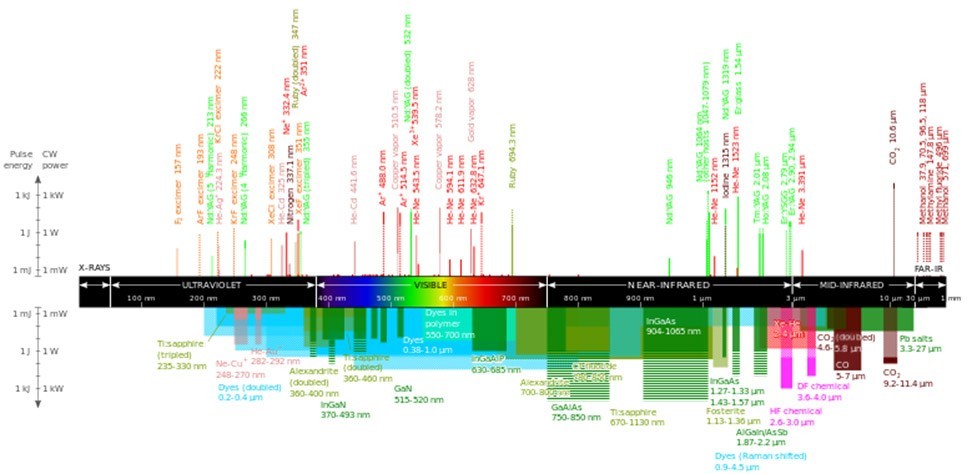
Wavelengths of different lasers
Lasers with clear lines of radiation are shown at the top, while lasers capable of radiating ranging wavelengths are shown below. The height of the lines and bands corresponds to the maximum energies of commercially available lasers; the solid lines denote continuous radiation, and the dotted lines denote pulsed. The solid green squares are the power of a single semiconductor laser, the horizontal green lines are the power increase of multiple lasers. For Ar + -Kr +, only the main lines are labeled, the rest are marked as short lines. The wavelength scale combines linear and logarithmic scales. The color highlights various materials of laser pumping (see the description of the figure). The data are given in accordance with the Handbook of laser wavelengths, with the table adding new types of lasers, including semiconductor ones.
Gas Lasers
| Laser working medium | Wavelength | Laser exciter | Application |
| HeNe lasers | 632,8 nm (543,5; 593,9; 611,8 nm, 1,1523; 1,52; 3,3913 um) | Electric discharge | Interferometry, holography, spectroscopy, barcode reading, demonstration of optical effects. |
| Argon lasers | 488,0; 514,5 nm, (351; 465,8; 472,7; 528,7 nm) | Electric discharge | Retina treatment, lithography, pumping of other lasers. |
| Kr lasers | 416; 530,9; 568,2; 647,1; 676,4; 752,5; 799,3 nm | Electric discharge | Scientific researches, laser shows, white light lasers (combined with Argon) |
| Xe lasers | Many spectral lines throughout the entire visible spectrum and partially in the UV and IR ranges. | Electric discharge | Scientific researches |
| N2 lasers | 337,1 nm (316; 357 nm) | Electric discharge | Dye laser pumping, atmospheric pollution research, research, educational lasers |
| Hydrogen-fluorine laser | 2,7—2,9 um (Hydrogen-fluorine) 3,6—4,2 um (deuterium fluoride) | The chemical reaction of combustion of ethylene and nitrogen trifluoride (NF3)), initiated by electric discharge (pulsed mode) | Operate in a continuous mode in the ranges of megawatt power and in a pulse mode in the range of terawatt power. One of the most powerful lasers. Laser weapons. Laser Thermonuclear Fusion (LTF). |
| Chemical oxygen iodine laser (COIL) | 1,315 um | The chemical reaction in the flame of singlet oxygen and iodine | Work in a continuous mode in the range of megawatt capacity. A pulse option is also available. Scientific research, laser weapons. Processing of materials. Laser Thermonuclear Fusion (LTF). In perspective: the source of pumping of neodymium lasers and X-ray laser systems.
|
| CO2 laser (CO2) | 10,6 um, (9,6 um) | Transverse (high power) or longitudinal (low power) electric discharge, chemical reaction (DF-CO2 laser) | Materials processing (cutting, welding), surgery. |
| Carbon monoxide laser (CO) | 2,5—4,2 um, 4,8—8,3 um | Electric discharge, chemical reaction | Materials processing (cutting, engraving etc.), photoacoustic spectroscopy |
| Excimer laser | 193 nm (ArF), 248 nm (KrF), 308 nm (XeCl), 353 nm (XeF) | Recombination of excimer molecules at the electric discharge | UV lithography in the semiconductor industry, laser surgery, vision correction. |
Dye Lasers
| Laser working medium | Wavelength | Laser exciter | Application |
| Dye Lasers | 390—435 nm (Stilbene), 460—515 нм (Coumarin102), 570—640 nm (Rhodamine 6G), others | Another laser, pulse lamp. | Researches, spectroscopy, cosmetic surgery, isotope separation. The operation range is determined by the dye type. |
Metal Vapor Lasers
| Laser working medium | Wavelength | Laser exciter | Application |
| Helium-cadmium metal vapor lasers
| 440 nm, 325 nm | Electric discharge in the mixture of metal vapors and Helium | Polygraphy, UV currency detectors, research. |
| He-Hg metal vapor lasers | 567 nm, 615 nm | Electric discharge in the mixture of metal vapors and Helium | Archeology, research, educational lasers. |
| He-Se metal vapor lasers | Up to 24 spectral bands, from red to UV Electric discharge in the mixture of metal vapors and Helium | Electrical discharge in the mixture of metal vapors and Helium | Archeology, research, educational lasers. |
| Copper vapor laser | 510,6 nm, 578,2 nm | Electric discharge | Dermatology, speed photography, Dye laser pumping |
| Gold vapor laser | 627 nm | Electric discharge | Archeology, medicine. |
Solid-State Lasers
| Laser working medium | Wavelength | Laser exciter | Application |
| Ruby lasers | 694,3 nm | Pulse lamp | Holography, tattoo removal. First represented type of the laser (1960). |
| Nd:YAG lasers | 1,064 um, (1,32 um) | Pulse lamp, laser diode | Material processing, laser range finders, laser target marker, surgery, research, pumping of other lasers. One of the most common high power lasers. Usually works in a pulse mode (fractions of nanoseconds). Often used in combination with a frequency doubling and a corresponding change in wavelength by 532 nm. Known designs with a quasi-continuous radiation mode.
|
| Neodymium-doped yttrium-lithium fluoride lasers (Nd:YLF) | 1,047 and 1,053 um | Pulse lamp, laser diode | Titanium-sapphire laser pumping using the effect of frequency-doubling in non-linear optics. |
| Nd:YVO4 lasers | 1,064 um | Laser diodes | Titanium-sapphire laser pumping using the effect of frequency-doubling in non-linear optics. |
| Nd: Glass lasers | ~1,062 um (Silicate glass), ~1,054 um (Phosphate glass) | Puls lamp, laser diodes | Lasers of ultrahigh power (terawatts) and energy (megajoules). Usually, work in the nonlinear mode of frequency tripling up to 351 nm in laser melting devices. Laser Thermonuclear Fusion (LTF). X-ray lasers pumping. |
| Titanium-sapphire lasers | 650—1100 nm | Other lasers | Spectroscopy, laser rangefinders, research. |
| Tm:YAG lasers | 2,0 um | Laser diodes | Laser radar (LIDAR) |
| Yb:YAG lasers | 1,03 um | Pulse lamp, laser diodes | Material processing, ultrashort pulse research, multiphoton microscopy, laser range finders. |
| Ho:YAG lasers | 2,1 um | Laser diodes | Medicine |
| Ce:LiSAF, Ce:LiCAF lasers | ~280-316 nm | Nd:YAG laser with frequency quadrupling, Excimer laser, Hg-vapor laser. | Atmospheric research, laser rangefinders, scientific research. |
| Chrome-doped alexandrite lasers | Has a range of 700-820 nm | Pulse lamp, laser diodes. Arc mercury lamp for continuous operation | Dermatology, laser rangefinders. |
| Erbium-doped fiber-optics lasers | 1,53-1,56 um | Laser diodes | Optical amplifiers in fiber-optic communication lines, metal processing (cutting, welding, engraving), thermal splitting of glass, medicine, cosmetology.
|
| Uranium-doped calcium fluoride lasers (U:CaF2) | 2,5 um | Pulse lamp | The first 4-level solid-state laser, the second operating type of laser (after the Mayman ruby laser), cooled with liquid helium, is not used anywhere today. |
| Zinc / cadmium chalcogenide lasers doped with transition metals (chromium, iron) (TM2+:AIIBVI, Cr2+:ZnSe, Fe2+:ZnSe) | Cr2+ 1,9-3,6 um, Fe2+ 4-5.5 um | for Cr2+-doped active medium — laser diode, Erbium or Thulium fiber lasers, for Fe2++ -doped active medium Er: YAG laser (2.94 um) | Wide-bandwidth solid-state lasers, generation of femtosecond laser pulses |
Semiconductor Lasers
| Laser working medium | Wavelength | Laser exciter | Application |
| Semiconductor laser diodes | The wavelength depends on the material and structure of the active zone: near UV, violet, blue – Ga, Al semiconductor nitrides; red, near infrared range – compounds based on Al, Ga, As; near and middle infrared range – compounds containing In, P, Sb; Medium IR — Far Infrared — lead salts; medium IR – terahertz range – semiconductor quantum-cascade lasers | Electric current, optical pumping | Telecommunications, holography, laser designators, laser printers, pumping of other laser types. AlGaAs lasers (aluminum-gallium-arsenide) operating at 780 nm are used in CD players and are the most common in the world. |
Other Types of Lasers
| Laser working medium | Wavelength | Laser exciter | Application |
| Free electron lasers | The x-ray laser wavelength ranges between 0,085 – 6 nm | Bundle of relativistic electrons | Atmospheric research, materials science, medicine, missile defense. |
| Pseudo-nickel samarie lasers | X-ray radiation 7,3—15 um | Radiation in a super-hot samarium plasma produced by double pulses of a neodymium laser. | The first demonstration laser operating in the range of hard x-rays. It can be used in ultra-high-resolution microscopes and holography. Its radiation lies in the “window of transparency” of water and allows to explore the structure of DNA, the activity of viruses in cells, the effect of drugs.
|
| Color center laser | Wavelength 0,8—4 um | Optic, flash lamp, laser lamp, electron beam
| Spectroscopy, medicine. |
based on Wikipedia and Marvin Weber.