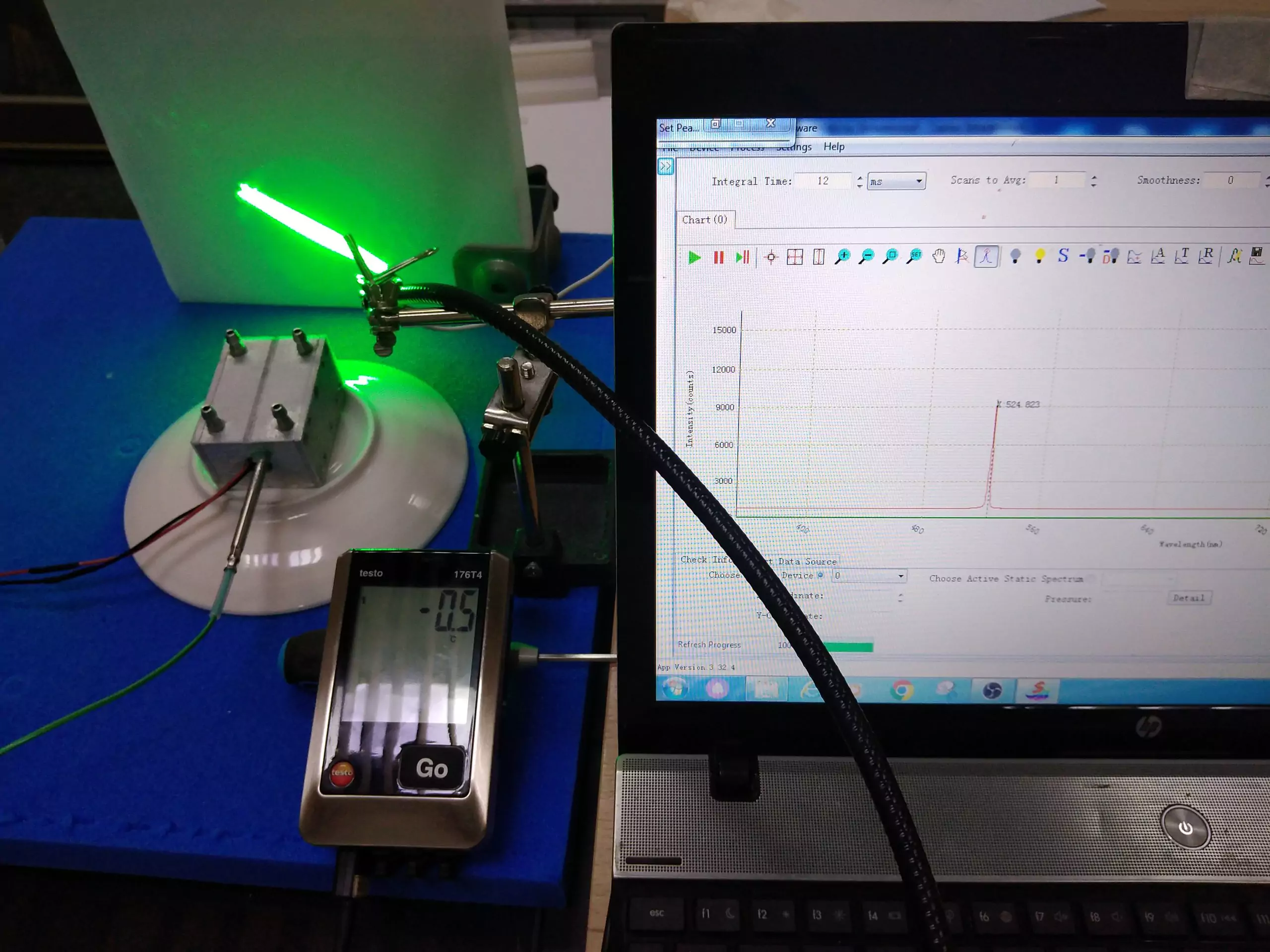
We plan to evaluate how the wavelength of laser diodes changes when they are cooled to negative temperatures.
For tests 3 laser diodes were used with emission in violet 405 nm , green 525 nm and red spectrum 635 nm . A freezer was used to cool the laser diodes, capable of cooling objects placed in it down to -80 ° C . To make the temperature of the laser diodes change more smoothly, each laser diode was installed in a water block before being installed in the freezer. Preliminarily, a concentrated automotive anti-freeze liquid based on isopropyl alcohol was poured into the water block. To measure the laser diode temperature, we used a Testo 176 T 4 temperature logger, the sensor of which was installed in a special hole on the water block. The temperature was measured with an interval of 15 seconds. To measure the wavelength, an Aurora 4000 spectrometer was used. The room temperature during the tests was around 25 ° C .
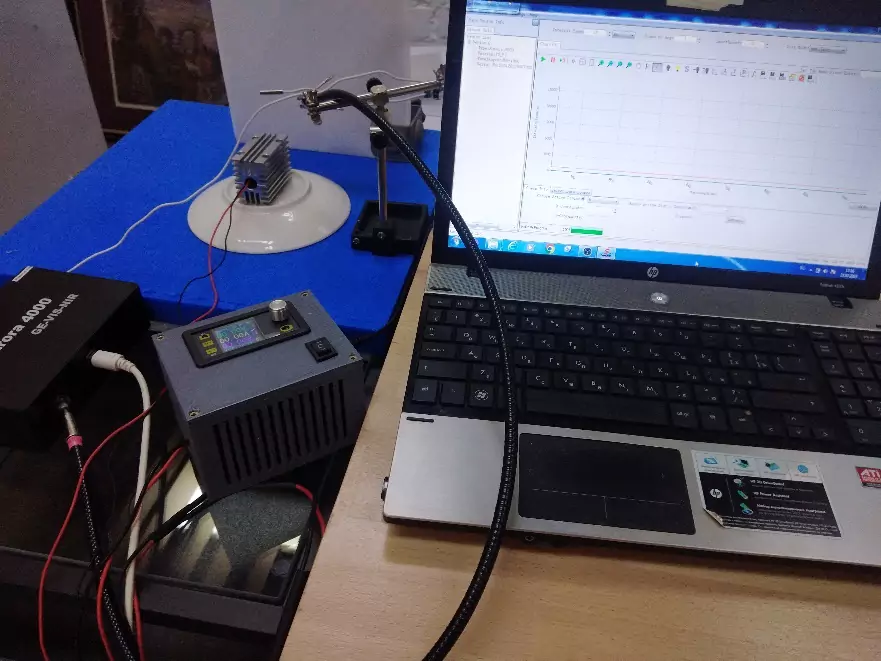

Fig.1 – General view of the test stand
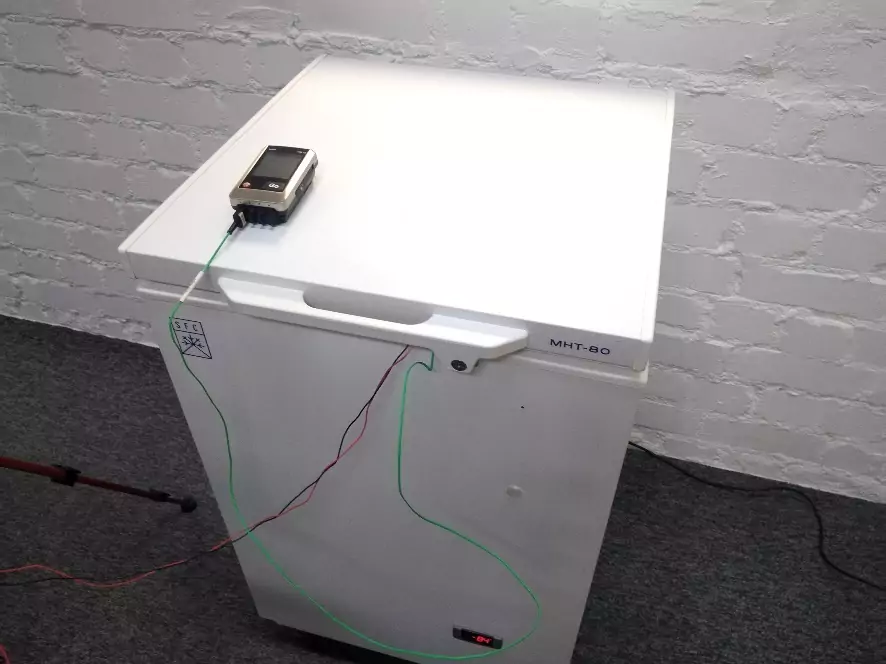
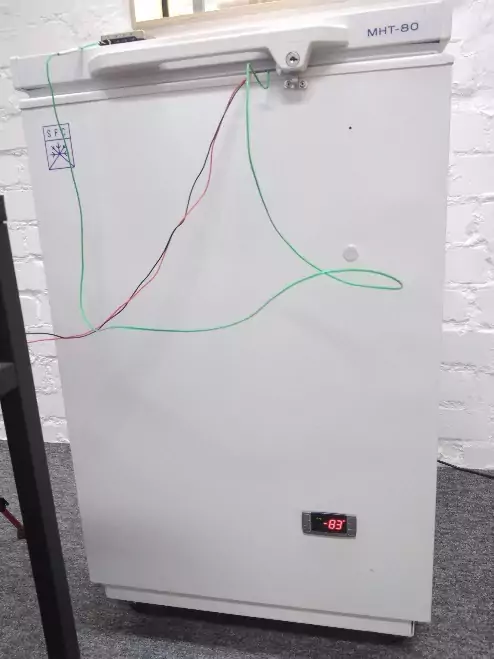

Fig. 2 – Freezer
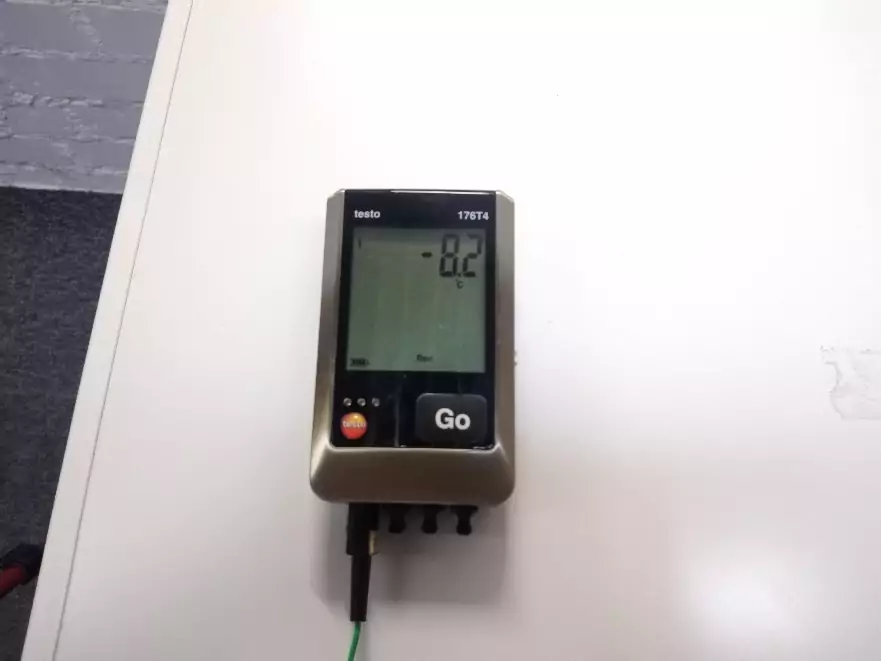

Fig.3 – Temperature logger
Test 1 – Laser diode emitting in the violet spectrum. (405 nm)
When measured at room temperature, the wavelength of the laser diode was 403 nm.

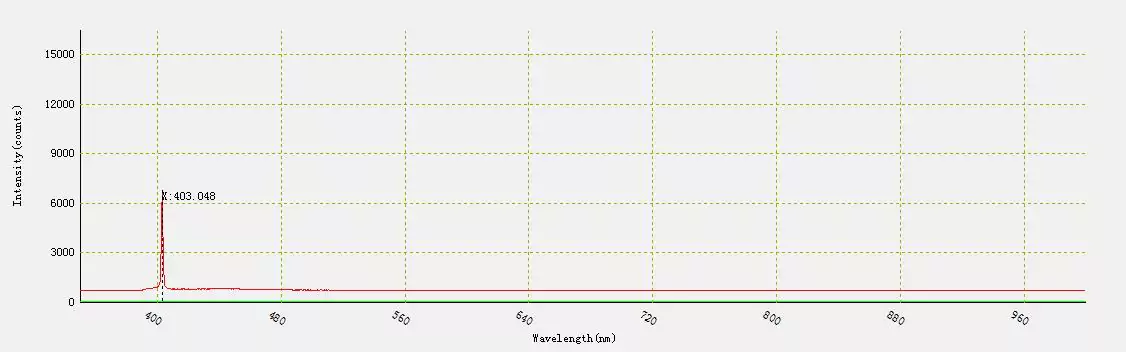
Fig.4 – Wavelength at 25 ° C
Then the laser diode was installed in a water block and placed in a freezer. After the laser diode had cooled down to -80 ° C , it was taken out and placed on the bench, but it was not possible to turn it on.
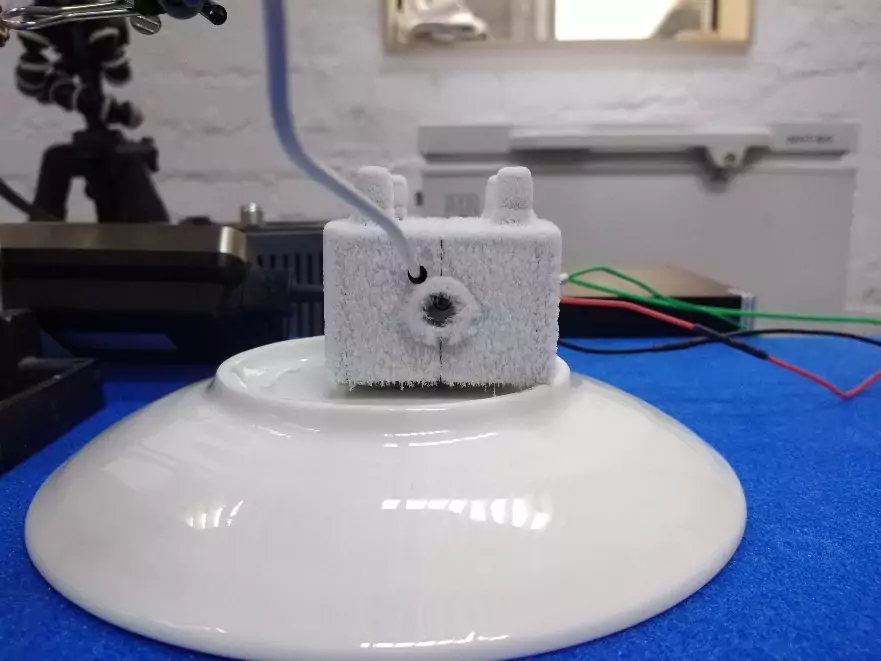
Fig. 5 – Water block with a laser diode after removal from the freezer
Gradually, the temperature of the laser diode began to rise. When the temperature reached -25 ° C , the laser diode was turned on. The measurement wavelength was about 400 nm.
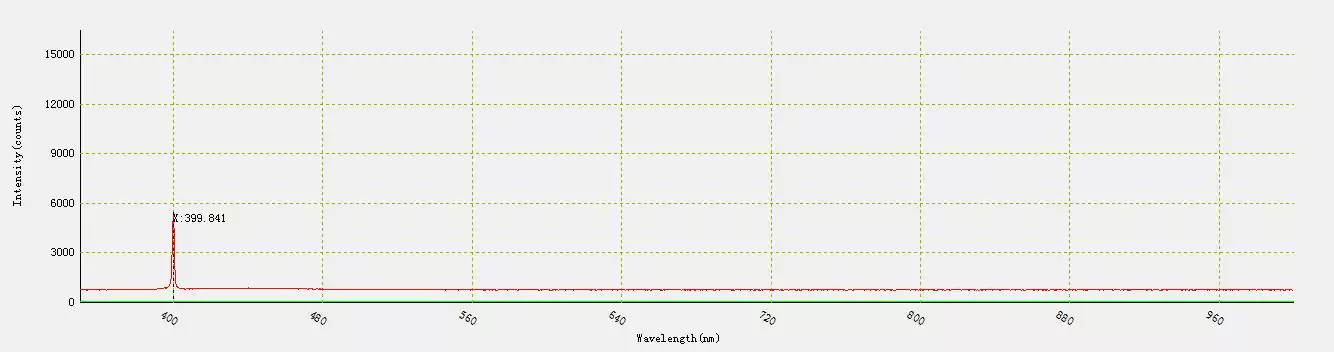
Fig.6 – Wavelength at -25 ° C
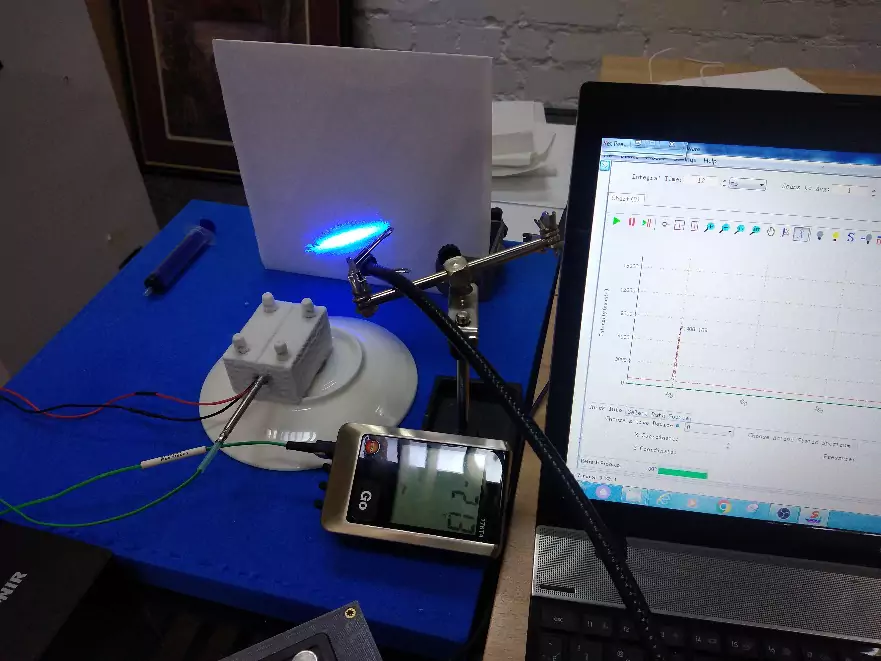

Fig.7 – Wavelength at -21.3 ° C
Based on the measurement results, a table was compiled
| Temperature | Wavelength |
| – 24.3 – -9.6 ° C | 400 nm |
| – 9.1 – 6.1 ° C | 401 nm |
| 6.4 – 19.8 ° C | 402 nm |
| 19.9 – 25 ° C | 403 nm |
At temperatures below -25C, the laser diode did not turn on.
Test 2 – Laser diode emitting in the green spectrum. (520 nm)
When measured at room temperature, the wavelength of the laser diode was 525 nm .
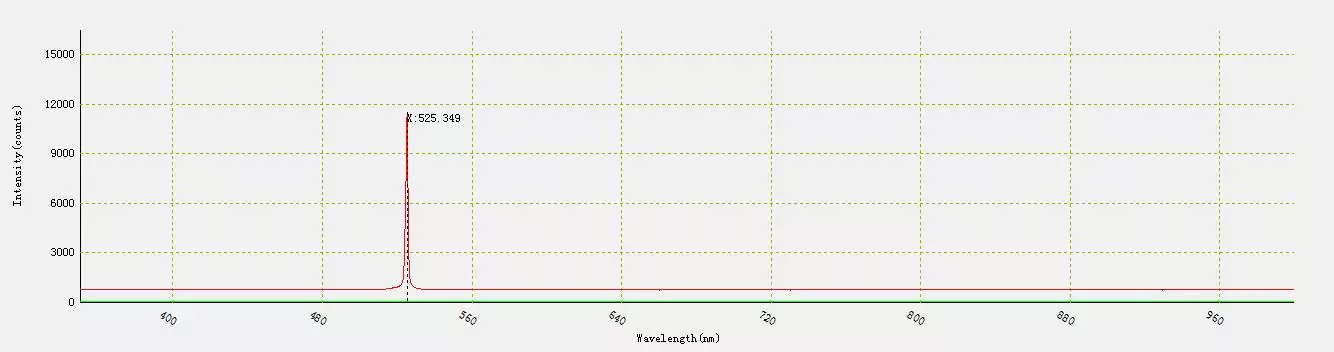
Fig.8 – Wavelength at 25 ° C
The laser diode was then cooled down to -70 ° C . The measured wavelength was 522 nm .
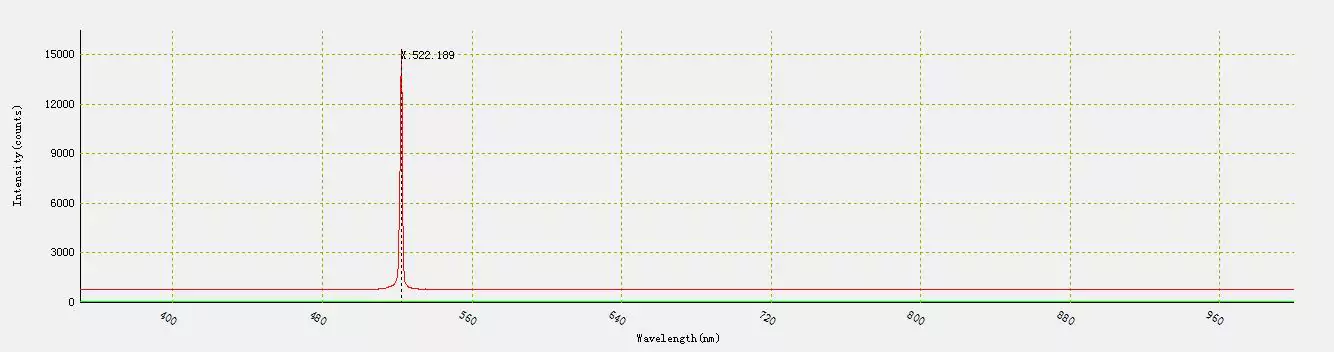
Fig.9 – Wavelength at -70 ° C

Fig.10 – Wavelength at -65.6 ° C
Based on the measurement results, a table was compiled
| Temperature | Wavelength |
| – 70.0 – -51.6 ° C | 522 nm |
| – 50.6 – -25.5 ° C | 523 nm |
| – 24.9 – -18.0 ° C | Fluctuates between 523 and 524 nm |
| – 17.4 – 2.1 ° C | 524 nm |
| 2.5 – 5.2 ° C | Fluctuates between 524 and 525 nm |
| 5.5 – 25 ° C | 525 nm |
nm dependence at 20-25 degrees Celsius.
Test 3 – Laser diode emitting in the red spectrum. (635 nm)
When measured at room temperature, the wavelength of the laser diode was 637 nm.
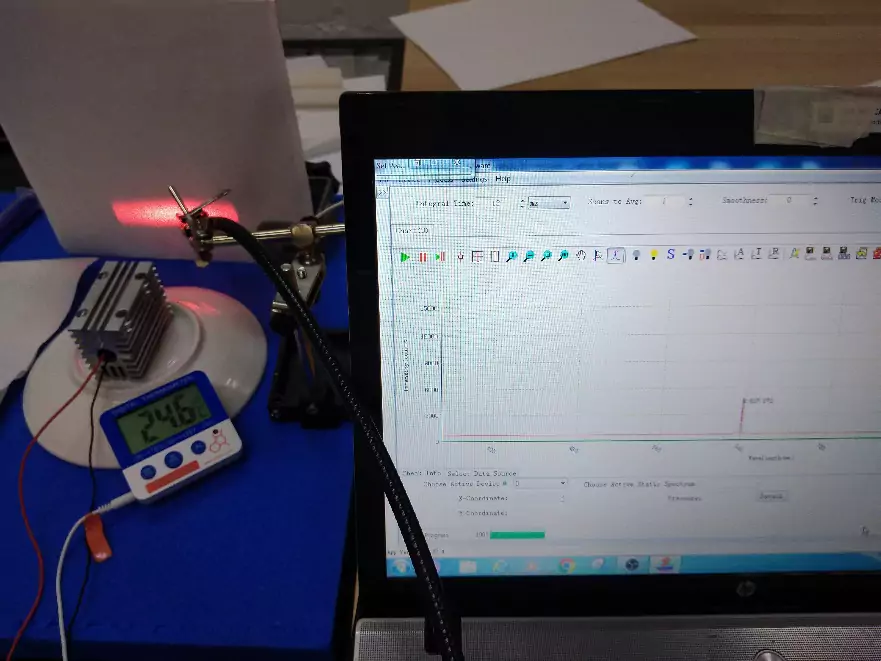
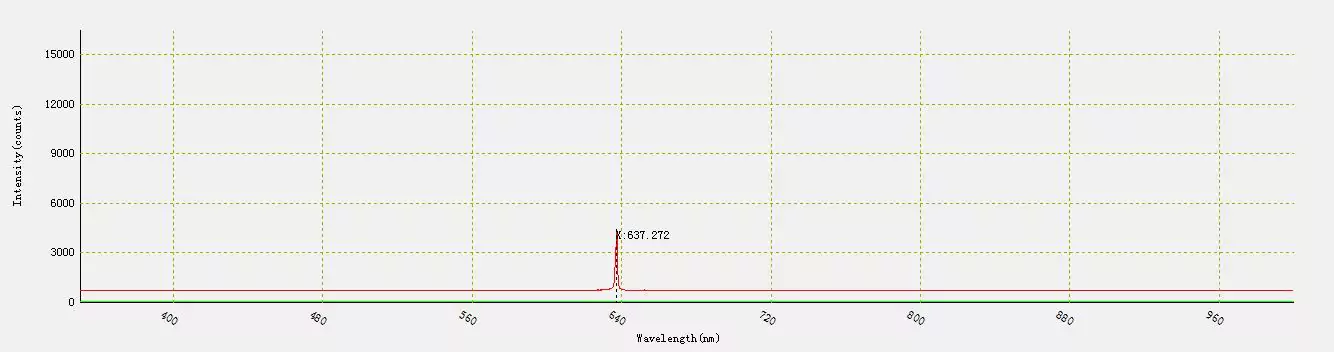
Fig.11 – Wavelength at 25 ° C
The laser diode was then cooled down to -73.5 ° C . The measurement wavelength was 621 nm.
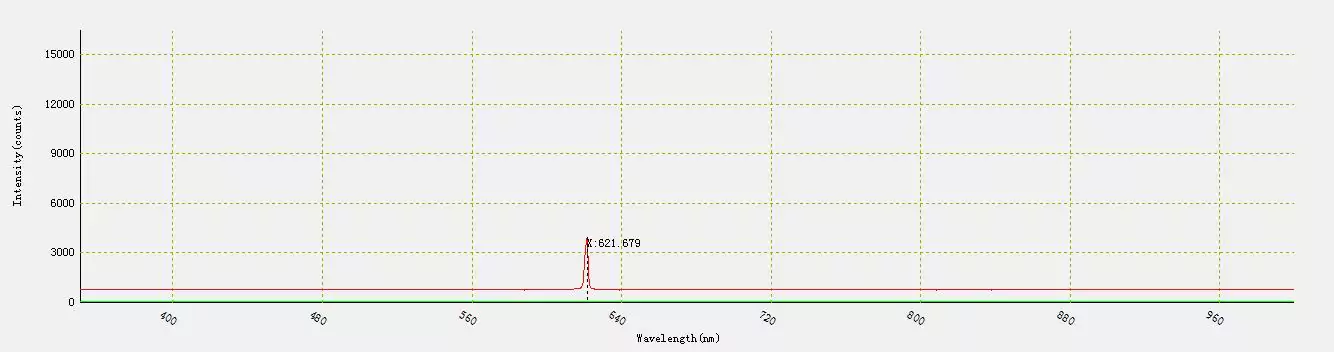
Fig.12 – Wavelength at -73.5 ° C
Fig.13 – Wavelength at -68.6 ° C
Based on the measurement results, a table was compiled
| Temperature | Wavelength |
| – 73.5 – -70.0 ° C | 621 nm |
| – 68.6 – -61.8 ° C | 622 nm |
| – 61.0 – -56.4 ° C | 623 nm |
| – 54.5 – -48.4 ° C | 624 nm |
| – 47.1 – -41.3 ° C | 625 nm |
| – 40.3 – -34.6 ° C | 626 nm |
| – 33.8 – -27.4 ° C | 627 nm |
| – 26.7 – -20.7 ° C | 628 nm |
| – 20.1 – -13.9 ° C | 629 nm |
| – 13.3 – -9.9 ° C | 630 nm |
| – 9.4 – -3.2 ° C | 631 nm |
| – 2.8 – -2.9 ° C | 632 nm |
| 3.2 – 8.1 ° C | 633 nm |
| 8.3 – 11.7 ° C | 634 nm |
After these experiments, we can conclude that different laser diodes have different temperature dependences on the spectrum. In other words, if for blue diodes this is a change of 1 nm per 20 degrees, then for a red diode it is 1 nm per 7 degrees.
This means that by cooling and maintaining the temperature of different laser diodes, one can obtain a spectrum shift, which may be necessary for certain practical or research work.
In fact, it makes sense to state that for almost any laser diode it is possible to achieve a spectrum shift to the lower side by 5-12 nm.
Most likely, this dependence for different laser diodes will be different, as in the case of the red one, where the spectrum has shifted more than in the green diode.
An important circumstance is that laser diodes continue to function at low temperatures.
An important circumstance is that it is necessary to control the formation of ice and condensate on the laser diode itself.
Endurance lasers LLC offers waterblocks and freezers for working with laser diodes at low temperatures.
We plan to further conduct tests at temperatures from -100-180C using liquid nitrogen.