Learn about laser crystals. Useful data!
In this post, we would like to educate you about laser crystals.
Explore about most popular laser crystals in one post: Diffusion-Bonded Crystals, Titanium-sapphire (Ti:Sapphire), Yb:KGW Crystals, Nd:KGW Crystals, Cr:LiSAF Crystals, Nd:YLF Crystals, Er:YAG Crystals, Yb:YAG Crystals, Nd:Ce:YAG Crystals, Ho:Cr:Tm:YAG crystals, Cr4+:YAG crystals, Nd:YAG Crystals, Nd:GdVO4 crystals, Nd:YVO4 Crystals, Er,Cr:YSGG Crystals.
Er,Cr:YSGG Crystals

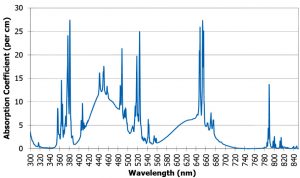
| Erbium- and chromium-doped yttrium-scandium-gallium garnet (Er, Cr: YSGG) is an effective laser crystal for lasing with a wavelength of 2800 nm, which is an important water absorption band. Er, Cr: YSGG crystal has a high conversion efficiency, stable chemical properties, and a long fluorescence lifetime. These crystals are widely used in dentistry, environmental studies, communication systems, military industry and remote sensing technologies.
Special features: – High conversion efficiency; – Excellent optical properties; – Lasing modes: continuous, free generation or Q-modulation; – The lowest generation threshold among standard erbium-doped crystals; – the highest differential quantum efficiency among standard erbium-doped crystals; – Natural disorder leading to an increase in the width of the spectral pumping line and in strength; – Flash lamp (chromium absorption bands) or diode (erbium bands) pumping; – Long fluorescence lifetime.
Main properties of Er,Cr:YSGG crystals:
|
Nd:YVO4 Crystals

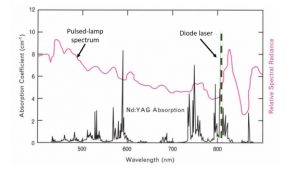
| Neodymium-doped yttrium-vanadate crystals (Nd:YVO4) are some of the most effective laser crystals for coherent sources with diode pumping, especially for sources with low and middle power density. Their absorption and emission properties are even better than those of Nd:YAG crystals. A laser diode-pumped Nd:YVO4 crystal was combined with crystals with a high non-linearity factor (LBO, BBO or KTP) to shift the frequency of the lasing output from the near-IR to the green, blue or even UV spectral region. This combination in solid-state lasers is an ideal tool for most common laser applications, including material processing, spectroscopy, wafer quality control systems, laser printing, etc. It is proven that diode-pumped ND: YVO4 solid-state lasers quickly gain markets where water-cooled ion lasers and lamp-pumped lasers traditionally dominate, especially when a compact design and emission with a single longitudinal mode are required.
Advantages of Nd:YVO4 lasers over Nd:YAG: – The absorption coefficient is 5 times greater in the whole wide pumping range around 808 nm (besides, the dependence on the pump wavelength is much lower, and there is also a strong tendency to form single-mode emission); – The stimulated emission cross-section is 3 times larger at a wavelength of 1064 nm; – Lower generation threshold and higher differential quantum efficiency; – Uniaxial crystal with double refraction: linearly polarized radiation.
Special features: – Doping: 0.1% – 3%; – Doping material concentration tolerance: ±0.05% (atoms%<1%), ±0.1% (atoms%≥1%); – Crystals of various sizes and of high quality; – 10 000 items Nd:YVO4 per month 3x3x0.5 – 4x4x8 mm3 in size; – Competing prices. Nd:YVO4 crystal absorption curve ( 0.5% doping, 4 mm thick) Nd:YVO4 crystal properties
Nd:YVO4 lasers properties 1. One of the most appealing properties of Nd:YVO4 crystals is their absorption coefficient, which is 5 times bigger than that of Nd:YAG crystals in a wide range with a peak around 808 nm, what corresponds to the standard wavelength of laser diodes of high power. It means that it is possible to use more compact crystals in lasers, resulting in size reduction of a coherent radiation source system as a whole. Besides, lower power of a pumping laser diode is needed, which, in its turn, increases the laser diode lifetime. The absorption bandwidth of Nd:YVO4 may be 2.4 – 6.3 times bigger than that of Nd:YAG crystals. High efficiency of pumping allows choosing less expensive laser diodes for pumping. 2. Nd:YVO4 crystals have a wider cross-section of stimulated emission at both 1064 nm and 1342 nm wavelengths. At 1064 nm wavelength lasing, this cross-section is 4 times as big as the cross-section of a similar Nd:YAG crystal; at 1340 nm lasing the cross-section is 18 times bigger. This enables Nd:YVO4 lasers to support powerful single-mode radiation at both wavelengths. 3. Unlike Nd:YAG crystals with cubic symmetry, Nd:YVO4 crystals are single uniaxial, which makes it possible to generate linear polarized emission. Though, the service lifetime of Nd:YVO4 is 2.7 times shorter than that of Nd:YAG, their differential quantum efficiency is rather high due to the high pumping efficiency. Comparison of Nd:YVO4 and Nd:YAG characteristics is given below: stimulated emission cross-section (σ), absorption coefficient (α), fluorescence lifetime (τ), absorption length (Lα), threshold power (Pth) and quantum efficiency of pumping (ηs). Nd:YVO4 and Nd:YAG characteristics
Comparison of Nd:YVO4 and diode-doped Nd:YAG lasers
Diode-pumped Nd:YVO4+KTP laser – 8 W green light generated by an Nd:YVO4 (0.5% doping, 15 W pumping laser diode. KTP crystal inside the resonator. – 200 mW green light generated by an Nd:YVO4 (2% doping, 1 W pumping laser diode. – KTP crystal: 2x2x5 mm3, Nd:YVO4 crystal: 3x3x1 mm3. Anti-reflective coating – Both butt-ends with anti-reflective coating for 1064/808 nm, R<0.2% at 1064 nm, R<2% at 808 nm; – 1 surface: high reflective coefficient coating at 1064&532 nm, with high transmittance coefficient for 808 nm, R>99.8% at 1064&532, T>90% at 808 nm; – 2 surface: anti-reflective coating at 1064&532 nm, R<0.2% at 1064 nm; R<0.5% at 532 nm; – 1 surface: high reflective coefficient coating at 1064 nm, with high transmittance coefficient for 808 nm, R>99.8% at 1064, T>95% at 808 nm; – 2 surface: anti-reflective coating at 1064 nm, R<0.1% at 1064 nm; – 1, 2 surface: anti-reflective coating, 3 surface: gilding / chrome plating; – Both butt-ends with anti-reflective coating at 1064 nm, 3 surface anti-reflection coating for 808 nm; – Other variants of coating at request. |
Nd:GdVO4 crystals

| Nd:GdVO4 crystals are used as the active substances in diode-pumped solid-state lasers. They have some advantages over Nd:YAG crystals: wide emission cross-section, wide absorption band, polarized lasing output.
Special features: – Wide cross-section of stimulated emission at the laser wavelength; – High absorption coefficient and wide operation range at the pumping wavelength; – Low pumping wavelength dependency; – High thermal conductivity; – Low lasing threshold, high differential quantum efficiency; – High damage threshold; – Highly polarized laser radiation;. Main properties: – Wavefront distortion: <λ/4 at 633 nm; – Crystal dimension limit: (W±0.1 mm)x(H±0.1 mm)x(L+0.2/-0.1mm); – Aperture: >90%; – Flatness: λ/8 at 633 nm, λ/4 at 633 nm for crystals< 2 mm thick; – Surface quality 10/5 Scratch/Dig (characteristic chip size) (MIL-PRF-13830B); – Parallelism: < 20 arcseconds; – Perpendicularity: ≤5 arcseconds; – Angle tolerance: <±30′. Nd:GdVO4 crystals characteristics+
Nd:GdVO4 and Nd:YVO4 properties comparison
Comparison of neodymium laser material properties
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nd:YAG Crystals

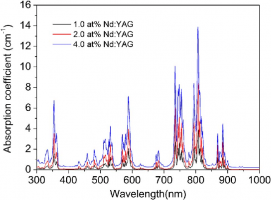
| Neodymium-doped aluminum yttrium garnet («YAG», Y3Al5O12) crystals are the most popular and long-used laser crystals. As long as these crystals combine plenty of property advantages, Nd:YAG are used in almost every solid-state laser of the near IR range, as well as in modules for generation of second, third, and higher harmonics.
Nd:YAG crystals advantages: – High gain coefficient; – Low lasing threshold; – High efficiency; – High optic characteristics; – Low losses at 1064 nm; – Good thermal conductivity and thermostability; – High mechanical toughness; – Lasing modes: continuous, pulse, Q modulation, mode synchronization. Special features: – Size: 15×180 mm2 – 40×2 mm2; – Nd doping: 0.3~2.0(±0.1) % atoms; – Diameter tolerance: ±0.05 mm; – Length tolerance: ±0.5 mm; – Perpendicularity: ≤5 angular minutes; – Parallelism: <10 angular minutes; – Wavefront distortion: λ/8; – Flatness: λ/10; – Surface quality: 10/5 (MIL-O-13830A); – Highly reflective coating: R>99.8% at 1064 nm, R< 5% at 808 nm; – Anti-reflective coating (one layer of MgF2): R<0.25% for each surface (at 1064 nm); – Other reflective coatings for 1064/532 nm, 946 nm, 1319 nm, etc.; – Damage threshold: >500 MW/ cm2. Nd:YAG crystals main features
Nd:YAG crystals optic parameters
Optional Nd:YAG rods and sheets are available for ordering, Nd:YAG rods for 946 nm and 1319 nm. Er:YAG, Yb:YAG and other ion-doped YAG crystals are delivered at request. |
Cr4+:YAG crystals
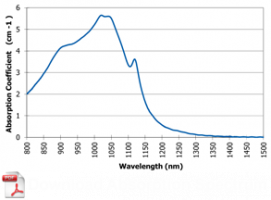
| Chrome-doped aluminum-yttrium garnet («YAG», Y3Al5O12) crystals are very good for work with Nd:YAG, Nd:YLF, Nd:YVO4 lasers or coherent sources with Nd- and Yb-doped crystals, passive Q-switching and diode or lamp pumping in the wavelength range of 0.8 – 1.2 um. Due to their chemical stability, durability, UV resistance, good thermal conductivity and high radiation resistance (> 500 MW / cm2), these crystals will soon replace the traditionally used materials (LiF, organic dyes and color centers). Cr 4+ :YAG crystals with doping in the range of 0.5 mole% – 3 mole% are available for ordering. Crystal sizes vary from 2×2 mm2 to 14×14 mm2 , from 0.1 mm to 12 mm long. The transmittance coefficient may vary from 10% to 92% according to the request. Preliminary experiments with Cr 4+: YAG crystals showed that the pulse width of passively Q-switched lasers can be shorter than 5 ns for diode-pumped Nd: YAG lasers, and a pulse repetition rate of 10 kHz for diode-pumped Nd: YV lasers. Cr 4+ :YAG crystals can be also used as laser crystals for lasers adjustable in the range of 1.35 – 1.55 um. When Nd:YAG laser pumped at a wavelength of 1.064 um, this source can generate ultrashort pulses. Attention: when ordering Cr 4+ :YAG crystals specify the size, coating type and crystal transmittance coefficient. Cr 4+ :YAG crystals properties
|
Ho:Cr:Tm:YAG crystals
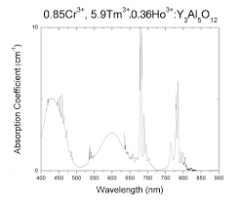
| Ho:Cr:Tm:YAG crystals are highly efficient material for active laser medium, enabling lasing with a wavelength of 2.1 um. They are widely used in surgery, dentistry, atmospheric analysis, etc. Specific features: – High differential quantum efficiency; – Lamp or diode pumping; – Operation at room temperature; – Operates at the eye-safe wavelength. Ho:Cr:Tm:YAG crystals technical features
|
Nd:Ce:YAG Crystals

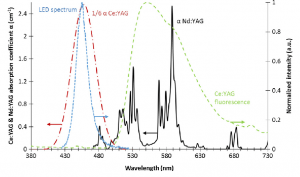
| In neodymium- and cerium-doped aluminum yttrium garnet (Nd:Ce:YAG) cerium is chosen as a neodymium ions (Nd3+) sensibilizer because of its strong UV-range absorption at lamp pumping and effective energy transfer to Nd3+ excitation. As a result, thermal deformations in Nd: Ce: YAG crystals are much smaller, and the output radiation energy is much greater than that of Nd: YAG crystals under similar pumping conditions. These properties make it possible to create high power lasers based on Nd: Ce: YAG crystals with excellent beam quality. The wavelength of such a laser will be 1064 nm. The radiation resistance and thermal conductivity of Nd: Ce: YAG crystals are similar to those of Nd: YAG crystals.
Special features: – High efficiency; – Low lasing threshold; – UV exposure resistance; – High thermal resistance; – High quality. Optic and spectral properties of Nd:Ce:YAG crystals
|
Yb:YAG Crystals

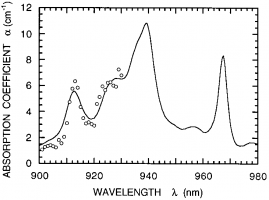
| Ytterbium-doped aluminum yttrium garnet (Yb:YAG) crystals are one of the most prospective materials better suited for diode doping than neodymium-doped (Nd) crystals. As compared to more popular Nd:YAG crystals, Yb:YAG crystals have a wider absorption band, which reduces requirements for thermal control systems, have a longer lifetime, and a 3-4 times less thermal capacity. Yb:YAG crystals emit radiation with a wavelength of 1030 nm and are excellent replacement for Nd:YAG crystals (1064 nm). The second harmonic wave of Yb:YAG laser radiation (515 nm) can serve as an alternative to argon (Ar) lasers (514 nm). Characteristic features: – Heating: less than 11 %; – High differential quantum efficiency; – Wide absorption band: 8 nm at 940 nm; – No absorption from excited state; – Reliable InGaAs diode pumping at 940 nm (or 970 nm); – High thermal conductivity and endurance; – Excellent optic qualities. Yb:YAG crystals technical features
|
Er:YAG Crystals

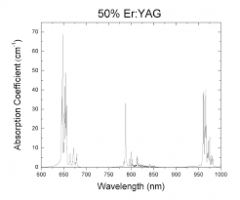
| Erbium-doped aluminum yttrium garnet (Er:YAG) crystals are very good for lasers with a wavelength of 2940 nm. Radiation with this wavelength corresponds to the water and hydroxylapatite absorption lines. These crystals are widely used for medical purposes, particularly, in dentistry, orthopedics etc. Specific features – High differential quantum efficiency; – Very good for operation at room temperature; – Works at a relatively eye-safe spectral wavelength range. Technical features of Er:YAG crystals
|
Nd:YLF Crystals

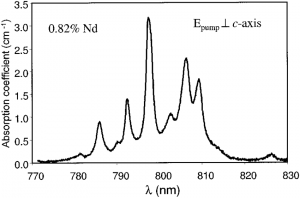
| Top-quality basic materials for crystal growth, crystal interferometry and strict quality control by way of He-Ne laser beam diffusion analyzing allow using of all these elements for solving tasks with highest level requirements. Special features: – Rod size (diameter), 1 – 150 mm(long); – Rod axis orientation against crystal axis: around 1; – Polished surface or anti-reflective coating; – Doping elements concentration (Nd): 0.4 – 1.2 at. %; – Other doping elements sizes and concentrations are available at request. Nd:YLF crystal optical properties
Nd:YLF crystals physical properties
Refraction index of Nd:YLF crystals
Thermo-optic coefficients of Nd:YLF dn/dT crystals
Sellmeyer’s ratio (λ in um) no2=1.38757+0.70757λ2/(λ2-0.00931)+0.18849λ2/(λ2-50.99741) ne2=1.31021+0.84903λ2/(λ2-0.00876)+0.53607λ2/(λ2-134.9566) Nd:YLF laser crystals specification
|
Cr:LiSAF Crystals

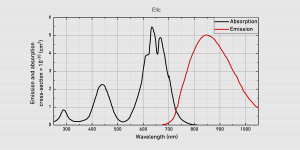
| They are very good for laser active medium, as they have high differential quantum efficiency. These crystals are also suitable for work with ultrashort pulses of high power. Today, gadgets based on Cr:LiSAF are widely used in systems with diode and lamp pumping. Specific features: – Sizes: from 2 to 6 mm (rod diameter), 1 – 180 mm (rod length); – Doping elements concentration (Cr): 0.5~1.0 mole%; – Parallelism: <10 ″; – Perpendicularity: <5 ′; – Angularity: 0.13±0.07 mm ×45°; – Surface quality: 10/5 (MIL-PRF-13830B); – Flatness: λ/8 at 632.8 nm; – Anti-reflective coating: R<0.10% at 850 nm. Other rod sizes and crystals with non-standard doping elements concentration are available at request. Cr:LiSAF crystals physical properties
Cr:LiSAF crystal optic properties:
Sellmeyer’s equations (λ in um) nc2 =1.98448+0.00235/(λ²-0.010936)-0.01057λ² na2=1.97673+0.00309/(λ²-0.00935)-0.00828λ²
|
Nd:KGW Crystals


| Neodymium-doped potassium gadolinium tungstate (Nd:KGd(WO4)2 or Nd:KGW) crystals are suitable to be used as laser active medium due to its low lasing threshold and wide emission cross-section. The effect of concentration quenching of fluorescence with neodymium ions (Nd3+) in KGW crystals can be weakened by a covalent W – O bond, therefore, this crystal has a higher concentration of active ions. Moreover, the Nd3+ absorption band at 808 nm in KGW crystals 12 nm wide (FWHM) matches well the emission wavelength of modern commercial laser diodes.
Nd:KGW: crystals main properties
Nd:KGW crystals properties:
Nd:KGW crystals specific features
Crystal transmittance curve Nd:KGW
|
Yb:KGW Crystals

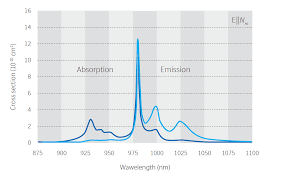
| Ytterbium-doped potassium gadolinium tungstate (Yb:KGd(WO4)2 or Yb:KGW) crystals are suitable to be used as laser-active medium and have distinct advantages over Nd3+ -doped KGW crystals. They are as follows: a wide emission spectrum in the range of 1023 – 1060 nm, the ability to generate short pulses (fs, ps), a wide absorption spectrum at 980 nm, аs well as a high pumping emission absorption coefficient that allows to effectively use the pumping radiation of laser diodes. As compared to YAG crystals, KGW crystals have a wider absorption cross-section, which reduces the required value of pumping intensity. Yb:KGW crystals main features
|
Titanium-sapphire (Ti:Sapphire) Crystals

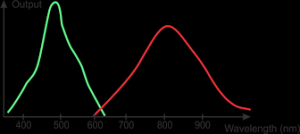
| Titanium-doped sapphire (Ti:Sapphire) crystals are widely used to create tuneable coherent sources with ultra-shot pulses, high gain coefficient and power. Azimut Photonics company supplies titanium-sapphire crystals, grown by thermal gradient method. The crystals have big dimensions (30 x30 mm), high quality (without diffusion), and density dislocation of less 102сm-2. Sapphire crystals grown by thermal gradient method are characterized with oriented growth (0001), high doping level (α490 = 4.0 cm-1), high gain coefficient and damage threshold. Application: – Tuneable wavelength in the range of 700 – 1000 nm makes Ti:Sapphire lasers a perfect alternative to dye lasers; – Ti:Sapphire lasers can be used for UV generation of far UV band (up to 193 nm) with the pulse length up to 10 fs using non-linear crystals (e.g. BBO) to double frequency; – Ti:Sapphire lasers are also widely used as pumping radiation sources for OPO (optical parametric oscillators) to increase the adjustment range. Special features: – Orientation: the optical axis С is perpendicular to the rod axis; – Concentration of Ti2O3: 0.06 – 0.2 mass %; – Quality index (FOM): 100~250 (>250 at request); – α490: 1.0~4.0 cm-1; – Diameter: 2~30 mm or as required; – Optical path length: 2~30 mm or as required; – Butt-end configuration: flat or Brewster angled; – Flatness: <λ/10 at 633 nm; – Parallelism: 10 angular seconds; – Surface quality: :<40/20 scratch/dig (MIL-PRF-13830B); – Wavefront distortion: <λ/4 per inch. Notes: Anti-reflective coating at request. Main properties of Ti:sapphire crystals
|
Diffusion-Bonded Crystals
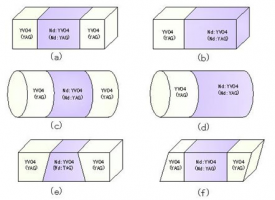
| Diffusion-bonded (diffusion-spliced) crystals consist of one laser crystal and one or two crystals without doping additives. The combination of crystals is carried out by the method of optical contact and further exposure to high temperature. Diffusion-bonded crystals help significantly reduce the lens effect that occurs when crystals are heated. There are 3 type of diffusion-bonded crystals: YVO4+Nd:YVO4+YVO4, YAG+ Nd:YAG+YAG, Cr:YAG+Nd:YAG Diffusion-bonded crystals
The following crystals are available to order: Diffuse-bonded crystals with different structure configuration are supplied by request. |
