All you need to know about Metal Laser Cutting
0.3 mm bronze laser cutting with 50 watt fiber laser emitter 1064 nm wavelength
30 / 50 watt fiber laser sources for your 3D printer / CNC or engraving machine
Laser cutting – basic tables
40-150W CO2 laser
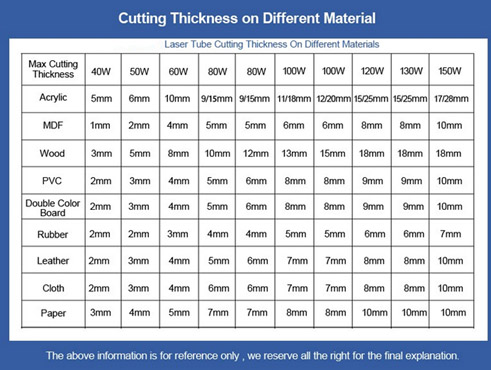
260W CO2 laser
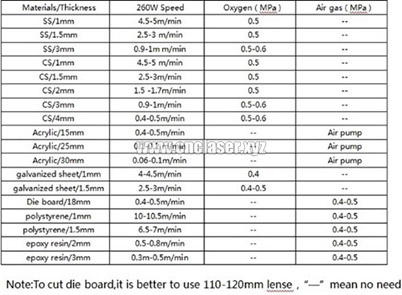
SS- stainless steel, CS- carbon steel
1-2 kW CO2 Laser Cutting
Mild steel
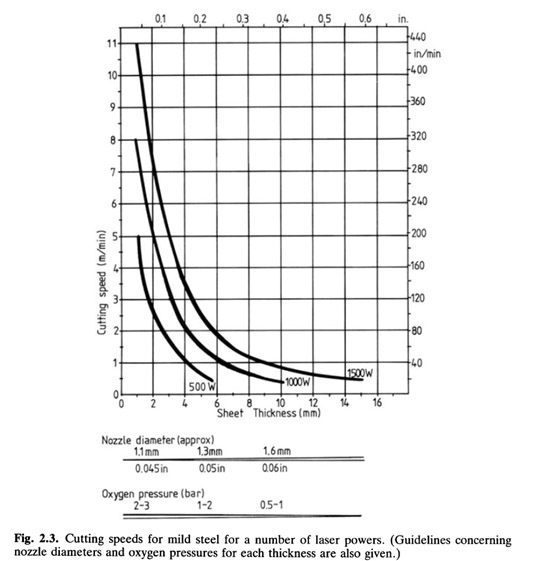
Figure 2.3 shows the cutting speeds possible for mild steel over a range of thickness and laser powers. 1,5kW of laser will cut 1mm thick mild steel at 10m/min and 10mm thick steel at 1m/min
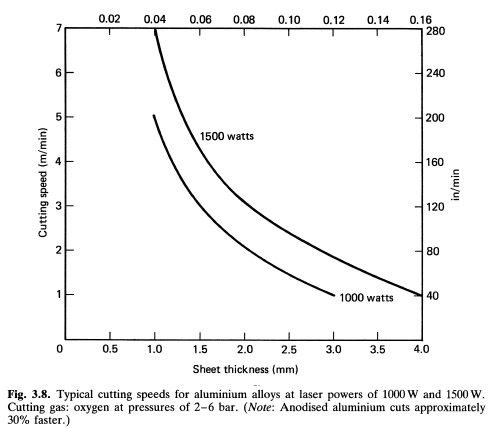
Aluminum alloys
Copper
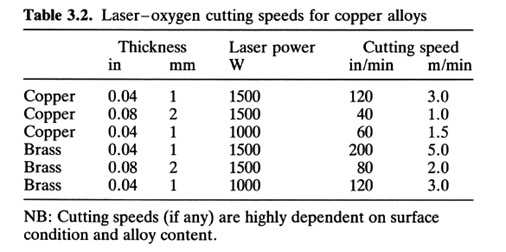
Nd:YAG laser 120-500 W
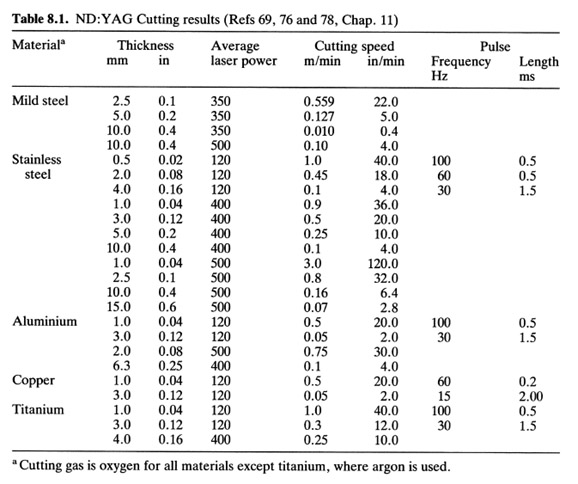
Features of Nd:YAG laser is the possibility of very high peak power pulses by Q switching and the possibility of second harmonic generation (green 532nm) and third harmonic generation (UV 355nm)
Fiber laser
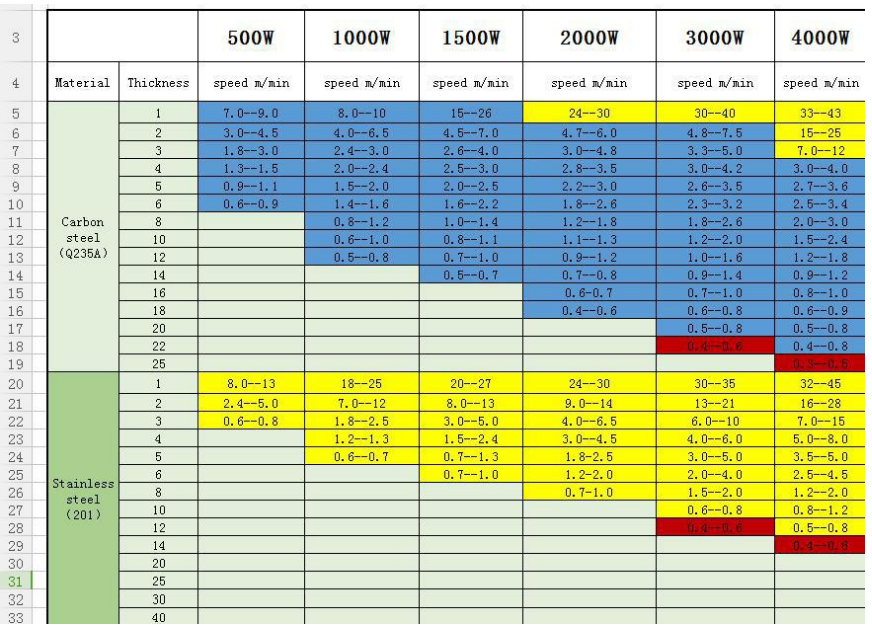
Fiber laser also need to assist gas as other laser types
References :
CO2 laser cutting book – ISBN: 9781852330477 , 10.1007/978-1-4471-1279-2
https://www.alibaba.com/product-detail/6040-cheap-60W-Co2-Laser-Marking_60659932697.html
MORE PDF GUIDEBOOKS
Innovation in high power fiber laser applications Read more >>>
About Fiber laser cutting machine SIGMA 1390 – 750w Read more >>>
Role of Combustion Energy in Laser Cutting of Austenitic Stainless Steel Learn more >>>
Laser cutting of variable thickness materials – Understanding the problem Read the paper >>>
THE FUTURE FOR FIBER AND DISC LASERS Explore >>>
Design and performance of a Cutting CO2 laser for industrial non-metallic
materials Read it >>>
The Role of the Assist Gas Nature in Laser Cutting of Aluminum
Alloys Check it out >>>
Mirco welding https://www.rdworldonline.com/best-option-for-micro-welding-ndyag-vs-fiber-laser/
Some more details about laser processing of metals
When processing metals with a 1 kW laser it is necessary to bear in mind the following parameters of the maximum cross-sections of metals:
Black metal (steels with various doping levels) — 40 mm.
Stainless steel — 25 mm.
Aluminum and its alloys — 12 mm.
Brass — 12mm.
Copper and alloys— 5 mm.
Laser type. Fiber lasers are suitable for cutting high-melting, extra hard metals as well as fragile and thin materials, since they have a much narrower beam spot due to short-wave radiation. Whereas, gas lasers fit for a wider range of materials that are easier to process.
Speed. It depends on the metal type, its thickness, and the power of the laser machine. For instance, the cutting speed of a 1000 W laser machine for carbon steel 0,5-8,0 mm thick will be around 0,6-15 m/min, for stainless steel 1,0-5,0 mm thick will be 0,8-18 m/min, for aluminum 1mm thick – 1,2-10 m/min, and for copper 1mm thick – 10 m/min.
Power. We choose the laser power depending on the type and thickness of the metal to be processed. In industry 1-10 kW fiber lasers and 1-6 kW gas lasers are used.
The quality of the laser cutting depends on the frequency and power of the laser radiance, speed and time delay at the step of initial burning of the material. It is also important to bear in mind that when working with thick metal you need to start cutting outside the cutting vector to make a perfect shape of the final workpiece.
| Co2 laser | ||
| Type of metal | Thickness in mm | Power (watt) |
| Steel (alloy, carbon) | 1 | 100 |
| 0,5 | 250 | |
| 1,2 | 400 | |
| 2,2 | 850 | |
| up to 40 mm | 5000 | |
| Brass | 12 | 5000 |
| Aluminum alloys | 12 | 5000 |
| Copper | 5 | 5000 |
| Titanium | 0,5 | 850 |
| 0,6 | 250 | |
| 1 | 600 | |
| Stainless steel | 1 | 100 |
| 0,5 | 250 | |
| 1,3 | 400 | |
| 2,5 | 400 | |
| 3,2 | 400 | |
| 9 | 850 | |
| up to 25 | 5000 | |
| Fiber laser | |||
| Material | Thickness in mm | Speed mm / sec | Extra gas |
| Black steel | 1 | 8 | oxygen |
| 2 | 6 | oxygen | |
| 3 | 3,2 | oxygen | |
| 4 | 2,7 | oxygen | |
| 5 | 2,5 | oxygen | |
| 6 | 2 | oxygen | |
| 8 | 1,3 | oxygen | |
| 10 | 1,1 | oxygen | |
| 12 | 0,9 | oxygen | |
| 14 | 0,8 | oxygen | |
| 16 | 0,8 | oxygen | |
| 18 | 0,7 | oxygen | |
| 20 | 0,65 | oxygen | |
| Aluminum & copper | 1 | 600 | Nitrogen |
| 2 | 300 | Nitrogen | |
| 3 | 100 | Nitrogen | |
| 4 | 80 | Nitrogen | |
| 5 | 65 | Nitrogen | |
| 6 | 55 | Nitrogen | |
| 7 | 35 | Nitrogen | |
| 10 | 15 | Nitrogen | |
| 12 | 8 | Nitrogen |








