can cut.
Basically for metal laser cutting you need:
- good laser power output,
- gas assist,
- suitable focusing system.
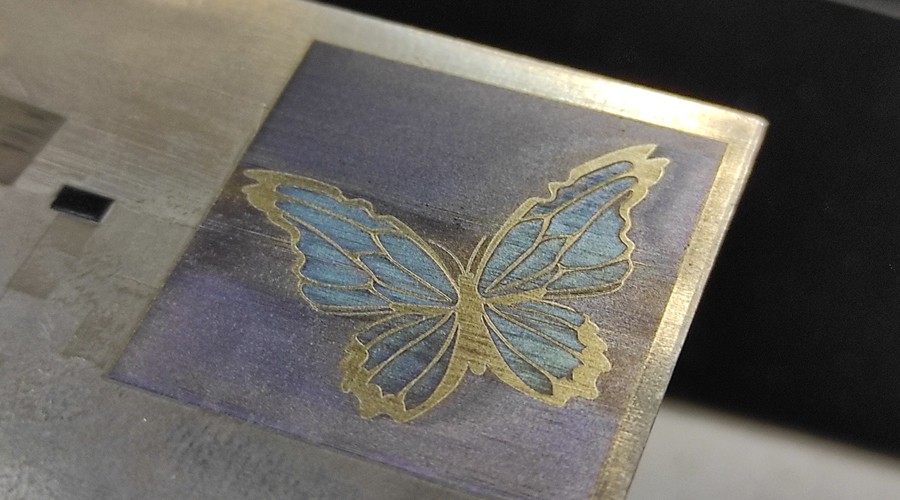
Samples of laser-cut items
Cutting of 0.5 mm stainless steel with 30 watt fiber laser
When do we need laser metal cutting?
Laser cutting is needed for making metal items of a complicated configuration and shape, including both flat and volumetric objects.
Due to some positive properties, laser cutting of metal is used to create:
- parts used in the production of various machines, mechanisms (plates, brackets, panels, etc.);
- equipment for trading halls, warehouse equipment (racks, shelves, racks, etc.);
- parts for furnaces, boilers, chimneys;
- templates, stencils, signage;
- auto parts, kitchenware, metal logos, elevators
- metal signs, metallurgical equipment, automobiles, metal works of art,
- metal crafts, metal gifts, metal foils, metal words
- machinery, subway parts, adornment, household appliances, ships, electrical appliances, metal profiles,
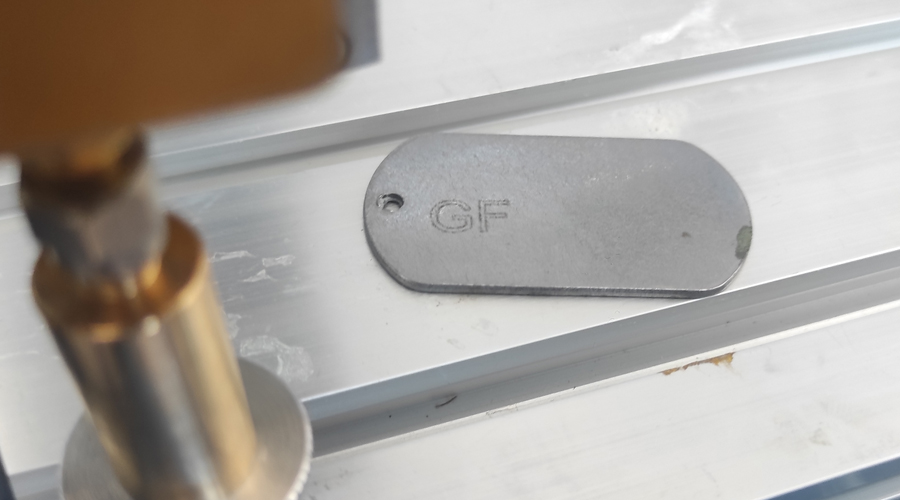
- metal tags, advertising, metal letters, precision components, metal tool fabrication
- elements of doors, gates, fences.
If you have any questions about laser engraving of metal – use the chat or ask a question through the consultation form ->
Areas of use
- Industry – mechanical engineering, instrumentation, electronics manufacturing, metal rolling, aircraft industry, shipbuilding, spaceflight
- Сonstruction – tool making, construction of houses, renovation and design
- Small business – workshops, home shops, blacksmith craft
- Hobby, education – DIY, education in schools and universities, research
Metal cutting with a Co2 laser
Co2 gas laser metal cutting (150 watt Co2 laser cutting)
Fiber laser metal cutting
What parameters do you need?
For Co2 metal cutting, it is important to have a short focal lens and oxygen assist.
Some nuances about laser metal cutting
It is important to have an autofocusing system for your laser metal cutter. Without proper focusing metal laser cutting will not be accurate or will not work at all.
What you must know when using a fiber laser cutting machine
- The type of the gas for air assist.
- The pressure of the gas.
- The laser power settings.
- The laser cutting speed.
- The focusing system (short focal lens)
Laser metal cutting parameters for 1000 watt fiber laser
When processing metals with a 1 kW laser it is necessary to bear in mind the following parameters of the maximum cross-sections of metals:
- Black metal (steels with various doping levels) — 40 mm.
- Stainless steel — 25 mm.
- Aluminum and its alloys — 12 mm.
- Brass — 12mm.
- Copper and alloys— 5 mm.
Laser type. Fiber lasers are suitable for cutting high-melting, extra hard metals as well as fragile and thin materials, since they have a much narrower beam spot due to short-wave radiation. Whereas, gas lasers fit for a wider range of materials that are easier to process.
Speed. It depends on the metal type, its thickness, and the power of the laser machine. For instance, the cutting speed of a 1000 W laser machine for carbon steel 0,5-8,0 mm thick will be around 0,6-15 m/min, for stainless steel 1,0-5,0 mm thick will be 0,8-18 m/min, for aluminum 1mm thick – 1,2-10 m/min, and for copper 1mm thick – 10 m/min.
Power. We choose the laser power depending on the type and thickness of the metal to be processed. In industry 1-10 kW fiber lasers and 1-6 kW gas lasers are used.
The quality of the laser cutting depends on the frequency and power of the laser radiance, speed and time delay at the step of initial burning of the material. It is also important to bear in mind that when working with thick metal you need to start cutting outside the cutting vector to make a perfect shape of the final workpiece.
Parameters of speed, power and thickness of metal cutting depending on the type of laser
| Co2 laser | ||
| Type of metal | Thickness in mm | Power (watt) |
| Steel (alloy, carbon) | 1 | 100 |
| 0,5 | 250 | |
| 1,2 | 400 | |
| 2,2 | 850 | |
| up to 40 mm | 5000 | |
| Brass | 12 | 5000 |
| Aluminum alloys | 12 | 5000 |
| Copper | 5 | 5000 |
| Titanium | 0,5 | 850 |
| 0,6 | 250 | |
| 1 | 600 | |
| Stainless steel | 1 | 100 |
| 0,5 | 250 | |
| 1,3 | 400 | |
| 2,5 | 400 | |
| 3,2 | 400 | |
| 9 | 850 | |
| up to 25 | 5000 | |
| Fiber laser | |||
| Material | Thickness in mm | Speed mm / sec | Extra gas |
| Black steel | 1 | 8 | oxygen |
| 2 | 6 | oxygen | |
| 3 | 3,2 | oxygen | |
| 4 | 2,7 | oxygen | |
| 5 | 2,5 | oxygen | |
| 6 | 2 | oxygen | |
| 8 | 1,3 | oxygen | |
| 10 | 1,1 | oxygen | |
| 12 | 0,9 | oxygen | |
| 14 | 0,8 | oxygen | |
| 16 | 0,8 | oxygen | |
| 18 | 0,7 | oxygen | |
| 20 | 0,65 | oxygen | |
| Aluminum & copper | 1 | 600 | Nitrogen |
| 2 | 300 | Nitrogen | |
| 3 | 100 | Nitrogen | |
| 4 | 80 | Nitrogen | |
| 5 | 65 | Nitrogen | |
| 6 | 55 | Nitrogen | |
| 7 | 35 | Nitrogen | |
| 10 | 15 | Nitrogen | |
| 12 | 8 | Nitrogen |
| Fiber metal cutting machine suitable for stainless steel, carbon steel, Aluminum, brass, copper, nickel, manganese, gold, silver, and all kind of metal materials. | |||
| Optimal cutting parameters | |||
| Material | Thickness(mm) | Cutting speed(m/min) | Auxiliary gas |
| Stainless | 1 | 20-22 | N2 |
| Stainless | 2 | 8-10 | N2 |
| Stainless | 3 | 3-3.5 | N2 |
| Stainless | 4 | 1.2-1.5 | N2 |
| Stainless | 5 | 0.7-0.8 | N2 |
| Carbon steel | 1 | 15-18 | 02 |
| Carbon steel | 2 | 7.0-8.0 | 02 |
| Carbon steel | 3 | 4.0-4.3 | 02 |
| Carbon steel | 4 | 22-2.5 | 02 |
| Carbon steel | 5 | 2.0-2.2 | 02 |
| Carbon steel | 6 | 15-23 | 02 |
| Carbon steel | 7 | 15-24 | 02 |
| Carbon steel | 8 | 15-25 | 02 |
| Carbon steel | 9 | 15-26 | 02 |
| Carbon steel | 10 | 15-27 | 02 |
| Carbon steel | 11 | 15-28 | 02 |
| Carbon steel | 12 | 15-29 | 02 |
| Carbon steel | 13 | 15-30 | 02 |
| Carbon steel | 14 | 15-31 | 02 |
| IPG 1000W Cutting Parameter | |||
| Material | THICKNESS (mm) | SPEED(m/min) | GAS |
| Mild steel | 1 | 9 | 02 |
| 2 | 5.5 | 02 | |
| 3 | 3 | 02 | |
| 4 | 2.7 | 02 | |
| 5 | 2. 1 | 02 | |
| 6 | 1.5 | 02 | |
| 8 | 1. 1 | 02 | |
| 10 | 0. 85 | 02 | |
| 12 | 0.6 | 02 | |
| Stainless Steel | 1 | 25 | N2 |
| 2 | 9 | N2 | |
| 3 | 3 | N2 | |
| 4 | 1.5 | N2 | |
| 5 | 1. 1 | N2 | |
| 6 | 0.5 | N2 | |
| Aluminum | 1 | 25 | N2 |
| 2 | 6 | N2 | |
| 3 | 2 | N2 |
| PRODUCT SELECTION | |||||||||||
| Material | Thickness | 500W | 1000W | 1500W | 2000W | 3000W | 4000W | 6000W | 8000W | 10000W | 12000W |
| (mm) | Cutting Speed(m/min) | ||||||||||
| Carbon Steel (02) | 1 | 7.0-8.0 | 7.0-90 | 7.0-110 | 7.0-120 | 7.0-12.0 | 7.0-12.0 | 7.0-120 | 7.0-120 | 7.0-12.0 | 7.0-12.0 |
| 2 | 4.06.0 | 5.06.0 | 5.06.5 | 5.0-65 | 5.0-70 | 5.0-70 | 5.0-7.0 | 50-7.0 | 5.0-70 | 5.0-70 | |
| 3 | 2.0-25 | 2.5-30 | 2.8-38 | 3.0-46 | 3.5-50 | 3.5-50 | 3.5-50 | 3.5-50 | 3.5-50 | 3.5-50 | |
| 4 | 1.5-20 | 20-2.4 | 25-3.2 | 2.8-40 | 3.0-42 | 3.0-42 | 3.0-42 | 3.0-42 | 3.0-42 | 3.0-42 | |
| 5 | 12-1.5 | 1.5-1.8 | 1.8-25 | 22-3.2 | 2.5-36 | 2.5-36 | 2.5-36 | 2.5-36 | 2.5-36 | 2.5-36 | |
| 6 | 1.0-1.4 | 1.4-1.6 | 1.6-22 | 2.0-28 | 2.4-30 | 2.4-30 | 2.4-3.0 | 24-3.0 | 2.4-3.0 | 2.4-30 | |
| 8 | 1.0-12 | 1.1-15 | 14-2.0_ | 1.8-2.4 | 18-2.4 | 18-24 | 1.8-24 | 18-2.4 | 18-2.4 | ||
| 10 | 0.7-0.85 | 1.0-12 | 11-1.4 | 12-18 | *12-18 | 12-1.8 | 12-18 | 12-1.8 | 12-1.8 | ||
| 12 | 0.6-07 | 0.9-10 | 0.9-12 | 10-15 | 10-15 | 10-15 | 10-15 | 1.0-15 | 10-15 | ||
| 16 | 0.6-0.75 | 0.7-0.85 | 0.7-0.85 | 0.7-0.85 | 0.7-0.85 | 0.7-0.85 | 0.7-0.85 | ||||
| 20 | 0.6-0.75 | 0.6-0.75 | 0.6-0.75 | 0.6-0.75 | 0.6-0.75 | 0.6-0.75 | |||||
| 22 | 0.5-0.65 | 0.5-0.65 | 0.5-0.65 | 0.5-0.65 | 0.5-0.65 | 0.5-0.65 | |||||
| 25 | 0.4-06 | 0.4-06 | 0.4-06 | 0.4-06 | 0.4-06 | 0.4-06 | |||||
‘
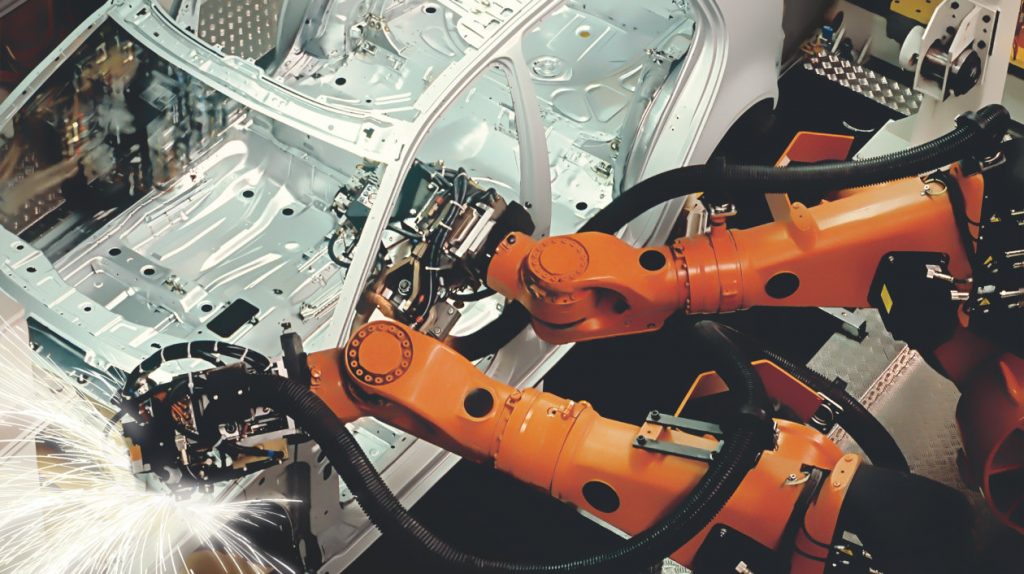
Some industrial lasers are installed (integrated) on a robotic arm.
Other ways to cut metal
Let’s explore other ways of metal cutting.
Plasma cutting
Plasma cutting is a process in which electrically conductive materials are cut through by means of an accelerated jet of hot plasma. Typical materials that can be cut with a plasma torch are steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, copper, and other conductive metals. Due to the high speed and precision cuts combined with low cost, plasma cutting sees widespread use from large-scale industrial CNC applications down to small hobbyist shops.
Metal milling
Metal milling is an effective way of processing aluminum mostly. Aluminum is a relatively light metal and easy for milling.
The milling is a good way once you need to make some sort of holes in the metal.
Waterjet cutting
Waterjet cutting is simply an accelerated erosion process within a selected material. Highly pressurised water is fired through a ruby or diamond nozzle into a mixing chamber. This pressure creates a vacuum and draws garnet sand into the stream where it is then fired at the object in place for cutting.
Metal cutting with oxygen
Gas cutting is a technology with a long tradition that is constantly being improved and developed. Oxygen cutting is one of the most popular methods used for processing steel, most often low-alloy and low-carbon steel. It is also used for cutting metal sheets covered with corrosion or in packages.
Wire EDM metal cutting
Wire EDM machining (Electrical Discharge Machining) is an electro thermal production process where a thin single-strand metal wire, along with de-ionized water (used to conduct electricity) allows the wire to cut through metal by the use of heat from electrical sparks while preventing rust.
Low power lasers are good for thin metal laser cutting
As you may see there are different ways of how you may cut metal for industrial purposes.
However, there are ways to cut 0.2-0.5 mm of steel, stainless steel, brass, copper, at home with a laser.
Even 10 (DPSS) – 30 watt (Fiber laser) is enough for that
0.5 mm metal cutting with 10 watt impulse DPSS Nd:Yag Endurance laser
As you can see there are different ways how you can do metal cutting.
Laser cutting is a very perspective and interesting way of metal processing.
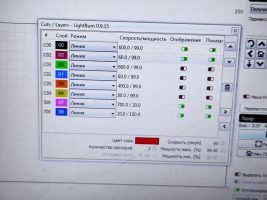
LASER CUTTING PARAMETERS by Bell lasers
Metal cutting parameters – values
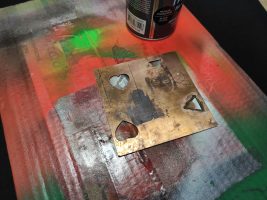
Laser 0.5 mm copper cutting with 10 watt DPSSL
Procedure for cutting a copper plate 0.5 mm thick with a DPSS Nd: YAG laser F = 30 mm.
1. Degrease the copper plate, then cover with a thin layer of black paint.
2. The plate is placed on the laser working table, cutting is carried out in the following modes:
– Speed 600 mm / min, power 100%, number of passes 4
– Speed 60 mm / min, power 100%, number of passes 2
– Speed 600 mm / min, power 20%, number of passes 4
– Speed 20 mm / min, power 100%, number of passes 1
3. After each cycle, the cutting site should be treated with a solution of ferric chloride.
4. Number of cycles 12
MORE PDF GUIDEBOOKS
Innovation in high power fiber laser applications Read more >>>
About Fiber laser cutting machine SIGMA 1390 – 750w Read more >>>
Role of Combustion Energy in Laser Cutting of Austenitic Stainless Steel Learn more >>>
Laser cutting of variable thickness materials – Understanding the problem Read the paper >>>
THE FUTURE FOR FIBER AND DISC LASERS Explore >>>
Design and performance of a Cutting CO2 laser for industrial non-metallic
materials Read it >>>
The Role of the Assist Gas Nature in Laser Cutting of Aluminum
Alloys Check it out >>>